|
Feline Cystitis
Feline idiopathic cystitis (FIC) or feline interstitial cystitis or cystitis in cats, is one of the most frequently observed forms of feline lower urinary tract disease (FLUTD). Feline cystitis means "inflammation of the bladder in cats". The term idiopathic disease, ''idiopathic'' means unknown cause; however, certain behaviours have been known to aggravate the illness once it has been initiated. It can affect both males and females of any breed of cat. It is more commonly found in female cats; however, when males do exhibit cystitis, it is usually more dangerous. Despite the shared terminology, cases of feline idiopathic cystitis, as opposed to human cystitis episodes, are sterile. In other words, they do not involve a primary bacterial infection. If upon investigation the inflammation of the feline bladder is in fact found to be the result of an infection, then it is described as a feline urinary tract infection (UTI) or less commonly, feline bacterial cystitis. In cats unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease
Feline lower urinary tract disease (FLUTD) is a generic category term to describe any disorder affecting the bladder or urethra of cats. It encompasses around 10 different diseases of the lower urinary tract, all of which can present with very similar symptoms: * frequent urination (polyuria) * blood in urine ( hematuria) * painful, frequent urination of small volumes that are expelled slowly only by straining ( stranguria) * difficult or painful urination ( dysuria) * urinating in "inappropriate" places or house-soiling (periurea) Some of these symptoms may be the result of a form of FLUTD which could result in a blockage of the male urethra (e.g. obstructive feline idiopathic cystitis). However the same symptoms can also present for a non-obstructive form of FLUTD. Therefore, a careful differential diagnosis needs to be undertaken to distinguish between an obstructive case (which is an emergency) and a non-obstructive case (which is not) given that the symptoms are very simi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
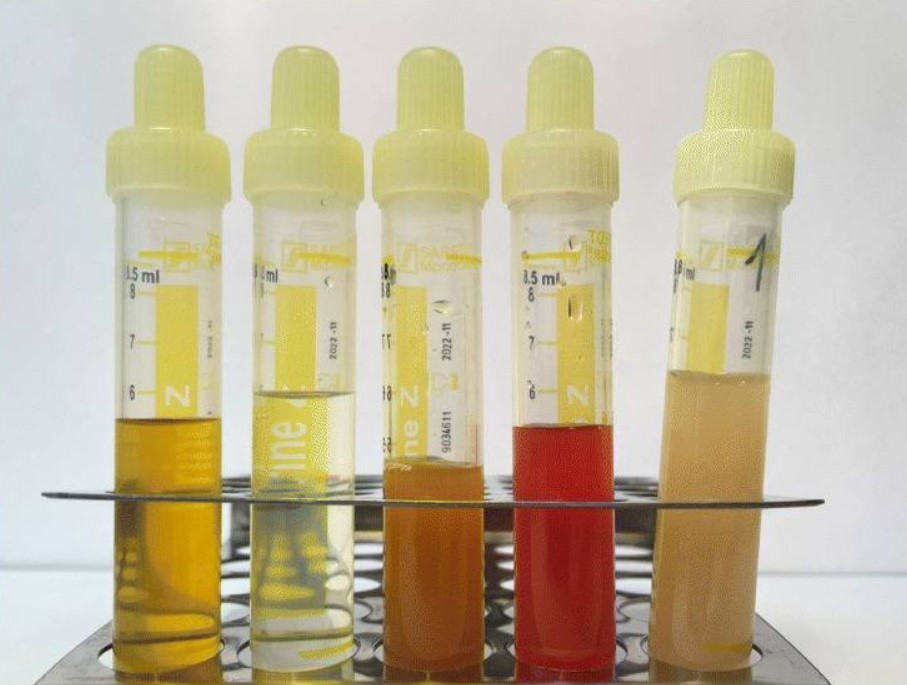
Urinalysis
Urinalysis, a portmanteau of the words ''urine'' and ''analysis'', is a Test panel, panel of medical tests that includes physical (macroscopic) examination of the urine, chemical evaluation using urine test strips, and #Microscopic examination, microscopic examination. Macroscopic examination targets parameters such as color, clarity, odor, and specific gravity; urine test strips measure chemical properties such as pH, glucose concentration, and protein levels; and microscopy is performed to identify elements such as Cell (biology), cells, urinary casts, Crystalluria, crystals, and organisms. Background Urine is produced by the filtration of blood in the kidneys. The formation of urine takes place in microscopic structures called nephrons, about one million of which are found in a normal human kidney. Blood enters the kidney though the renal artery and flows through the kidney's vasculature into the Glomerulus (kidney), glomerulus, a tangled knot of capillaries surrounded by Bow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of Human, humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The Ancient Greek name for the stomach is ''gaster'' which is used as ''gastric'' in medical terms related to the stomach. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach is involved in the gastric phase, gastric phase of digestion, following the cephalic phase in which the sight and smell of food and the act of chewing are stimuli. In the stomach a chemical breakdown of food takes place by means of secreted digestive enzymes and gastric acid. It also plays a role in regulating gut microbiota, influencing digestion and overall health. The stomach is located between the esophagus and the small intestine. The pyloric sphincter controls the passage of partially digested food (chyme) from the stomach into the duodenum, the first and shortest part of the small intestine, where p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organ (anatomy), organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal artery, renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the urinary bladder, bladder. The kidney participates in the control of the volume of various body fluids, fluid osmolality, Acid-base homeostasis, acid-base balance, various electrolyte concentrations, and removal of toxins. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus (kidney), glomerulus: one-fifth of the blood volume that enters the kidneys is filtered. Examples of substances reabsorbed are solute-free water, sodium, bicarbonate, glucose, and amino acids. Examples of substances secreted are hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robenacoxib
Robenacoxib, sold under the brand name Onsior, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used in veterinary medicine for the relief of pain and inflammation in cats and dogs. It is a COX-2 inhibitor Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors (COX-2 inhibitors), also known as coxibs, are a type of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that directly target cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), an enzyme responsible for inflammation and pain. Targeting selectivity ... (''coxib''). References COX-2 inhibitors Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs Fluoroarenes Anilines Carboxylic acids Veterinary drugs {{musculoskeletal-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meloxicam
Meloxicam, sold under the brand name Mobic among others, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat pain and inflammation in rheumatic diseases and osteoarthritis. It is taken by mouth or given by injection into a vein. It is recommended that it be used for as short a period as possible and at a low dose. Common side effects include abdominal pain, dizziness, swelling, headache, and a rash. Serious side effects may include heart disease, stroke, kidney problems, and stomach ulcers. Use is not recommended in the third trimester of pregnancy. It blocks cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) more than it blocks cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1). It is in the oxicam family of chemicals and is closely related to piroxicam. Meloxicam was patented in 1977 and approved for medical use in the United States in 2000. It was developed by Boehringer Ingelheim and is available as a generic medication. In 2022, it was the 29th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Blockage
Mechanical may refer to: Machine * Machine (mechanical), a system of mechanisms that shape the actuator input to achieve a specific application of output forces and movement * Mechanical calculator, a device used to perform the basic operations of arithmetic * Mechanical energy, the sum of potential energy and kinetic energy * Mechanical system, a system that manages the power of forces and movements to accomplish a task * Mechanism (engineering), a portion of a mechanical device Other * Mechanical (character), one of several characters in Shakespeare's ''A Midsummer Night's Dream'' * A kind of typeface in the VOX-ATypI classification See also * Machine, especially in opposition to an electronic item * ''Mechanical Animals'', the third full-length studio release by Marilyn Manson * Manufactured or artificial, especially in opposition to a biological or natural component * Automation, using machine decisions and processing instead of human * Mechanization, using machine labor inst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spayed
Neutering, from the Latin ('of neither sex'), is the removal of a non-human animal's reproductive organ, either all of it or a considerably large part. The male-specific term is castration, while spaying is usually reserved for female animals. Colloquially, both terms are often referred to as fixing. In male horses, castrating is referred to as gelding. An animal that has not been neutered is sometimes referred to as entire or intact. Often the term ''neuter ng' is used to specifically mean castration, e.g. in phrases like "spay and neuter". Neutering is the most common method for animal sterilization. Humane societies, animal shelters, and rescue groups urge pet owners to have their pets neutered to prevent the births of unwanted litters, which contribute to the overpopulation of unwanted animals in the rescue system. Many countries require that all adopted cats and dogs be sterilized before going to their new homes. Methods of sterilization Females (spaying) Spaying is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutered
Neutering, from the Latin ('of neither sex'), is the removal of a non-human animal's reproductive organ, either all of it or a considerably large part. The male-specific term is castration, while spaying is usually reserved for female animals. Colloquially, both terms are often referred to as fixing. In male horses, castrating is referred to as gelding. An animal that has not been neutered is sometimes referred to as entire or intact. Often the term ''neuter ng' is used to specifically mean castration, e.g. in phrases like "spay and neuter". Neutering is the most common method for animal sterilization. Humane societies, animal shelters, and rescue groups urge pet owners to have their pets neutered to prevent the births of unwanted litters, which contribute to the overpopulation of unwanted animals in the rescue system. Many countries require that all adopted cats and dogs be sterilized before going to their new homes. Methods of sterilization Females (spaying) Spaying i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease
Feline lower urinary tract disease (FLUTD) is a generic category term to describe any disorder affecting the bladder or urethra of cats. It encompasses around 10 different diseases of the lower urinary tract, all of which can present with very similar symptoms: * frequent urination (polyuria) * blood in urine ( hematuria) * painful, frequent urination of small volumes that are expelled slowly only by straining ( stranguria) * difficult or painful urination ( dysuria) * urinating in "inappropriate" places or house-soiling (periurea) Some of these symptoms may be the result of a form of FLUTD which could result in a blockage of the male urethra (e.g. obstructive feline idiopathic cystitis). However the same symptoms can also present for a non-obstructive form of FLUTD. Therefore, a careful differential diagnosis needs to be undertaken to distinguish between an obstructive case (which is an emergency) and a non-obstructive case (which is not) given that the symptoms are very simi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', ''dolor'', ''rubor'', ''tumor'', and ''functio laesa''). Inflammation is a generic response, and therefore is considered a mechanism of innate immunity, whereas adaptive immunity is specific to each pathogen. Inflammation is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators. The function of inflammation is to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury, clear out damaged cells and tissues, and initiate tissue repair. Too little inflammation could lead to progressive tissue destruction by the harmful stimulus (e.g. bacteria) and compromise the survival of the organism. However inflammation can also have negative effects. Too much inflammation, in the form of chronic inflammation, is associated with variou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |