|
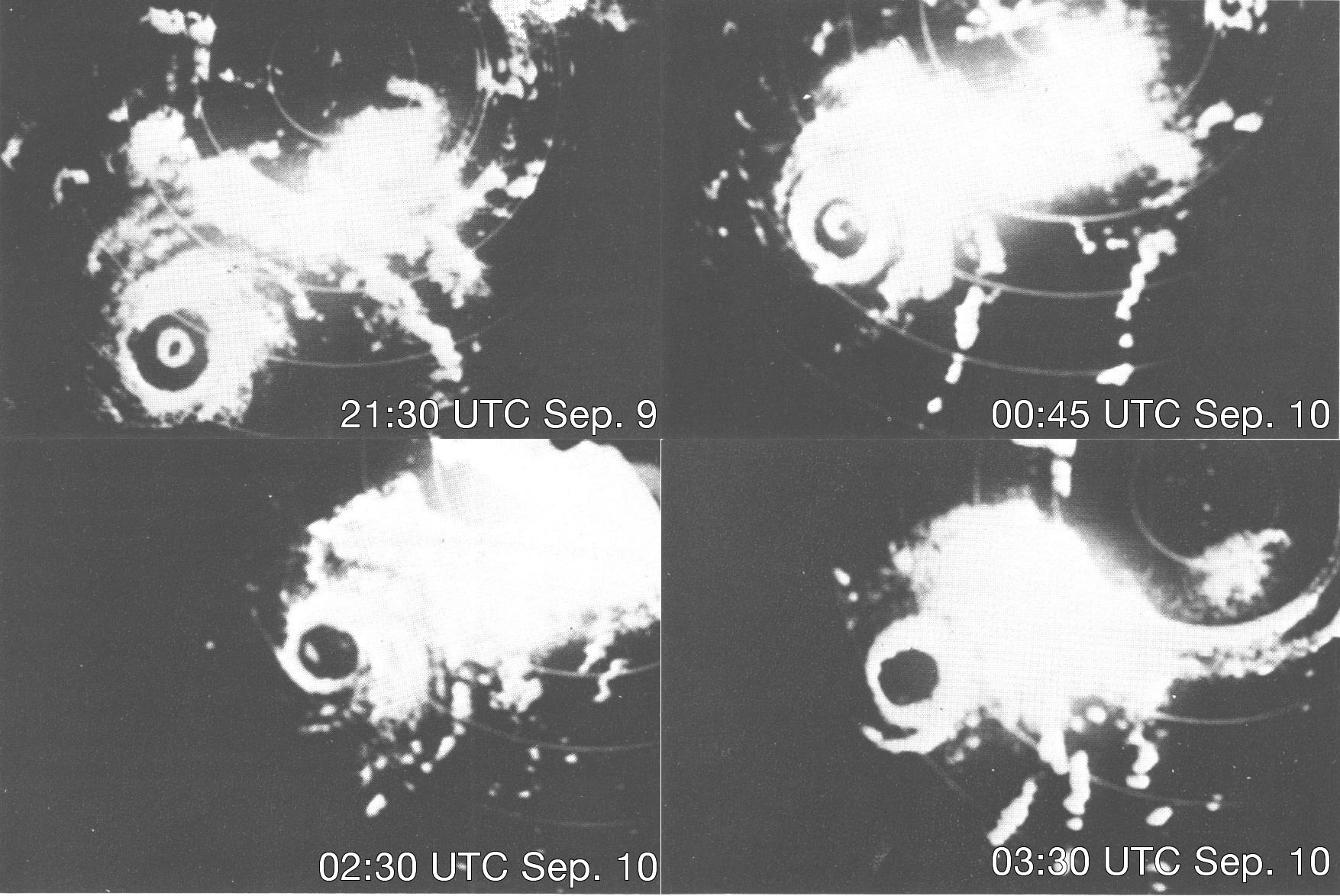
Eyewall Replacement Cycle
In meteorology, eyewall replacement cycles, also called concentric eyewall cycles, naturally occur in intense tropical cyclones with maximum sustained winds greater than , or hurricane-force, and particularly in major hurricanes of Saffir–Simpson scale, Saffir–Simpson category 3 to 5. In such storms, some of the outer rainbands may strengthen and organize into a ring of thunderstorms—a new, outer Eye (cyclone), eyewall—that slowly moves inward and robs the original, inner eyewall of its needed moisture and angular momentum. Since the strongest winds are in a tropical cyclone's Eye (cyclone), eyewall, the storm usually weakens during this phase, as the inner wall is "choked" by the outer wall. Eventually the outer eyewall replaces the inner one completely, and the storm may re-intensify. The discovery of this process was partially responsible for the end of the U.S. government's hurricane modification experiment Project Stormfury. This project set out to cloud seeding, seed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Milton Eyewall Replacement Cycle Infrared Loop
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its location and strength, a tropical cyclone is called a hurricane (), typhoon (), tropical storm, cyclonic storm, tropical depression, or simply cyclone. A hurricane is a strong tropical cyclone that occurs in the Atlantic Ocean or northeastern Pacific Ocean. A typhoon is the same thing which occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. In the Indian Ocean and South Pacific, comparable storms are referred to as "tropical cyclones". In modern times, on average around 80 to 90 named tropical cyclones form each year around the world, over half of which develop hurricane-force winds of or more. Tropical cyclones tropical cyclogenesis, typically form over large bodies of relatively warm water. They derive their energy through the evaporation of water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1975 Pacific Typhoon Season
The 1975 Pacific typhoon season was the deadliest Pacific typhoon season, tropical cyclone seasons on record, with nearly 229,000 fatalities occurring during the season. Despite this, it was one of the least active on record, with only 21 named storms forming throughout the year. It had no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1975, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. Tropical Storms formed in the entire west pacific basin were assigned a name by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Tropical depressions in this basin have the "W" suffix added to their number. Tropical depressions that enter or form in the Philippine area of responsibility are assigned a name by the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration or PAGASA. This can often result in the same storm havi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latent Heat
Latent heat (also known as latent energy or heat of transformation) is energy released or absorbed, by a body or a thermodynamic system, during a constant-temperature process—usually a first-order phase transition, like melting or condensation. Latent heat can be understood as hidden energy which is supplied or extracted to change the state of a substance without changing its temperature or pressure. This includes the latent heat of fusion (solid to liquid), the latent heat of vaporization (liquid to gas) and the latent heat of sublimation (solid to gas). The term was introduced around 1762 by Scottish chemist Joseph Black. Black used the term in the context of calorimetry where a heat transfer caused a volume change in a body while its temperature was constant. In contrast to latent heat, sensible heat is energy transferred as heat, with a resultant temperature change in a body. Usage The terms ''sensible heat'' and ''latent heat'' refer to energy transferred between a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inertial Instability
In classical physics and special relativity, an inertial frame of reference (also called an inertial space or a Galilean reference frame) is a frame of reference in which objects exhibit inertia: they remain at rest or in uniform motion relative to the frame until acted upon by external forces. In such a frame, the laws of nature can be observed without the need to correct for acceleration. All frames of reference with zero acceleration are in a state of constant rectilinear motion (straight-line motion) with respect to one another. In such a frame, an object with zero net force acting on it, is perceived to move with a constant velocity, or, equivalently, Newton's first law of motion holds. Such frames are known as inertial. Some physicists, like Isaac Newton, originally thought that one of these frames was absolute — the one approximated by the fixed stars. However, this is not required for the definition, and it is now known that those stars are in fact moving, relative to o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Theory
A scientific theory is an explanation of an aspect of the universe, natural world that can be or that has been reproducibility, repeatedly tested and has corroborating evidence in accordance with the scientific method, using accepted protocol (science), protocols of observation, measurement, and evaluation of results. Where possible, theories are tested under controlled conditions in an experiment. In circumstances not amenable to experimental testing, theories are evaluated through principles of abductive reasoning. Established scientific theories have withstood rigorous scrutiny and embody scientific knowledge. A scientific theory differs from a scientific fact: a fact is an observation and a theory organizes and explains multiple observations. Furthermore, a theory is expected to make predictions which could be confirmed or refuted with addition observations. Stephen Jay Gould wrote that "...facts and theories are different things, not rungs in a hierarchy of increasing certai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver Iodide
Silver iodide is an inorganic compound with the formula Ag I. The compound is a bright yellow solid, but samples almost always contain impurities of metallic silver that give a grey colouration. The silver contamination arises because some samples of AgI can be highly photosensitive. This property is exploited in silver-based photography. Silver iodide is also used as an antiseptic and in cloud seeding. Structure The structure adopted by silver iodide is temperature dependent: * Below 420 K, the β phase of AgI, with the wurtzite structure, is most stable. This phase is encountered in nature as the mineral iodargyrite. * Above 420 K, the α phase becomes more stable. This motif is a body-centered cubic structure which has the silver centers distributed randomly between 6 octahedral, 12 tetrahedral and 24 trigonal sites. At this temperature, Ag+ ions can move rapidly through the solid, allowing fast ion conduction. The transition between the β and α forms repre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at normally-encountered concentrations it is odorless. As the source of carbon in the carbon cycle, atmospheric is the primary carbon source for life on Earth. In the air, carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared, infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. Carbon dioxide is soluble in water and is found in groundwater, lakes, ice caps, and seawater. It is a trace gas Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, in Earth's atmosphere at 421 parts per million (ppm), or about 0.042% (as of May 2022) having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm or about 0.028%. Burning fossil fuels is the main cause of these increased concentrations, which are the primary cause of climate change.IPCC (2022Summary for pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puerto Rico
; abbreviated PR), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, is a Government of Puerto Rico, self-governing Caribbean Geography of Puerto Rico, archipelago and island organized as an Territories of the United States, unincorporated territory of the United States under the designation of Commonwealth (U.S. insular area), commonwealth. Located about southeast of Miami, Miami, Florida between the Dominican Republic in the Greater Antilles and the United States Virgin Islands, U.S. Virgin Islands in the Lesser Antilles, it consists of the eponymous main island and numerous smaller islands, including Vieques, Puerto Rico, Vieques, Culebra, Puerto Rico, Culebra, and Isla de Mona, Mona. With approximately 3.2 million Puerto Ricans, residents, it is divided into Municipalities of Puerto Rico, 78 municipalities, of which the most populous is the Capital city, capital municipality of San Juan, Puerto Rico, San Juan, followed by those within the San Juan–Bayamón–Caguas metro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Beulah
Hurricane Beulah was an intense Category 5 hurricane which impacted the Greater Antilles, Mexico, and Texas in September 1967. The second tropical storm, second hurricane, only major hurricane, and strongest storm in the 1967 Atlantic hurricane season, Beulah tracked through the Caribbean, struck the Yucatán Peninsula of Mexico as a major hurricane, and moved west-northwestward into the Gulf of Mexico, briefly becoming a Category 5 hurricane. The hurricane made landfall just north of the mouth of the Rio Grande as a Category 3 hurricane. It spawned 115 tornadoes across Texas, which established a new record for the highest amount of tornadoes produced by a tropical cyclone. Due to its slow movement over Texas, Beulah led to significant flooding. Throughout its path, at least 59 people were killed and total damage reached $234.6 million (1967 USD), of which $200 million occurred in the United States, $26.9 million occurred in Mexico, and $7.65 million occurred in the eastern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Donna
Hurricane Donna, known in Puerto Rico as Hurricane San Lorenzo, was the strongest hurricane of the 1960 Atlantic hurricane season, and caused severe damage to the Lesser Antilles, the Greater Antilles, and the East Coast of the United States, especially Florida, in August and September. The fifth tropical cyclone, third hurricane, and first major hurricane of the season, Donna developed south of Cape Verde on August 29, spawned by a tropical wave to which 63 deaths from a plane crash in Senegal were attributed. The depression strengthened into Tropical Storm Donna by the following day. Donna moved west-northwestward at roughly and by September 1, it reached hurricane status. Over the next three days, Donna deepened significantly and reached maximum sustained winds of on September 4. Thereafter, it maintained intensity as it struck the Lesser Antilles later that day. On Sint Maarten, the storm left a quarter of the island's population homeless and killed s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1956 Pacific Typhoon Season
The 1956 Pacific typhoon season has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1956, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. The scope of this article is limited to the Pacific Ocean, north of the equator and west of the International Date Line. Storms that form east of the date line and north of the equator are called hurricanes; see 1956 Pacific hurricane season. Tropical storms forming in the entire west Pacific basin were assigned a name by the Fleet Weather Center on Guam. Systems ImageSize = width:1002 height:290 PlotArea = top:10 bottom:80 right:25 left:20 Legend = columns:3 left:30 top:58 columnwidth:270 AlignBars = early DateFormat = dd/mm/yyyy Period = from:01/01/1956 till:31/01/1957 TimeAxis = orientation:horizontal ScaleMinor = grid:black unit:month increment:1 start:01/01/1956 Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |