|
February Revolution
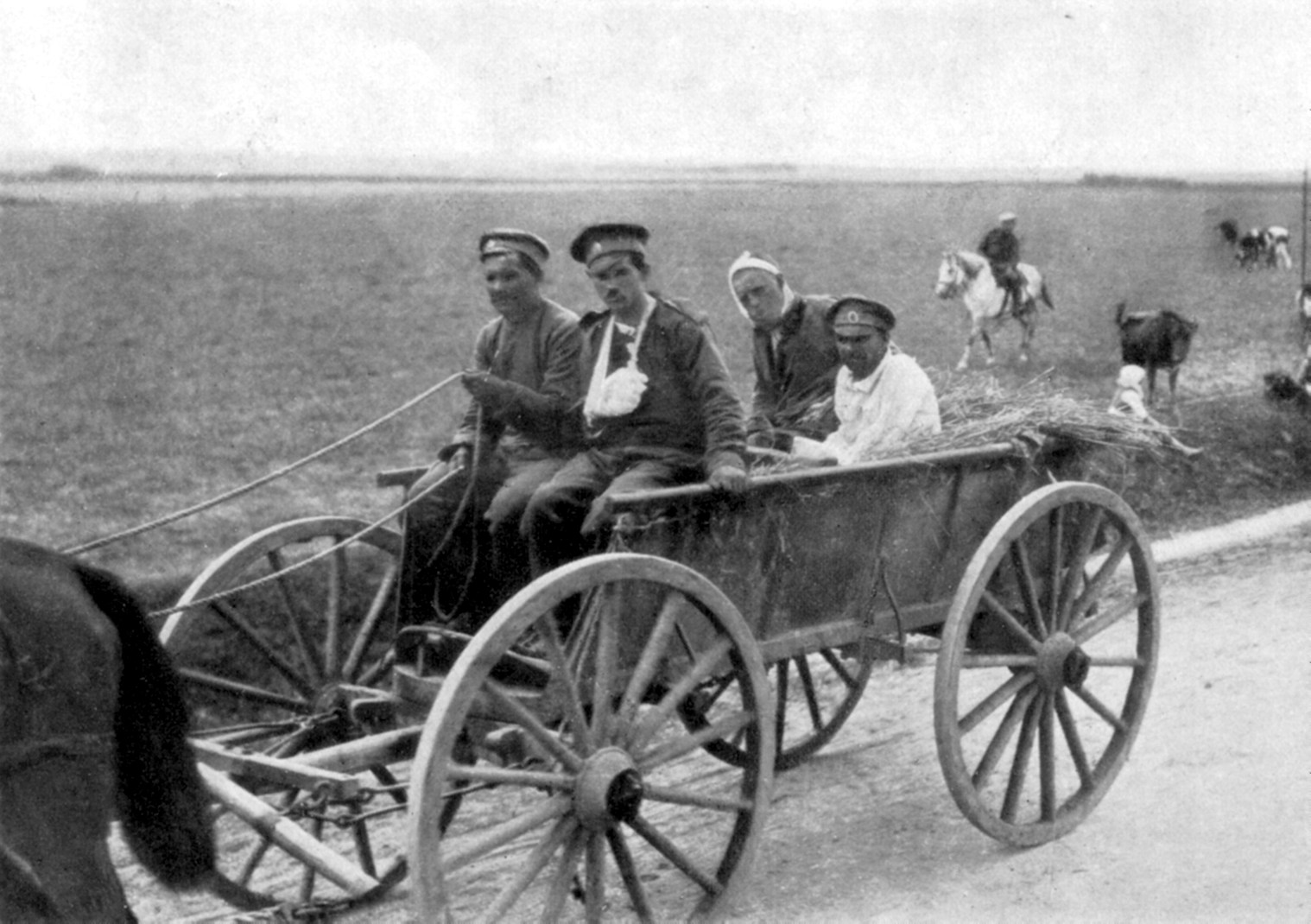
The February Revolution (), known in Soviet historiography as the February Bourgeois Democratic Revolution and sometimes as the March Revolution or February Coup was the first of Russian Revolution, two revolutions which took place in Russia in 1917. The main events of the revolution took place in and near Petrograd (now Saint Petersburg), the then-capital of Russia, where long-standing discontent with the monarchy erupted into mass protests against food rationing on 23 February Old Style and New Style dates, Old Style (8 March Old Style and New Style dates, New Style). Revolutionary activity lasted about eight days, involving mass demonstrations and violent armed clashes with police and Special Corps of Gendarmes, gendarmes, the last loyal forces of the Russian monarchy. On 27 February O.S. (12 March N.S.), most of the forces of the capital's garrison sided with the revolutionaries. In the same day, the Russian Provisional Government, made up by left-leaning State Duma (Russ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of Political revolution (Trotskyism), political and social revolution, social change in Russian Empire, Russia, starting in 1917. This period saw Russia Dissolution of the Russian Empire, abolish its monarchy and adopt a socialist form of government following two successive revolutions and Russian Civil War, a civil war. It can be seen as the precursor for Revolutions of 1917–1923, other revolutions that occurred in the aftermath of World War I, such as the German Revolution of 1918–1919. The Russian Revolution was a key events of the 20th century, key event of the 20th century. The Russian Revolution was inaugurated with the February Revolution in 1917, in the midst of World War I. With the German Empire inflicting defeats on the front, and increasing logistical problems causing shortages of bread and grain, the Russian Army was losing morale, with large scale mutiny looming. Officials were convinced that if Tsar Nicholas II abdicated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Hundreds
The Black Hundreds were reactionary, monarchist, and ultra-nationalist groups in Russia in the early 20th century. They were staunch supporters of the House of Romanov, and opposed any retreat from the autocracy of the reigning monarch. Their name arose from the medieval concept of "black", or common (non-noble) people, organized into militias. The Black Hundreds were noted for extremism and incitement to pogroms, nationalistic Russocentric doctrines, as well as various xenophobic beliefs, including anti-Ukrainian sentiment, anti-Polish sentiment, and anti-Semitism. The ideology of the movement is based on a slogan formulated by Count Sergey Uvarov: "Orthodoxy, Autocracy, and Nationality". Terminology The term was intended to be pejorative in revolutionary newspapers, but adherents used it in their own literature. They traced the term back to the "black lands", where peasants, merchants, and craftsmen paid taxes to the government (compare to Black council), meanwhile land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Of October 17
The Union of 17 October (, ''Soyuz 17 Oktyabrya''), commonly known as the Octobrist Party (Russian: Октябристы, ''Oktyabristy''), was a liberal-reformist constitutional monarchist political party in late Imperial Russia. It represented moderately right-wing, anti-revolutionary and constitutionalist views. History The party's programme of moderate constitutionalism called for the fulfilment of Tsar Nicholas II's '' October Manifesto'', granted on 30 October .S. 17 October1905 at the peak of the Russian Revolution of 1905. Founded shortly afterwards, from 1906 it was led by the industrialist Alexander Guchkov, who drew support from centrist-liberal gentry, businessmen and some bureaucrats. Unlike their immediate neighbours to the left, the Constitutional Democrats, the Octobrists were firmly committed to a system of constitutional monarchy. At the same time they emphasised the need for a strong parliament and a government that would be responsible to it. They we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitutional Democratic Party
The Constitutional Democratic Party (, K-D), also called Constitutional Democrats and formally the Party of People's Freedom (), was a political party in the Russian Empire that promoted Western constitutional monarchy—among other policies—and attracted a base ranging from moderate conservatives to mild socialists. Party members were called Kadets (or Cadets) from the abbreviation K-D of the party name. Konstantin Kavelin's and Boris Chicherin's writings formed the theoretical basis of the party's platform. Historian Pavel Miliukov was the party's leader throughout its existence. The Kadets' base of support were primarily intellectuals and professionals; university professors and lawyers were particularly prominent within the party. Many Kadet party members were veterans of the zemstvo, local councils. The Constitutional Democratic Party formed from the merger of several liberal groupings, namely the Union of Liberation, the Union of Zemstvo Constitutionalists and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progressive Bloc (Russia)
The Progressive Bloc was an alliance of political forces in the Russian Empire and occupied 236 of the 442 seats in the Imperial Duma. It was formed when the State Duma of the Russian Empire was recalled to session during World War I, the response of Nicholas II of Russia to mounting social tensions. On instigation of Pavel Milyukov the Progressist Party combined with the Kadet Party, left Octobrists, and progressive nationalists and individual politicians as Vasily Shulgin to form a political front in the Duma that called for a "government of confidence". According to the Bolsheviks it supported a social-chauvinist stance towards the continuation of World War I. The program content was determined by the desire to find common ground for an agreement with the government on the basis of a minimum of liberal reforms. "The Progressive Bloc's program included demands for political and religious amnesty, the abolition of restrictions on nationalities and faiths (Poles, Jews, etc.) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dashnaks
The Armenian Revolutionary Federation (, abbr. ARF (ՀՅԴ) or ARF-D), also known as Dashnaktsutyun (Armenian: Դաշնակցություն, lit. "Federation"), is an Armenian nationalist and socialist political party founded in 1890 in Tiflis, Russian Empire by Christapor Mikaelian, Stepan Zorian, and Simon Zavarian. , the party operates in Armenia, Lebanon, Iran and in countries where the Armenian diaspora is present. The party was also active in Artsakh until the Azerbaijani offensive in September 2023. Although it has long been the most influential political party in the Armenian diaspora, it has a comparatively smaller proportional presence in the Republic of Armenia. , the party was represented in two national parliaments, with ten seats in the National Assembly of Armenia and three seats in the Parliament of Lebanon as part of the March 8 Alliance. The ARF has traditionally advocated socialist democracy and has been a full member of the Socialist International si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mensheviks
The Mensheviks ('the Minority') were a faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) which split with Vladimir Lenin's Bolshevik faction at the Second Party Congress in 1903. Mensheviks held more moderate and reformist views as compared to the Bolsheviks, and were led by figures including Julius Martov and Pavel Axelrod. The initial point of disagreement was the Mensheviks' support for a broad party membership, as opposed to Lenin's support for a smaller party of professional revolutionaries. The Bolsheviks gained a majority on the Central Committee in 1903, although the power of the two factions fluctuated in the following years. Mensheviks were associated with Georgi Plekhanov's position that a bourgeois-democratic revolution and period of capitalism would need to occur before the conditions for a socialist revolution emerged. Some Mensheviks, notably Alexander Potresov, called for the party to suspend illegal revolutionary work to focus more on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks, led by Vladimir Lenin, were a radical Faction (political), faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) which split with the Mensheviks at the 2nd Congress of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party, Second Party Congress in 1903. The Bolshevik party, formally established in 1912, seized power in Russia in the October Revolution of 1917, and was later renamed the Russian Communist Party, All-Union Communist Party, and ultimately the Communist Party of the Soviet Union. Its ideology, based on Leninism, Leninist and later Marxism–Leninism, Marxist–Leninist principles, became known as Bolshevism. The origin of the RSDLP split was Lenin's support for a smaller party of professional revolutionaries, as opposed to the Menshevik desire for a broad party membership. The influence of the factions fluctuated in the years up to 1912, when the RSDLP formally split in two. The political philosophy of the Bolsheviks was based on the Leninist pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Social Democratic Labour Party
The Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP), also known as the Russian Social Democratic Workers' Party (RSDWP) or the Russian Social Democratic Party (RSDP), was a socialist political party founded in 1898 in Minsk, Russian Empire. The party emerged from the merger of various Marxist groups operating under Tsarist repression, and was dedicated to the overthrow of the autocracy and the establishment of a socialist state based on the revolutionary leadership of the Russian proletariat. The RSDLP's formative years were marked by ideological and strategic disputes culminating at its Second Congress in 1903, where the party split into two main factions: the Bolsheviks, led by Vladimir Lenin, who advocated a tightly organized vanguard of professional revolutionaries; and the Mensheviks, led by Julius Martov and others, who favored a more moderate, broad-based model. During and in the years after the 1905 Revolution, the RSDLP operated both legally and underground, publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socialist Revolutionary Party
The Socialist Revolutionary Party (SR; ,, ) was a major socialist political party in the late Russian Empire, during both phases of the Russian Revolution, and in early Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Soviet Russia. The party members were known as Esers (). The SRs were Agrarian socialism, agrarian socialists and supporters of a Democratic socialism, democratic socialist Russian republic. The ideological heirs of the Narodniks, the SRs won a mass following among the Russian peasantry by endorsing the overthrow of the Russian Empire, Tsar and the Land reform, redistribution of land to the peasants. The SRs boycotted the 1906 Russian legislative election, elections to the First State Duma (Russian Empire), Duma following the 1905 Russian Revolution, Revolution of 1905 alongside the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party, but chose to run in the elections to the Second Duma and received the majority of the few seats allotted to the peasantry. Following the Coup of Jun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socialism
Socialism is an economic ideology, economic and political philosophy encompassing diverse Economic system, economic and social systems characterised by social ownership of the means of production, as opposed to private ownership. It describes the Economic ideology, economic, Political philosophy, political, and Social theory, social theories and Political movement, movements associated with the implementation of such systems. Social ownership can take various forms, including State ownership, public, Community ownership, community, Collective ownership, collective, cooperative, or Employee stock ownership, employee.: "Just as private ownership defines capitalism, social ownership defines socialism. The essential characteristic of socialism in theory is that it destroys social hierarchies, and therefore leads to a politically and economically egalitarian society. Two closely related consequences follow. First, every individual is entitled to an equal ownership share that earns an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |