|
Fibrosis
Fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, is the development of fibrous connective tissue in response to an injury. Fibrosis can be a normal connective tissue deposition or excessive tissue deposition caused by a disease. Repeated injuries, chronic inflammation and repair are susceptible to fibrosis, where an accidental excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix components, such as the collagen, is produced by fibroblasts, leading to the formation of a permanent fibrotic scar. In response to injury, this is called scarring, and if fibrosis arises from a single cell line, this is called a fibroma. Physiologically, fibrosis acts to deposit connective tissue, which can interfere with or totally inhibit the normal architecture and function of the underlying organ or tissue. Fibrosis can be used to describe the pathological state of excess deposition of fibrous tissue, as well as the process of connective tissue deposition in healing. Defined by the pathological accumulation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystic Fibrosis
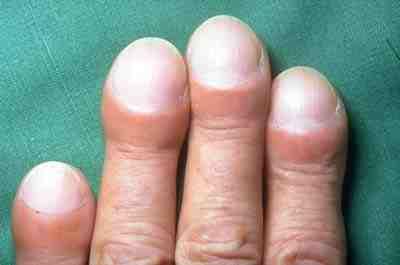
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder inherited in an autosomal recessive manner that impairs the normal clearance of Sputum, mucus from the lungs, which facilitates the colonization and infection of the lungs by bacteria, notably ''Staphylococcus aureus''. CF is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. The hallmark feature of CF is the accumulation of thick mucus in different organs. Long-term issues include Shortness of breath, difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent pneumonia, lung infections. Other signs and symptoms may include Sinusitis, sinus infections, failure to thrive, poor growth, Steatorrhea, fatty stool, Nail clubbing, clubbing of the fingers and toes, and infertility in most males. Different people may have different degrees of symptoms. Cystic fibrosis is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. It is caused by the presence of mutations in both copies (alleles) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonary Fibrosis
Pulmonary fibrosis is a condition in which the lungs become scarred over time. Symptoms include shortness of breath, a dry cough, feeling tired, weight loss, and nail clubbing. Complications may include pulmonary hypertension, respiratory failure, pneumothorax, and lung cancer. Causes include environmental pollution, certain medications, connective tissue diseases, infections, and interstitial lung diseases. But in most cases the cause is unknown ( idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis). Diagnosis may be based on symptoms, medical imaging, lung biopsy, and lung function tests. No cure exists and treatment options are limited. Treatment is directed toward improving symptoms and may include oxygen therapy and pulmonary rehabilitation. Certain medications may slow the scarring. Lung transplantation may be an option. At least 5 million people are affected globally. Life expectancy is generally less than five years. Signs and symptoms Symptoms of pulmonary fibrosis are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) synonymous with cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis is a rare, progressive illness of the respiratory system, characterized by the thickening and stiffening of lung tissue, associated with the formation of scar tissue. It is a type of chronic pulmonary fibrosis characterized by a progressive and irreversible decline in lung function. The tissue in the lungs becomes thick and stiff, which affects the tissue that surrounds the air sacs in the lungs. Symptoms typically include gradual onset of dypsnea, shortness of breath and a dry cough. Other changes may include feeling tired, and nail clubbing, clubbing abnormally large and dome shaped finger and toenails. Complications may include pulmonary hypertension, heart failure, pneumonia or pulmonary embolism. The cause is unknown, hence the term Idiopathic disease, idiopathic. Risk factors include cigarette smoking, gastroesophageal reflux disease, certain viral infections, and genetic predisposition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
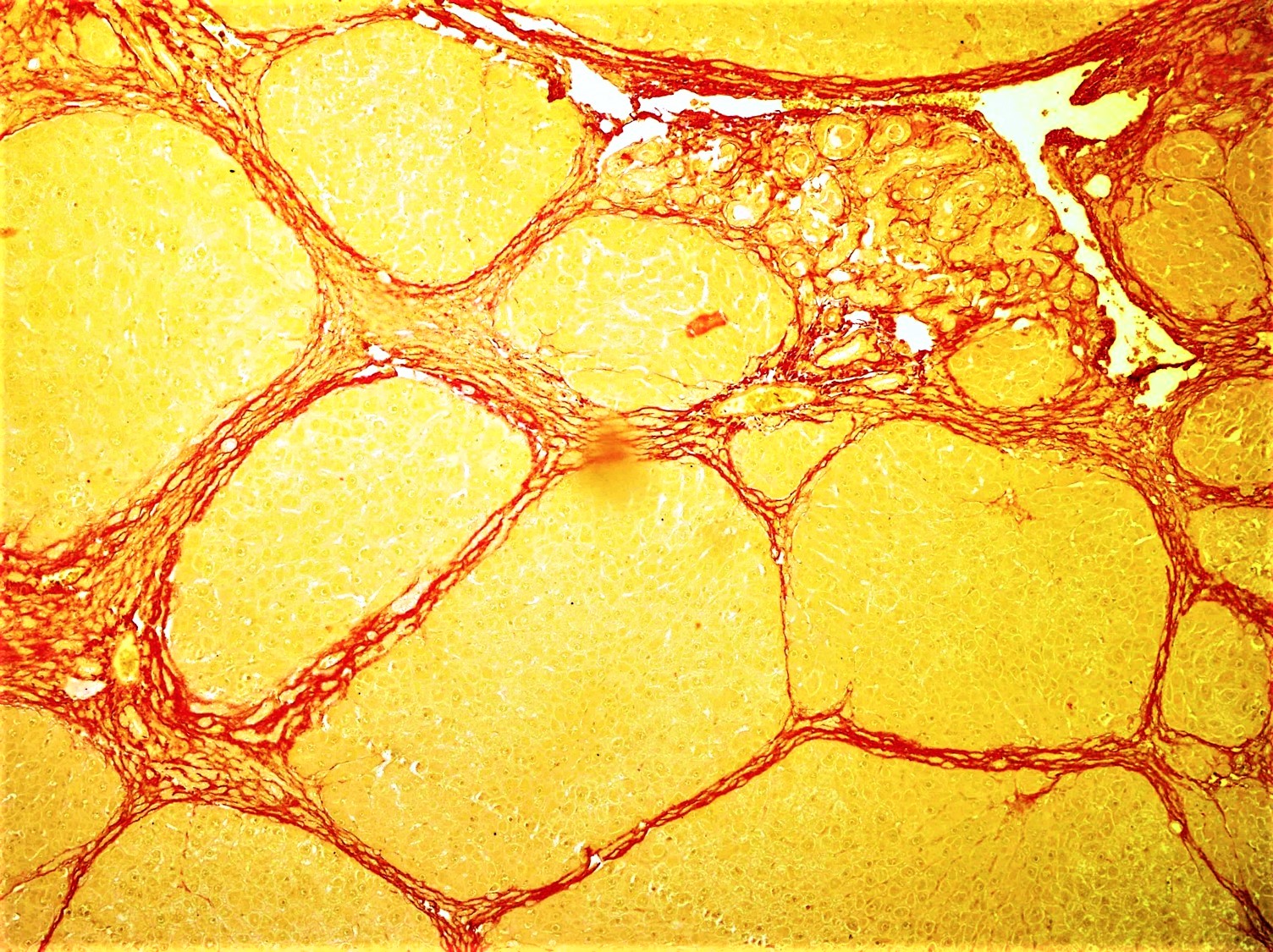
Cirrhosis High Mag
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, chronic liver failure or chronic hepatic failure and end-stage liver disease, is a chronic condition of the liver in which the normal functioning tissue, or parenchyma, is replaced with scar tissue (fibrosis) and regenerative nodule (medicine), nodules as a result of chronic liver disease. Damage to the liver leads to repair of liver tissue and subsequent formation of scar tissue. Over time, scar tissue and nodules of regenerating hepatocytes can replace the parenchyma, causing increased resistance to blood flow in the liver's capillaries—the hepatic sinusoids—and consequently portal hypertension, as well as impairment in other aspects of liver function. The disease typically develops slowly over months or years. Stages include compensated cirrhosis and decompensated cirrhosis. Early symptoms may include Fatigue (medicine), tiredness, Asthenia, weakness, Anorexia (symptom), loss of appetite, weight loss, unexpla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibrothorax
Fibrothorax is a medical condition characterised by severe scarring ( fibrosis) and fusion of the layers of the pleural space surrounding the lungs resulting in decreased movement of the lung and ribcage. The main symptom of fibrothorax is shortness of breath. There also may be recurrent fluid collections surrounding the lungs. Fibrothorax may occur as a complication of many diseases, including infection of the pleural space known as an empyema or bleeding into the pleural space known as a haemothorax. Fibrosis in the pleura may be produced intentionally using a technique called pleurodesis to prevent recurrent punctured lung (pneumothorax), and the usually limited fibrosis that this produces can rarely be extensive enough to lead to fibrothorax. The condition is most often diagnosed using an X-ray or CT scan, the latter more readily detecting mild cases. Fibrothorax is often treated conservatively with watchful waiting but may require surgery. The outlook is usually good as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CTGF
CTGF, also known as CCN2 or connective tissue growth factor, is a matricellular protein of the CCN family of extracellular matrix-associated heparin-binding proteins (see also CCN intercellular signaling protein). CTGF has important roles in many biological processes, including cell adhesion, migration, proliferation, angiogenesis, skeletal development, and tissue wound repair, and is critically involved in fibrotic disease and several forms of cancers. Structure and binding partners Members of the CCN protein family, including CTGF, are structurally characterized by having four conserved, cysteine-rich domains. These domains are, from N- to C-termini, the insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP) domain, the von Willebrand type C repeats ( vWC) domain, the thrombospondin type 1 repeat (TSR) domain, and a C-terminal domain (CT) with a cysteine knot motif. CTGF exerts its functions by binding to various cell surface receptors in a context-dependent manner, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transforming Growth Factor Beta
Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is a multifunctional cytokine belonging to the transforming growth factor superfamily that includes three different mammalian isoforms (TGF-β 1 to 3, HGNC symbols TGFB1, TGFB2, TGFB3) and many other signaling proteins. TGFB proteins are produced by all white blood cell lineages. Activated TGF-β complexes with other factors to form a serine/threonine kinase complex that binds to TGF-β receptors. TGF-β receptors are composed of both type 1 and type 2 receptor subunits. After the binding of TGF-β, the type 2 receptor kinase phosphorylates and activates the type 1 receptor kinase that activates a signaling cascade. This leads to the activation of different downstream substrates and regulatory proteins, inducing transcription of different target genes that function in differentiation, chemotaxis, proliferation, and activation of many immune cells. TGF-β is secreted by many cell types, including macrophages, in a latent form in whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
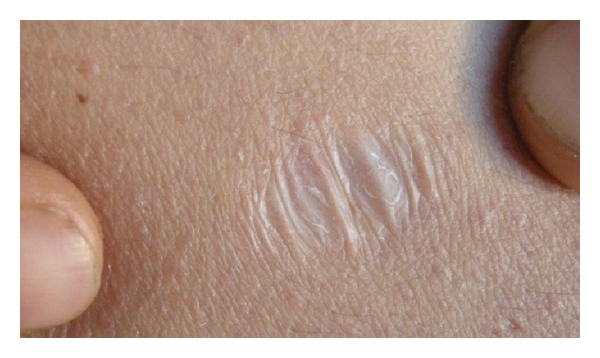
Scar
A scar (or scar tissue) is an area of fibrosis, fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin after an injury. Scars result from the biological process of wound repair in the skin, as well as in other Organ (anatomy), organs, and biological tissue, tissues of the body. Thus, scarring is a natural part of the healing process. With the exception of very minor lesions, every wound (e.g., after accident, disease, or surgery) results in some degree of scarring. An exception to this are animals with complete Regeneration (biology), regeneration, which regrow tissue without scar formation. Scar tissue is composed of the same protein (collagen) as the tissue that it replaces, but the fiber composition of the protein is different; instead of a random basketweave formation of the collagen fibers found in normal tissue, in fibrosis the collagen cross-links and forms a pronounced alignment in a single direction. This collagen scar tissue alignment is usually of inferior functional quality to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridging Fibrosis
In histology (microscopic anatomy), the lobules of liver, or hepatic lobules, are small divisions of the liver defined at the microscopic scale. The hepatic lobule is a building block of the liver tissue, consisting of portal triads, hepatocytes arranged in linear cords between a capillary network, and a central vein. Lobules are different from the lobes of liver: they are the smaller divisions of the lobes. The two-dimensional microarchitecture of the liver can be viewed from different perspectives: The term "hepatic lobule", without qualification, typically refers to the classical lobule. Structure The hepatic lobule can be described in terms of metabolic "zones", describing the hepatic acinus (terminal acinus). Each zone is centered on the line connecting two portal triads and extends outwards to the two adjacent central veins. The periportal zone I is nearest to the entering vascular supply and receives the most oxygenated blood, making it least sensitive to ischemic in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation-induced Lung Injury
Radiation-induced lung injury (RILI) is a general term for damage to the lungs as a result of exposure to ionizing radiation. In general terms, such damage is divided into early inflammatory damage (''radiation pneumonitis'') and later complications of chronic scarring (''radiation fibrosis''). Pulmonary radiation injury is an unavoidable risk of radiation therapy administered to treat thoracic or lung cancer. Symptoms and signs The lungs are a radiosensitive organ, and radiation pneumonitis can occur leading to pulmonary insufficiency and death (100% after exposure to 50 gray of radiation) in a few months. Radiation pneumonitis is characterized by: *Loss of epithelial cells * Edema * Inflammation *Occlusions airways, air sacs and blood vessels * Fibrosis Symptoms of radiation pneumonitis include: fever, cough A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages which can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and Microorganism, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extracellular Matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix (ICM), is a network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM. The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest. Each type of connective tissue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |