|
Federal Technology Transfer Act Of 1986
The United States Federal Technology Transfer Act of 1986 (P.L. 99-502) was, after the Stevenson-Wydler Technology Innovation Act of 1980, the second major piece of legislation focused on technology transfer from federal government agencies to the commercial sector. The act established the Federal Laboratory Consortium and enabled federal laboratories to enter into Cooperative Research and Development Agreements (CRADAs) and to negotiate licenses for patented inventions made at the laboratory. Follow up legislation The 'Small Business Technology Transfer Act of 1992' was enacted to increase opportunities for small businesses and non profit organizations to collaborate with federal research laboratories. Agencies with a more than $1 billion extramural research and development budget must reserve 0.3% of their extramural research budget for Small Business Technology Transfer (STTR) awards. In parallel, in December 1992, the related 'Small Business Research and Development Enhancem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cooperative Research And Development Agreement
In the United States, a cooperative research and development agreement (CRADA or CRDA) is an agreement between a government agency and another government agency, a private company, non-profit, or university to work together on research and development. Description Designated under the Federal Technology Transfer Act of 1986 (P.L. 99-502) (which amended the Stevenson-Wydler Technology Innovation Act of 1980 (P.L. 96-480)), a CRADA is intended to speed the commercialization of technology, optimize resources, and protect the private company involved. A CRADA allows both parties to keep research results confidential for up to five years under the Freedom of Information Act. The Office of Scientific and Technical Information (OSTI) is responsible for preserving the scientific and technical information generated through a CRADA and making this information readily available to the scientific community as well as the public. Private corporations participating in a CRADA are allowed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Office Of Research And Technology Applications
The Office of Research and Technology Applications (ORTA) is an organizational structure established in United States federal laboratories through the Stevenson-Wydler Technology Innovation Act of 1980 (P.L. 96-480), specified in 15 USC § 3710. The acronym "ORTA" has evolved to refer to those who perform the functions of the ORTA organization. By law, the ORTA must be staffed by at least one full-time person in any laboratory with 200 or more scientific, engineering, or related technical positions, in order to coordinate and promote technology transfer. Functions According to 15 USC § 3710, the ORTA's function is to: *Prepare application assessments for selected research and development projects in which that laboratory is engaged and which in the opinion of the laboratory may have potential commercial applications; *Provide and disseminate information on federally owned or originated products, processes, and services having potential application to State and local governments a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Educational Technology
Educational technology (commonly abbreviated as edutech, or edtech) is the combined use of computer hardware, software, and educational theory and practice to facilitate learning. When referred to with its abbreviation, edtech, it often refers to the industry of companies that create educational technology. In addition to the practical educational experience, educational technology is based on theoretical knowledge from various disciplines such as communication, education, psychology, sociology, artificial intelligence, and computer science. It encompasses several domains including learning theory, computer-based training, online learning, and m-learning where mobile technologies are used. Definition The Association for Educational Communications and Technology (AECT) has defined educational technology as "the study and ethical practice of facilitating learning and improving performance by creating, using and managing appropriate technological processes and resources". It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayh–Dole Act
The Bayh–Dole Act or Patent and Trademark Law Amendments Act ( Pub. L. 96-517, December 12, 1980) is United States legislation permitting ownership by contractors of inventions arising from federal government-funded research. Sponsored by senators, Birch Bayh of Indiana and Bob Dole of Kansas, the Act was adopted in 1980, is codified at 94 Stat. 3015, and in 35 U.S.C. § 200–212, and is implemented by 37 C.F.R. 401 for federal funding agreements with contractors and 37 C.F.R 404 for licensing of inventions owned by the federal government. A key change made by Bayh–Dole was in the procedures by which federal contractors that acquired ownership of inventions made with federal funding could retain that ownership. Before the Bayh–Dole Act, the Federal Procurement Regulation required the use of a patent rights clause that in some cases required federal contractors or their inventors to assign inventions made under contract to the federal government unless the funding agency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
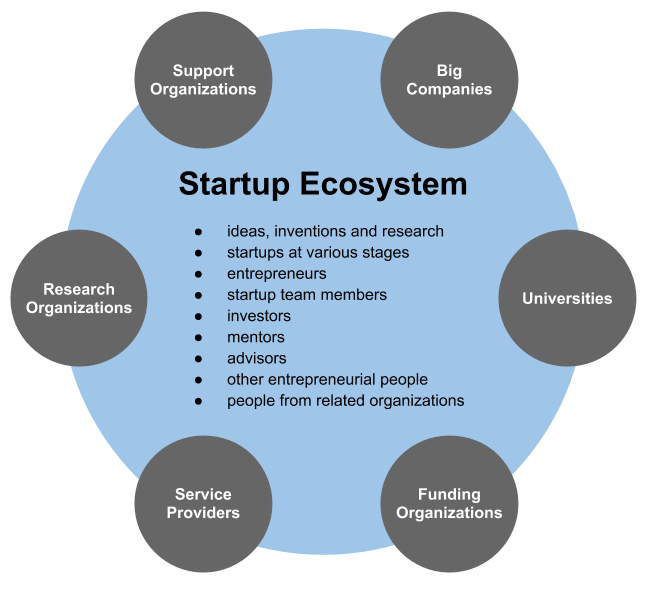
Startup Company
A startup or start-up is a company or project undertaken by an entrepreneur to seek, develop, and validate a scalable business model. While entrepreneurship refers to all new businesses, including self-employment and businesses that never intend to become registered, startups refer to new businesses that intend to grow large beyond the solo founder. At the beginning, startups face high uncertainty and have high rates of failure, but a minority of them do go on to be successful and influential.Erin Griffith (2014)Why startups fail, according to their founders Fortune.com, 25 September 2014; accessed 27 October 2017 Actions Startups typically begin by a founder (solo-founder) or co-founders who have a way to solve a problem. The founder of a startup will begin market validation by problem interview, solution interview, and building a minimum viable product (MVP), i.e. a prototype, to develop and validate their business models. The startup process can take a long period of time (by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint Venture
A joint venture (JV) is a business entity created by two or more parties, generally characterized by shared ownership, shared returns and risks, and shared governance. Companies typically pursue joint ventures for one of four reasons: to access a new market, particularly Emerging market; to gain scale efficiencies by combining assets and operations; to share risk for major investments or projects; or to access skills and capabilities. According to Gerard Baynham of Water Street Partners, there has been much negative press about joint ventures, but objective data indicate that they may actually outperform wholly owned and controlled affiliates. He writes, "A different narrative emerged from our recent analysis of U.S. Department of Commerce (DOC) data, collected from more than 20,000 entities. According to the DOC data, foreign joint ventures of U.S. companies realized a 5.5 percent average return on assets (ROA), while those companies’ wholly owned and controlled affiliates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laboratory
A laboratory (; ; colloquially lab) is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific or technological research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. Laboratory services are provided in a variety of settings: physicians' offices, clinics, hospitals, and regional and national referral centers. Overview The organisation and contents of laboratories are determined by the differing requirements of the specialists working within. A physics laboratory might contain a particle accelerator or vacuum chamber, while a metallurgy laboratory could have apparatus for casting or refining metals or for testing their strength. A chemist or biologist might use a wet laboratory, while a psychologist's laboratory might be a room with one-way mirrors and hidden cameras in which to observe behavior. In some laboratories, such as those commonly used by computer scientists, computers (sometimes supercomputers) are used for either simulations or the analysis of data ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invention
An invention is a unique or novel device, method, composition, idea or process. An invention may be an improvement upon a machine, product, or process for increasing efficiency or lowering cost. It may also be an entirely new concept. If an idea is unique enough either as a stand alone invention or as a significant improvement over the work of others, it can be patented. A patent, if granted, gives the inventor a proprietary interest in the patent over a specific period of time, which can be licensed for financial gain. An inventor creates or discovers an invention. The word ''inventor'' comes from the Latin verb ''invenire'', ''invent-'', to find. Although inventing is closely associated with science and engineering, inventors are not necessarily engineers or scientists. Due to advances in artificial intelligence, the term "inventor" no longer exclusively applies to an occupation (see human computers). Some inventions can be patented. The system of patents was established to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an sufficiency of disclosure, enabling disclosure of the invention."A patent is not the grant of a right to make or use or sell. It does not, directly or indirectly, imply any such right. It grants only the right to exclude others. The supposition that a right to make is created by the patent grant is obviously inconsistent with the established distinctions between generic and specific patents, and with the well-known fact that a very considerable portion of the patents granted are in a field covered by a former relatively generic or basic patent, are tributary to such earlier patent, and cannot be practiced unless by license thereunder." – ''Herman v. Youngstown Car Mfg. Co.'', 191 F. 579, 584–85, 112 CCA 185 (6th Cir. 1911) In most countries, patent rights fall under private law ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Laboratory Consortium
The Federal Laboratory Consortium for Technology Transfer (FLC) is a U.S.-based nationwide network of federal laboratories that provides a forum to develop strategies and opportunities to help transfer laboratory mission technologies into commercial products for the global marketplace. The FLC was organized in 1974 and formally chartered by the Federal Technology Transfer Act of 1986. Its host agency is the National Institute of Standards and Technology. More than 250 federal laboratories and centers and their parent departments and agencies are currently FLC members. In accordance with the Act and related federal policy, the FLC's mission is to promote and facilitate the rapid movement of federal laboratory research results and technologies into the mainstream of the U.S. economy. Specifically, the FLC develops and tests transfer methods, addresses barriers to the process, provides training, highlights grass-roots transfer efforts, and emphasizes national initiatives in which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commerce And Trade
Commerce is the large-scale organized system of activities, functions, procedures and institutions directly and indirectly related to the exchange (buying and selling) of goods and services among two or more parties within local, regional, national or international economies. More specifically, commerce is not business, but rather the part of business which facilitates the movement and distribution of finished or unfinished but valuable goods and services from the producers to the end consumers on a large scale, as opposed to the sourcing of raw materials and manufacturing of those goods. Commerce is subtly different from trade as well, which is the final transaction, exchange or transfer of finished goods and services between a seller and an end consumer. Commerce not only includes trade as defined above, but also a series of transactions that happen between the producer and the seller with the help of the auxiliary services and means which facilitate such trade. These auxiliar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |