|
F(ab')2
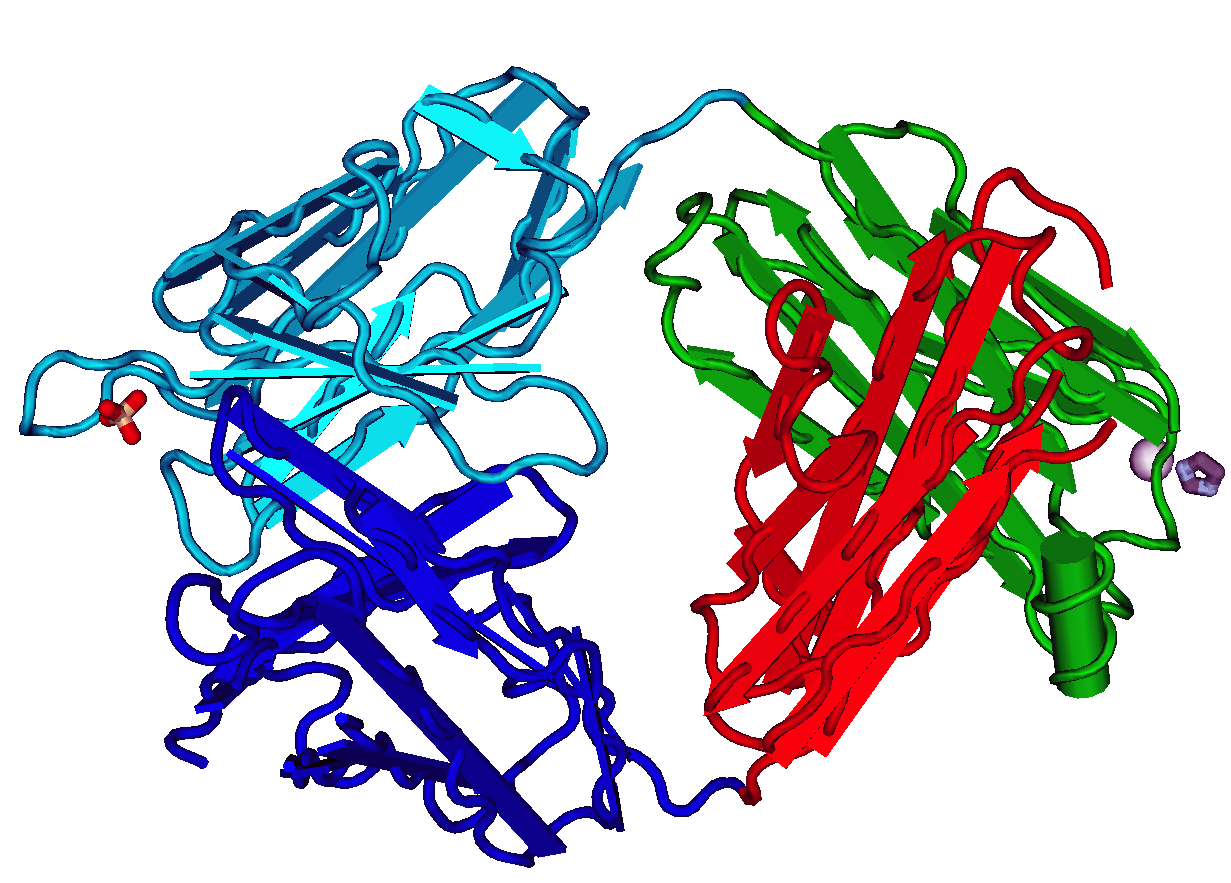
The fragment antigen-binding region (Fab region) is a region on an antibody that binds to antigens. It is composed of one constant and one variable domain of each of the heavy and the light chain. The variable domain contains the paratope (the antigen-binding site), comprising a set of complementarity-determining regions, at the amino terminal end of the monomer. Each arm of the Y thus binds an epitope on the antigen. Preparation In an experimental setting, Fc and Fab fragments can be generated in the laboratory. The enzyme papain can be used to cleave an immunoglobulin monomer into two Fab fragments and an Fc fragment. Conversely, the enzyme pepsin cleaves below the hinge region, so the result instead is a F(ab')2 fragment and a pFc' fragment. Recently another enzyme for generation of F(ab')2 has been commercially available. The enzyme IdeS (Immunoglobulin degrading enzyme from ''Streptococcus pyogenes'', trade name FabRICATOR) cleaves IgG in a sequence specific manner at ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pepsin
Pepsin is an endopeptidase that breaks down proteins into smaller peptides and amino acids. It is one of the main digestive enzymes in the digestive systems of humans and many other animals, where it helps digest the proteins in food. Pepsin is an aspartic protease, using a catalytic aspartate in its active site. It is one of three principal endopeptidases (enzymes cutting proteins in the middle) in the human digestive system, the other two being chymotrypsin and trypsin. There are also exopeptidases which remove individual amino acids at both ends of proteins (carboxypeptidases produced by the pancreas and aminopeptidases secreted by the small intestine). During the process of digestion, these enzymes, each of which is specialized in severing links between particular types of amino acids, collaborate to break down dietary proteins into their components, i.e., peptides and amino acids, which can be readily absorbed by the small intestine. The cleavage specificity o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fc Region
The fragment crystallizable region (Fc region) is the tail region of an antibody that interacts with cell surface receptors called Fc receptors and some proteins of the complement system. This region allows antibodies to activate the immune system, for example, through binding to Fc receptors. In IgG, IgA and IgD antibody isotypes, the Fc region is composed of two identical protein fragments, derived from the second and third constant domains of the antibody's two heavy chains; IgM and IgE Fc regions contain three heavy chain constant domains (CH domains 2–4) in each polypeptide chain. The Fc regions of IgGs bear a highly conserved N-glycosylation site. Glycosylation of the Fc fragment is essential for Fc receptor-mediated activity. The N-glycans attached to this site are predominantly core- fucosylated diantennary structures of the complex type. In addition, small amounts of these N-glycans also bear bisecting GlcNAc and α-2,6 linked sialic acid residues. The other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
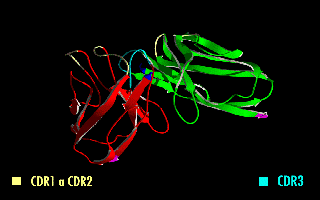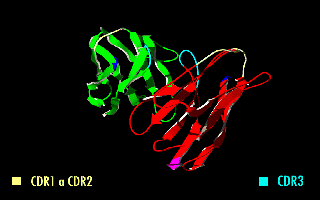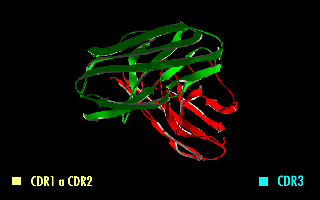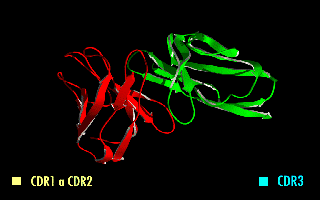
Single-chain Variable Fragment
A single-chain variable fragment (scFv) is not actually a fragment of an antibody, but instead is a fusion protein of the variable regions of the heavy (VH) and light chains (VL) of immunoglobulins, connected with a short linker peptide of ten to about 25 amino acids. The linker is usually rich in glycine for flexibility, as well as serine or threonine for solubility, and can either connect the N-terminus of the VH with the C-terminus of the VL, or ''vice versa''. This protein retains the specificity of the original immunoglobulin, despite removal of the constant regions and the introduction of the linker. The image to the right shows how this modification usually leaves the specificity unaltered. These molecules were created to facilitate phage display, where it is highly convenient to express the antigen-binding domain as a single peptide. As an alternative, scFv can be created directly from subcloned heavy and light chains derived from a hybridoma. ScFvs have many uses, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platelet
Platelets or thrombocytes () are a part of blood whose function (along with the coagulation#Coagulation factors, coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping to form a thrombus, blood clot. Platelets have no cell nucleus; they are fragments of cytoplasm from megakaryocytes which reside in bone marrow or Lung, lung tissue, and then enter the circulation. Platelets are found only in mammals, whereas in other vertebrates (e.g. birds, amphibians), thrombocytes circulate as intact agranulocyte, mononuclear cells. One major function of platelets is to contribute to hemostasis: the process of stopping bleeding at the site where the lining of vessels (endothelium) has been interrupted. Platelets gather at the site and, unless the interruption is physically too large, they plug the hole. First, platelets attach to substances outside the interrupted endothelium: ''adhesion (medicine), adhesion''. Second, they change shape, turn on receptors and secret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa Inhibitors
In medicine, glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors, also GpIIb/IIIa inhibitors, is a class of antiplatelet agents. Several GpIIb/IIIa inhibitors exist: * abciximab (abcixifiban) (ReoPro) * eptifibatide (Integrilin) * tirofiban (Aggrastat) * roxifiban * orbofiban Use Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors are frequently used during percutaneous coronary intervention (angioplasty with or without intracoronary stent placement). They work by preventing platelet aggregation and thrombus formation. They do so by inhibition of the GpIIb/IIIa receptor on the surface of the platelet Platelets or thrombocytes () are a part of blood whose function (along with the coagulation#Coagulation factors, coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping to form a thrombus, blood clot. Platelets have no ...s. They may also be used to treat acute coronary syndromes, without percutaneous coronary intervention, depending on TIMI risk. They should be given intravenou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abciximab
Abciximab, a glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor antagonist manufactured by Janssen Biologics BV and distributed by Eli Lilly under the trade name ReoPro, is a platelet aggregation inhibitor mainly used during and after coronary artery procedures like angioplasty to prevent platelets from sticking together and causing thrombus (blood clot) formation within the coronary artery. It is a glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor. While abciximab has a short plasma half-life, due to its strong affinity for its receptor on the platelets, it may occupy some receptors for weeks. In practice, platelet aggregation gradually returns to normal about 96 to 120 hours after discontinuation of the drug. Abciximab is made from the Fab fragments of an immunoglobulin that targets the glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor on the platelet membrane. Indications for use Abciximab is indicated for use in individuals undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (angioplasty with or without stent placement). The use of abci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoclonal Antibodies
A monoclonal antibody (mAb, more rarely called moAb) is an antibody produced from a Lineage (evolution), cell lineage made by cloning a unique white blood cell. All subsequent antibodies derived this way trace back to a unique parent cell. Monoclonal antibodies are identical and can thus have Valence (chemistry), monovalent affinity, binding only to a particular epitope (the part of an antigen that is recognized by the antibody). In contrast, polyclonal antibodies are mixtures of antibodies derived from multiple plasma cell lineages which each bind to their particular target epitope. Artificial antibodies known as bispecific monoclonal antibodies can also be engineered which include two different antigen binding sites (Fragment antigen-binding region, FABs) on the same antibody. It is possible to produce monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to almost any suitable substance; they can then serve to detect or purify it. This capability has become an investigative tool in b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis (Greek: 'up' + 'guarding') is a serious, potentially fatal allergic reaction and medical emergency that is rapid in onset and requires immediate medical attention regardless of the use of emergency medication on site. It typically causes more than one of the following: an itchy rash, throat closing due to swelling that can obstruct or stop breathing; severe tongue swelling that can also interfere with or stop breathing; shortness of breath, vomiting, lightheadedness, loss of consciousness, low blood pressure, and medical shock. These symptoms typically start in minutes to hours and then increase very rapidly to life-threatening levels. Urgent medical treatment is required to prevent serious harm and death, even if the patient has used an epinephrine autoinjector or has taken other medications in response, and even if symptoms appear to be improving. Cause, mechanism, and diagnosis Common causes include allergies to insect bites and stings, allergies to fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drug Saf
Pharmacovigilance (PV, or PhV), also known as drug safety, is the pharmaceutical science relating to the "collection, detection, assessment, monitoring, and prevention" of adverse effects with pharmaceutical products. The etymological roots for the word "pharmacovigilance" are: (Greek for drug) and (Latin for to keep watch). As such, pharmacovigilance heavily focuses on adverse drug reactions (ADR), which are defined as any response to a drug which is noxious and unintended. That definition includes lack of efficacy: that means that the doses normally used for prevention, diagnosis, or treatment of a disease—or, especially in the case of device, for the modification of physiological disorder function. In 2010, the European Union expanded PV to include medication errors such as overdose, misuse, and abuse of a drug as well as drug exposure during pregnancy and breastfeeding. These are monitored even in the absence of an adverse event, because they may result in an adverse dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tricyclic Antidepressant
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are a class of medications that are used primarily as antidepressants. TCAs were discovered in the early 1950s and were marketed later in the decade. They are named after their chemical structure, which contains three rings of atoms. Tetracyclic antidepressants (TeCAs), which contain four rings of atoms, are a closely related group of antidepressant compounds. Although TCAs are sometimes prescribed for depressive disorders, they have been largely replaced in clinical use in most parts of the world by newer antidepressants such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (NRIs). Adverse effects have been found to be of a similar level between TCAs and SSRIs. Medical uses The TCAs are used primarily in the clinical treatment of mood disorders such as major depressive disorder (MDD), dysthymia, and treatment-resistant variants. They are also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |