|
Facial Feminization Surgery
Facial feminization surgery (FFS) is a set of reconstructive surgical procedures that alter typically male facial features to bring them closer in shape and size to typical female facial features. FFS can include various bony and soft tissue procedures such as brow lift, rhinoplasty, cheek implantation, and lip augmentation. Faces contain secondary sex characteristics that make male and female faces readily distinguishable, including the shape of the forehead, nose, lips, cheeks, chin, and jawline; the features in the upper third of the face seem to be the most important, and subtle changes in the lips can have a strong effect. Candidates For some transgender women and non binary people, FFS is medically necessary to treat gender dysphoria. It can be just as important or even more important than genital forms of sex reassignment surgery (SRS) in reducing gender dysphoria and helping trans women integrate socially as women; data on these sorts of outcomes are limited by small st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgery
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery such as gastric bypass), to reconstruct or alter aesthetics and appearance (cosmetic surgery), or to remove unwanted tissue (biology), tissues (body fat, glands, scars or skin tags) or foreign bodies. The act of performing surgery may be called a surgical procedure or surgical operation, or simply "surgery" or "operation". In this context, the verb "operate" means to perform surgery. The adjective surgical means pertaining to surgery; e.g. surgical instruments, operating theater, surgical facility or surgical nurse. Most surgical procedures are performed by a pair of operators: a surgeon who is the main operator performing the surgery, and a surgical assistant who provides in-procedure manual assistance during surgery. Modern surgical opera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
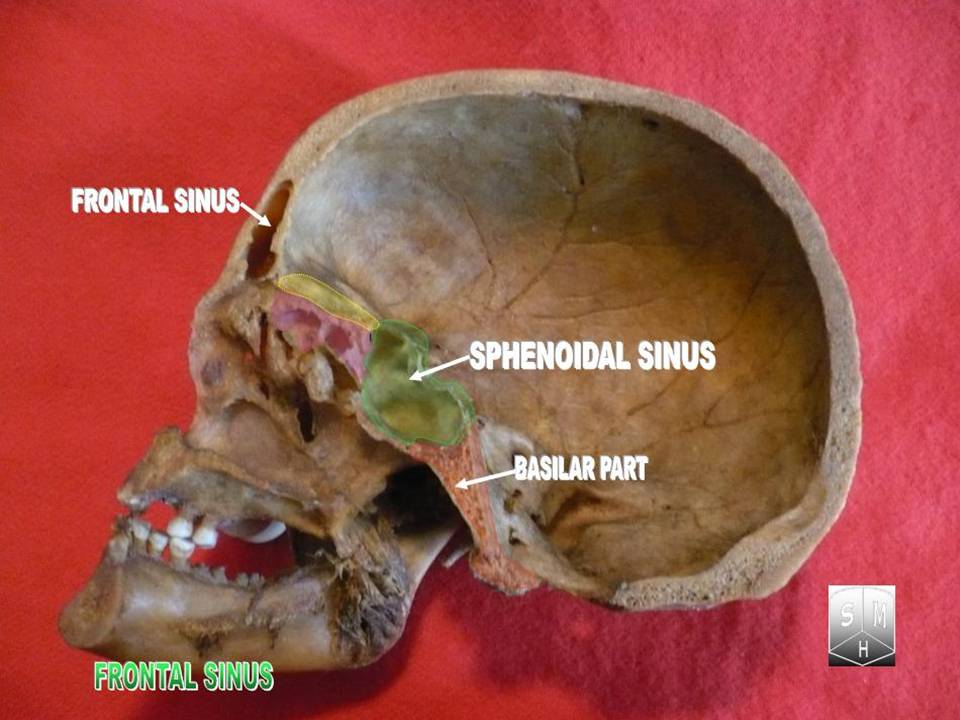
Frontal Sinus
The frontal sinuses are one of the four pairs of paranasal sinuses that are situated behind the brow ridges. Sinuses are mucosa-lined airspaces within the bones of the face and skull. Each opens into the anterior part of the corresponding middle nasal meatus of the nose through the frontonasal duct which traverses the anterior part of the labyrinth of the ethmoid. These structures then open into the semilunar hiatus in the middle meatus. Structure Each frontal sinus is situated between the external and internal plates of the frontal bone. Their average measurements are as follows: height 28 mm, breadth 24 mm, depth 20 mm, creating a space of 6-7 ml. Each frontal sinus extends into the squamous part of the frontal bone superiorly, and into the orbital part of frontal bone posteriorly to come to occupy the medial part of the roof of the orbit. Each sinus drains through an opening in its inferomedial part into the frontonasal duct. Vasculature The mucous me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaw Reduction
Jaw reduction or mandible angle reduction is a type of surgery to narrow the lower one-third of the face—particularly the contribution from the mandible and its muscular attachments. There are several techniques for treatment—including surgical and non-surgical methods. A square lower jaw can be considered a masculine trait, especially in Asian countries. As a result, whereas square lower jaws are often considered a positive trait in men, a wide mandible can be perceived as discordant or masculine on women, or sometimes in certain men, particularly when there is asymmetry. A wide lower face can primarily be caused by a wide mandibular bone or large masseter muscle. A large masseter muscle can be reduced in apparent size with the use of botox injections whereas having a wide mandibular bone requires surgical intervention to reduce the size of the bones. Consultation and patient evaluation A facial structure with a larger mandible arch and wide zygoma is common, particularly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sliding Genioplasty
Chin augmentation using surgical implants alter the underlying structure of the face, intended to balance the facial features. The specific medical terms mentoplasty and genioplasty are used to refer to the reduction and addition of material to a patient's chin. This can take the form of chin height reduction or chin rounding by osteotomy, or chin augmentation using implants. Altering the facial balance is commonly performed by modifying the chin using an implant inserted through the mouth. The intent is to provide a suitable projection of the chin as well as the correct height of the chin which is in balance with the other facial features. This operation is often, but not always, performed at the time of rhinoplasty to help balance the facial proportions. Chin augmentation may be achieved by manipulation of the jaw bone (mandible) and augmentation utilizing this technique usually provides a more dramatic correction than with the use of prosthetic implants. Chin implants are used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acellular Dermis
Acellular dermis is a type of biomaterial derived from processing human or animal tissues to remove cells and retain portions of the extracellular matrix (ECM). These materials are typically cell-free, distinguishing them from classical allografts and xenografts, can be integrated or incorporated into the body, and have been FDA approved for human use for more than 10 years in a wide range of clinical indications.Cornwell, K.G., Landsman, A., James, K.S. ''Extracellular Matrix Biomaterials for Soft Tissue Repair.'' Clin Podiatr Med Surg 26 (2009) 507–52(Original Article)/ref> Harvesting and processing All ECM samples originate from mammalian tissues, such as dermis, pericardium, and small intestinal submucosa (SIS). After explantation from the source, the ECM biomaterial retains some characteristics of the original tissue. The ECM tissues can be harvested from varying stages in the developmental stages in mammalian species such as human, porcine, equine, and bovine. Although th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lip Augmentation
Lip augmentation is a cosmetic procedure that modifies the shape of the lips using fillers, such as collagen or implants. The procedure may be performed to increase lip size, correct asymmetry, create protrusion, or adjust the ratio of the top and bottom lips. The procedure typically involves surgical injection, though temporary non-surgical alternatives exist. Swelling and bruising are common after lip augmentation, and irritation or allergic reactions may also occur. Lip augmentations can have undesired cosmetic effects, including scarring and lumping, and implants pose the risk of shifting underneath the lip or breaking through the skin. History Around 1900, surgeons tried injecting Paraffin wax, paraffin into the lips without success. Liquid silicone was used for lip augmentation, starting in the early 1960s but was abandoned thirty years later due to fears about the effects of silicone on general health and long term aesthetic outcome. In about 1980, injectable bovine col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteotomy
An osteotomy is a surgical operation whereby a bone is cut to shorten or lengthen it or to change its alignment. It is sometimes performed to correct a hallux valgus, or to straighten a bone that has healed crookedly following a fracture. It is also used to correct a coxa vara, genu valgum, and genu varum. The operation is done under a general anaesthetic. Osteotomy is one method to relieve pain of arthritis, especially of the hip and knee. It is being replaced by joint replacement in the older patient. Due to the serious nature of this procedure, recovery may be extensive. Careful consultation with a physician is important in order to ensure proper planning during a recovery phase. Tools exist to assist recovering patients who may have non– weight bearing requirements and include bedpans, dressing sticks, long-handled shoe-horns, grabbers/reachers and specialized walkers and wheelchairs. Osteotomies of the hip Two main types of osteotomies are used in the correction of h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygomatic Bone
In the human skull, the zygomatic bone (from ), also called cheekbone or malar bone, is a paired irregular bone, situated at the upper and lateral part of the face and forming part of the lateral wall and floor of the orbit, of the temporal fossa and the infratemporal fossa. It presents a malar and a temporal surface; four processes (the frontosphenoidal, orbital, maxillary, and temporal), and four borders. Etymology The term ''zygomatic'' derives from the Ancient Greek , ''zygoma'', meaning "yoke". The zygomatic bone is occasionally referred to as the zygoma, but this term may also refer to the zygomatic arch. Structure Surfaces The ''malar surface'' is convex and perforated near its center by a small aperture, the zygomaticofacial foramen, for the passage of the zygomaticofacial nerve and vessels; below this foramen is a slight elevation, which gives origin to the zygomaticus muscle. The ''temporal surface'', directed posteriorly and medially, is concave, prese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomy Of The Human Nose
The human nose is the first organ of the respiratory system. It is also the principal organ in the olfactory system. The shape of the nose is determined by the nasal bones and the nasal cartilages, including the nasal septum, which separates the nostrils and divides the nasal cavity into two. The nose has an important function in breathing. The nasal mucosa lining the nasal cavity and the paranasal sinuses carries out the necessary conditioning of inhaled air by warming and moistening it. Nasal conchae, shell-like bones in the walls of the cavities, play a major part in this process. Filtering of the air by nasal hair in the nostrils prevents large particles from entering the lungs. Sneezing is a reflex to expel unwanted particles from the nose that irritate the mucosal lining. Sneezing can transmit infections, because aerosols are created in which the droplets can harbour pathogens. Another major function of the nose is olfaction, the sense of smell. The area of olfactory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecanthus
Telecanthus, or dystopia canthorum, refers to increased distance between the inner corners of the eyelids (medial canthi), while the inter-pupillary distance is normal. This is in contrast to hypertelorism, in which the distance between the whole eyes is increased. Telecanthus and hypertelorism are each associated with multiple congenital disorders. The distance between the inner corners of the Eyelid, eyelids is called the intercanthal distance. In most people, the intercanthal distance is equal to the width of each eye (the distance between the inner and outer corners of each eye). The average interpupillary distance is 60–62 millimeters (mm), which corresponds to an intercanthal distance of approximately 30–31 mm. ''Traumatic telecanthus'' refers to telecanthus resulting from traumatic injury to the nasal-Orbit (anatomy), orbital-Ethmoid bone, ethmoid (NOE) complex. The diagnosis of traumatic telecanthus requires a measurement in excess of those normative values. The path ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraorbital Ridge
The brow ridge, or supraorbital ridge known as superciliary arch in medicine, is a bony ridge located above the eye sockets of all primates and some other animals. In humans, the Eyebrow, eyebrows are located on their lower margin. Structure The brow ridge is a nodule or crest of bone situated on the frontal bone of the skull. It forms the separation between the forehead portion itself (the squama frontalis) and the roof of the eye sockets (the Orbital part of frontal bone, pars orbitalis). Normally, in humans, the ridges arch over each eye, offering mechanical protection. In other primates, the ridge is usually continuous and often straight rather than arched. The ridges are separated from the frontal eminences by a shallow groove. The ridges are most prominent medially, and are joined to one another by a smooth elevation named the glabella. Typically, the arches are more prominent in men than in women, and vary between different human populations. Behind the ridges, deeper in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |