|
Federal Road (Cherokee Lands)
The Federal Road through Cherokee lands, originally called the Georgia Road, was a federal toll highway passing through the Cherokee Nation in the northern part of the U.S. state of Georgia. From 1805 to the 1840s, the road linked Savannah, Georgia with Knoxville, Tennessee. The road also opened Cherokee lands to settlement. Another Federal Road (Creek lands) passed through southern Alabama. Geography The Federal Road ran from the location of modern-day Ringgold to Athens, Georgia, passing southeast through the Cherokee Nation and the modern day Georgia counties of Walker, Catoosa, Whitfield, Murray, Gilmer, Pickens, Dawson, Forsyth, Hall, Jackson, and Clarke counties. History The Georgia Road was built from 1803 to 1805 through the newly formed Cherokee Nation on a land concession secured with the 1805 Treaty of Tellico. The Georgia Road opened in 1805. In 1819 the road was improved and called 'the Federal Road' but no federal funds were used in its creation. As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherokee Nation (19th Century)
The Cherokee Nation ( or ) is the largest of three federally recognized tribes of Cherokees in the United States. It includes people descended from members of the Old Cherokee Nation who relocated, due to increasing pressure, from the Southeast to Indian Territory and Cherokees who were forced to relocate on the Trail of Tears. The tribe also includes descendants of Cherokee Freedmen and Natchez Nation. As of 2024, over 466,000 people were enrolled in the Cherokee Nation. Headquartered in Tahlequah, Oklahoma, the Cherokee Nation has a reservation spanning 14 counties in the northeastern corner of Oklahoma. These are Adair, Cherokee, Craig, Delaware, Mayes, McIntosh, Muskogee, Nowata, Ottawa, Rogers, Sequoyah, Tulsa, Wagoner, and Washington counties. History Late 18th century through 1907 After Cherokee removal on the Trail of Tears, the Cherokee Nation existed in Indian Territory. After the American Civil War, the United States promised the Cherokee Nation "a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hall County, Georgia
Hall County is a county in the Northeast region of the U.S. state of Georgia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 203,136, up from 179,684 at the 2010 census. The county seat is Gainesville. The entirety of Hall County comprises the Gainesville, Georgia, Metropolitan Statistical Area, which is also part of the Atlanta- Athens-Clarke County- Sandy Springs, Combined Statistical Area. History Hall County was created on December 15, 1818, from Cherokee lands ceded by the Treaty of Cherokee Agency (1817) and Treaty of Washington (1819). The county is named for Lyman Hall, a signer of the Declaration of Independence and governor of Georgia as both colony and state. Geography According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of , of which is land and (8.5%) is water. The county is located in the upper Piedmont region of the state in the foothills of the Blue Ridge Mountains to the north. Slightly more than half of Hall County, the eastern portion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historic Trails And Roads In Tennessee
History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some theorists categorize history as a social science, while others see it as part of the humanities or consider it a hybrid discipline. Similar debates surround the purpose of history—for example, whether its main aim is theoretical, to uncover the truth, or practical, to learn lessons from the past. In a more general sense, the term ''history'' refers not to an academic field but to the past itself, times in the past, or to individual texts about the past. Historical research relies on primary and secondary sources to reconstruct past events and validate interpretations. Source criticism is used to evaluate these sources, assessing their authenticity, content, and reliability. Historians strive to integrate the perspectives of several sources to develop a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franklin County, Georgia
Franklin County is a county in the Northeast region of the U.S. state of Georgia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 23,424. The county seat is Carnesville. On February 25, 1784, Franklin and Washington became Georgia's eighth and ninth counties, with Franklin named in honor of patriot Benjamin Franklin. In its original form, Franklin County included all of the territory now in Banks, Barrow, Clarke, Jackson, Oconee, and Stephens counties, and parts of the modern-day Gwinnett, Hall, Hart, and Madison counties, as well as three counties that are now part of South Carolina. Franklin County has several miles of shoreline on Lake Hartwell. Economic development The Franklin County Industrial Building Authority, one of only seven created by a Georgia constitutional amendment, actively seeks and recruits new industries to the county. The Authority consists of seven members: each of the five mayors from the cities within Franklin County, and two at-large members selected by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
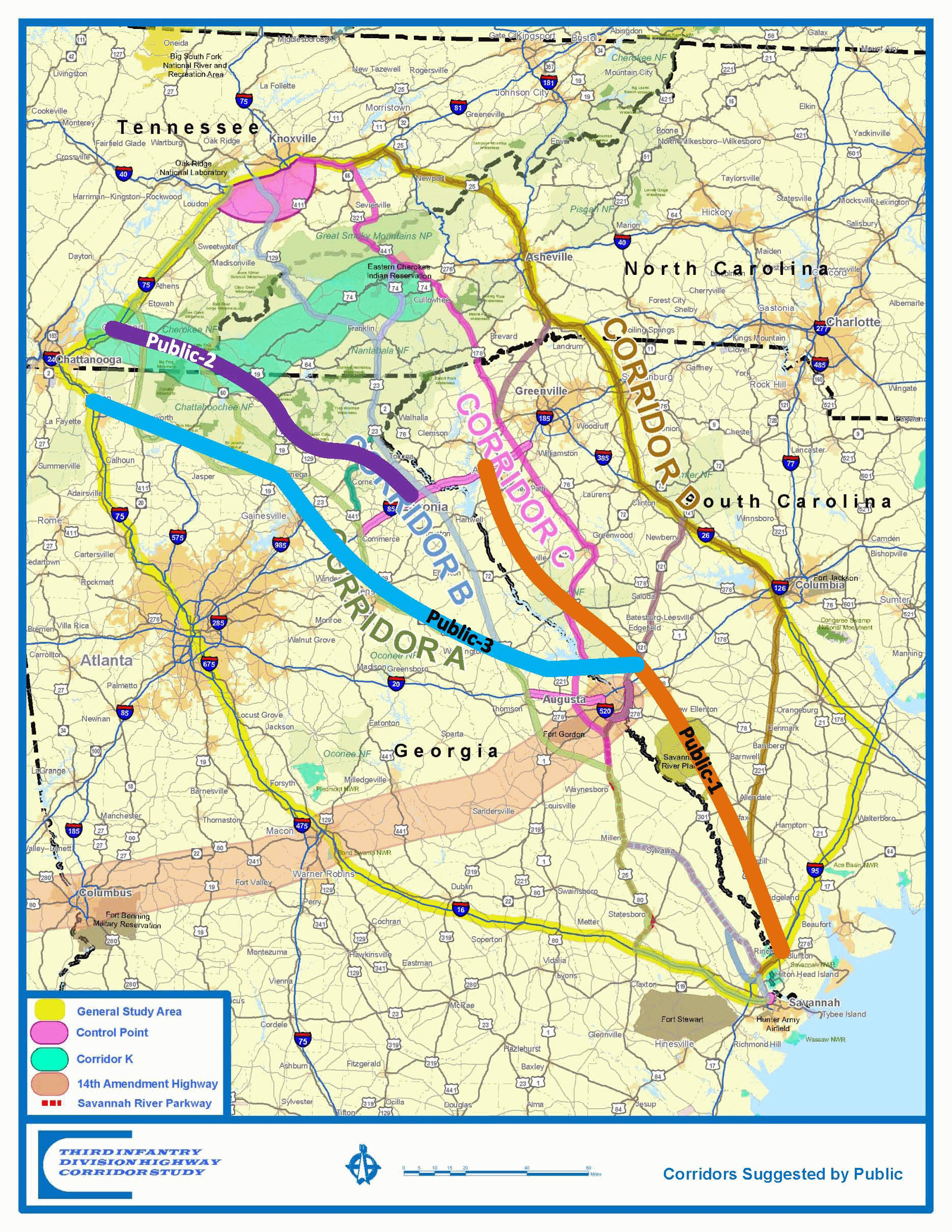
Interstate 3
Interstate 3 (I-3), the 3rd Infantry Division Highway, is a proposed Interstate Highway in the United States to run from Savannah, Georgia, north to Augusta, Georgia, and Knoxville, Tennessee. The roadway was proposed in the same federal highway measure that gave birth to a proposal for I-14. History In 2005, the Safe, Accountable, Flexible, Efficient Transportation Equity Act: A Legacy for Users (SAFETEA-LU) was signed into law by then-President George W. Bush. The act included the proposed corridors for the planned I-14 (specifically as the 14th Amendment Highway), and I-3 (as the 3rd Infantry Division Highway). The legislation did not provide the official numbering nor did it provide funding for the highways. The proposed numbering of the highway does not follow the pattern of the existing Interstate Highway grid but is noted to salute and honor the 3rd Infantry Division of the US Army, based at Fort Stewart, near Savannah, Georgia. According to the Georgia Depa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trading Path
The Trading Path (a.k.a. Occaneechi Path, Unicoi Trail, Catawba Road etc.) was a corridor of roads and trails between the Tsenacommacah or Chesapeake Bay region (mainly the Petersburg, Virginia area) and the Cherokee, Catawba, and other Native-American countries in the Piedmont region of North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia. Indigenous folks had used and maintained much of the path for their expansive trading network for centuries prior to its use by Europeans and/or European-Americans. Native and later European/European-American settlements occupied key points along the path. That section of the Trading Path through the Carolina piedmont was also known as the Upper Road, and a portion between North Carolina and Georgia was called the Lower Cherokee Traders Path. The terminus of the path was near present-day Augusta, Georgia, a distance of 500 miles from the start of the trading path on the James River. On this southern terminus the path connected with other important path ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trail Of Tears
The Trail of Tears was the forced displacement of about 60,000 people of the " Five Civilized Tribes" between 1830 and 1850, and the additional thousands of Native Americans and their black slaves within that were ethnically cleansed by the United States government. As part of Indian removal, members of the Cherokee, Muscogee, Seminole, Chickasaw, and Choctaw nations were forcibly removed from their ancestral homelands in the Southeastern United States to newly designated Indian Territory west of the Mississippi River after the passage of the Indian Removal Act in 1830. The Cherokee removal in 1838 was the last forced removal east of the Mississippi and was brought on by the discovery of gold near Dahlonega, Georgia, in 1828, resulting in the Georgia Gold Rush. The relocated peoples suffered from exposure, disease, and starvation while en route to their newly designated Indian reserve. Thousands died from disease before reaching their destinations or shortly after. A variet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Vann
James Vann (c. 1762–64 – February 19, 1809) was a Cherokee leader, one of the triumvirate with Major Ridge and Charles R. Hicks, who led the Upper Towns of East Tennessee and North Georgia as part of the ᎤᏪᏘ ᏣᎳᎩ ᎠᏰᎵ (Uwet Tsalag Ayetl or Old Cherokee Nation). He was the son of ᏩᎵ (Wali) Vann and Indian trader Joseph John Vann. He was born into his mother's Clan, ᎠᏂᎪᏓᎨᏫ (Anigodagewi or Wild Potato Clan, also called Blind Savannah Clan).Miles (2010), p. 40 Vann was among the younger leaders of the Old Cherokee Nation who thought its people needed to acculturate to deal with the European Americans and the United States government. He encouraged the Moravians to establish a mission school on Cherokee land, and became a wealthy plantation owner and slave owner. Early life and education James Vann was born the oldest of three children, most likely in South Carolina near his father-in-law's trading post on the Savannah River. By 1764 his fam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Echota
New Echota was the capital of the Cherokee Nation (1794–1907), Cherokee Nation in the Southeastern United States from 1825 until their Cherokee removal, forced removal in the late 1830s. New Echota is located in present-day Gordon County, Georgia, Gordon County, in northwest Georgia, north of Calhoun, Georgia, Calhoun. It is south of Resaca, Georgia, Resaca, next to present day New Town, Georgia, New Town, known to the Cherokee as Ꭴꮝꮤꮎꮅ, ''Ustanali''. The site has been preserved as a state park and a historic site. It was designated in 1973 as a National Historic Landmark District. The site is at the confluence of the Coosawattee River, Coosawattee and Conasauga River, Conasauga rivers, which join to form the Oostanaula River, a tributary of the Coosa River. Archeological evidence has shown that the site of New Echota had been occupied by ancient indigenous cultures for thousands of years prior to the Cherokee. It was known as Ꭶꮎꮜꭹᏹ, ''Gansagiyi'' or Ꭶ� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chief Vann House Historic Site
The Chief Vann House is the first brick residence in the Cherokee Nation, and has been called the "Showplace of the Cherokee Nation (19th century), Cherokee Nation". Owned by the Cherokee Chief James Vann, the Vann House is a Georgia Historic Site on the National Register of Historic Places and one of the oldest remaining structures in the northern third of the state of Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia. It is located in Murray County, Georgia, Murray County, on the outskirts of Chatsworth, Georgia, Chatsworth in northwest Georgia, which has a commanding view of the land around it and of the Cohutta Mountains, about to the east. Construction of the Vann House When James Vann was rising to become the wealthiest businessman and chief in the Cherokee Nation, he decided to build a two-story brick house which would reflect his status. He brought in professional architects for its design. In addition to providing an education to local Cherokees, the Moravian Church, Moravians contrib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tellico Blockhouse
The Tellico Blockhouse was an early American outpost located along the Little Tennessee River in what developed as Vonore, Monroe County, Tennessee. Completed in 1794, the blockhouse was a US military outpost that operated until 1807; the garrison was intended to keep peace between the nearby Overhill Cherokee towns and encroaching early Euro-American pioneers in the area in the wake of the Cherokee–American wars. The Tellico Blockhouse was the site where several treaties were negotiated between the United States and the Cherokee, by which the latter ceded large portions of land in present-day Tennessee and Georgia in order to try to gain peace. The US provided various financial incentives for these actions. During this period, the blockhouse was the site of official liaisons between the United States government and the Cherokee. It was designated as the Tellico Blockhouse State Historic Area and listed in 1975 on the National Register of Historic Places. It is administered b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |