|
Fatma Sultan (daughter Of Selim II)
Fatma Sultan ( 1558 – October 1580; ) was an Ottoman princess, daughter of Sultan Selim II (reign 1566–1574) of the Ottoman Empire and an unknown concubine. So she was the granddaughter of Suleiman the Magnificent (reign 1520–66) and Hürrem Sultan, half-sister of Sultan Murad III (reign 1574–1595) and aunt of Sultan Mehmed III (reign 1595–1603). Early life Fatma was born circa 1558 during Selim's princedom, at Konya where he served as sanjakbey, or provincial governor, at the time. She was her father's youngest daughter. Her mother's identity is uncertain; it's likely that she was the fourth daughter of Nurbanu Sultan, however the claim remains disputed. She had three older sisters, Şah Sultan, Gevherhan Sultan and Ismihan Sultan, an older brother, Murad III, and seven younger half-brothers who died infants when Murad became Sultan and he applicated the Law of Fraticide. Marriage In 1573, she married Kanijeli Siyavuş Pasha (died 1602), then Beylerbey (governor-gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanijeli Siyavuş Pasha
Kanijeli Siyavuş Pasha (, , died 1602, Istanbul) was an Ottoman statesman from the Sanjak of Bosnia. He was Grand Vizier between 24 December 1582 and 28 July 1584, 15 April 1586 and 2 April 1589,İsmail Hâmi Danişmend, ''Osmanlı Devlet Erkânı'', Türkiye Yayınevi, İstanbul, 1971, p. 23. and 4 April 1592 and 28 January 1593. He was from Kanizsa in modern-day Hungary, then part of first the Sanjak and then the Eyalet of Bosnia. Marriage and issue In 1573 he married Fatma Sultan, the youngest daughter of Sultan Selim II and Nurbanu Sultan. They had four sons and a daughter: *Sultanzade Ahmed Bey (1573 – 1582/1583) *Sultanzade Mustafa Paşah (1575 – April 1599). He had issue. *Sultanzade Abdülkaadir Bey (1577 – 1583) *Sultanzade Süleyman Bey (1579 – 1583) *''Fülane'' Hanımsultan (October 1580 – October 1580). She birth before the time and died three days after. Her mother died in childbirth. See also * List of Ottoman grand viziers The grand vizier of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gevherhan Sultan (daughter Of Selim II)
Gevherhan Sultan (, "''Gem of the Khan''"; sometimes wrote as Gevhermülük Sultan; 1544 – 1624) was an Ottoman princess, the daughter of Sultan Selim II (reign 1566–1574) and his favorite Nurbanu Sultan. She was the granddaughter of Suleiman the Magnificent (reign 1520–66) and Roxelana, Hürrem Sultan, sister of Sultan Murad III (reign 1574–95) and aunt of Sultan Mehmed III (reign 1595–1603). Early life Gevherhan Sultan was born in Manisa in 1544. Her father was Şehzade Selim (future Selim II), son of Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent and Hurrem Sultan. She spent her early life in Manisa and Konya, where her father served as a sanjak-bey. Her mother was Nurbanu Sultan, Selim’s favorite concubine and his future Haseki Sultan and legal wife. She had an older sister, Şah Sultan (daughter of Selim II), Şah Sultan, two younger sisters, Ismihan Sultan and Fatma Sultan (daughter of Selim II), Fatma Sultan, a younger brother, Murad III, and seven younger half-brother who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1550s Births
Year 155 ( CLV) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Severus and Rufinus (or, less frequently, year 908 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 155 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events * The Council of Rome, a pre-ecumenical church council, is held and presided over by Bishop of Rome Anicetus. Births * Cao Cao, Chinese statesman and warlord (d. 220) * Dio Cassius, Roman historian (d. c. 235) * Tertullian, Roman Christian theologian (d. c. 240) * Sun Jian, Chinese general and warlord (d. 191) Deaths * Pius I, Roman bishop * Polycarp, bishop of Smyrna (b. AD 65 AD 65 ( LXV) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Nerva and Vestinus (or, less frequently, year 818 ''Ab urbe condita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deaths In Childbirth
Death is the end of life; the irreversible cessation of all biological functions that sustain a living organism. Death eventually and inevitably occurs in all organisms. The remains of a former organism normally begin to decompose shortly after death. Some organisms, such as '' Turritopsis dohrnii'', are biologically immortal; however, they can still die from means other than aging. Death is generally applied to whole organisms; the equivalent for individual components of an organism, such as cells or tissues, is necrosis. Something that is not considered an organism, such as a virus, can be physically destroyed but is not said ''to die'', as a virus is not considered alive in the first place. As of the early 21st century, 56 million people die per year. The most common reason is aging, followed by cardiovascular disease, which is a disease that affects the heart or blood vessels. As of 2022, an estimated total of almost 110 billion humans have died, or roughly 94% of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Konya
The term "the people" refers to the public or common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. In contrast, a people is any plurality of persons considered as a whole. Used in politics and law, the term "a people" refers to the collective or community of an ethnic group or nation. Concepts Legal Chapter One, Article One of the Charter of the United Nations states that "peoples" have the right to self-determination. Though the mere status as peoples and the right to self-determination, as for example in the case of Indigenous peoples (''peoples'', as in all groups of indigenous people, not merely all indigenous persons as in ''indigenous people''), does not automatically provide for independent sovereignty and therefore secession. Indeed, judge Ivor Jennings identified the inherent problems in the right of "peoples" to self-determination, as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quran
The Quran, also Romanization, romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a Waḥy, revelation directly from God in Islam, God (''Allah, Allāh''). It is organized in 114 chapters (, ) which consist of individual verses ('). Besides its religious significance, it is widely regarded as the finest work in Arabic literature, and has significantly influenced the Arabic, Arabic language. It is the object of a modern field of academic research known as Quranic studies. Muslims believe the Quran was orally revealed by God to the final Islamic Prophets and messengers in Islam, prophet Muhammad in Islam, Muhammad through the Angel#Islam, angel Gabriel#Islam, Gabriel incrementally over a period of some 23 years, beginning on the Night of Power, Laylat al-Qadr, when Muhammad was 40, and concluding in 632, the year of his death. Muslims regard the Quran as Muhammad's most important Islamic view of miracles, miracle, a proof of his prophet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Istanbul
Istanbul is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, constituting the country's economic, cultural, and historical heart. With Demographics of Istanbul, a population over , it is home to 18% of the Demographics of Turkey, population of Turkey. Istanbul is among the List of European cities by population within city limits, largest cities in Europe and List of cities proper by population, in the world by population. It is a city on two continents; about two-thirds of its population live in Europe and the rest in Asia. Istanbul straddles the Bosphorus—one of the world's busiest waterways—in northwestern Turkey, between the Sea of Marmara and the Black Sea. Its area of is coterminous with Istanbul Province. Istanbul's climate is Mediterranean climate, Mediterranean. The city now known as Istanbul developed to become one of the most significant cities in history. Byzantium was founded on the Sarayburnu promontory by Greek colonisation, Greek col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars. For most of its history the Empire comprised the entirety of the modern countries of Germany, Czechia, Austria, the Netherlands, Belgium, Switzerland, Slovenia, and Luxembourg, most of north-central Italy, and large parts of modern-day east France and west Poland. On 25 December 800, Pope Leo III crowned the Frankish king Charlemagne Roman emperor, reviving the title more than three centuries after the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476. The title lapsed in 924, but was revived in 962 when Otto I, OttoI was crowned emperor by Pope John XII, as Charlemagne's and the Carolingian Empire's successor. From 962 until the 12th century, the empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephan Gerlach
Stephan Gerlach (Latin: ''Stephanus Gerlachius'') was a German Lutheran theologian. Gerlach was an extremely important figure in the second half of the 16th century. He was tasked with a special mission in Constantinople, namely to establish an alliance between Orthodoxy and Lutheranism against Catholicism. This mission failed, nevertheless, he signed the Brest Union. From 1573 to 1578 he was in Constantinople as the first assistant and clergyman of the ambassador of the Holy Roman Empire - Baron David Ungnad von Sonnegg. He wrote a diary, one of the most cited sources in the historical literature about the situation in Constantinople in recent years of the " Kingdom of the Slavs", i.e. after the death of Selim II and just before the outbreak of the Long Turkish War. Upon his return, he became professor of theology (1586) and head of the Protestant district in Tübingen, and he wrote against Calvinists and Jesuits The Society of Jesus (; abbreviation: S.J. or SJ), also kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Vizier
Grand vizier (; ; ) was the title of the effective head of government of many sovereign states in the Islamic world. It was first held by officials in the later Abbasid Caliphate. It was then held in the Ottoman Empire, the Mughal Empire, the Sokoto Caliphate, the Safavid dynasty, Safavid Empire and Morocco, Cherifian Empire of Morocco. In the Ottoman Empire, the grand vizier held the imperial seal and could convene all other viziers to attend to affairs of the state; the viziers in conference were called "''Kubbealtı'' viziers" in reference to their meeting place, the ''Kubbealtı'' ('under the dome') in Topkapı Palace. His offices were located at the Sublime Porte. Today, the Prime Minister of Pakistan is referred to in Urdu as ''Wazir-e-azam'', which translates literally to grand vizier. Initially, the grand viziers were exclusively of Turk origin in the Ottoman Empire. However, after there were troubles between the Turkish grand vizier Çandarlı Halil Pasha the Younger and S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
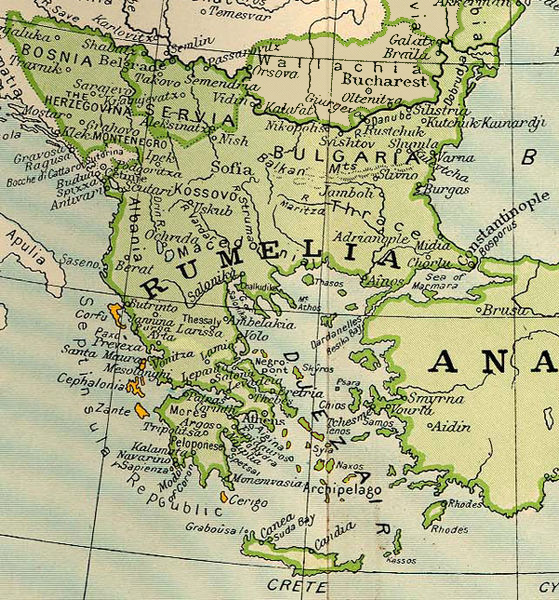
Rumelia
Rumelia (; ; ) was a historical region in Southeastern Europe that was administered by the Ottoman Empire, roughly corresponding to the Balkans. In its wider sense, it was used to refer to all Ottoman possessions and Vassal state, vassals in Europe. These would later be geopolitically classified as "the Balkans", although Hungary and Moldova are sometimes excluded. In contemporary English sources, Rumelia was known as Turkey in Europe. Etymology ''Rûm'' in this context means 'Roman' and ''ėli'' means 'land', and thus ''Rumelia'' (, ''Rūm-ėli''; Turkish language, Turkish: ''Rumeli'') means 'Land of the Romans' in Ottoman Turkish language, Ottoman Turkish. It refers to the lands conquered by the Ottoman Empire in the Balkans, most of which formerly belonged to the Byzantine Empire, known by its contemporaries as the Eastern Roman Empire, Roman Empire. Although the term ''Byzantine Empire'' is used by modern historians, the empire's citizens and emperors called themselves Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |