|
Extinct Languages Of The Marañón River Basin
The Marañón River basin, at a low point in the Andes which made it an attractive location for trade between the Inca Empire and the Amazon basin, once harbored numerous languages which have been poorly attested or not attested at all. Those of the middle reaches of the river, above the Amazon basin, were replaced in historical times by Aguaruna, a Jivaroan language from the Amazon which is still spoken there. The languages further upriver are difficult to identify, due to lack of data. The region was multilingual at the time of the Conquest, and the people largely switched to Spanish rather than to Quechua, though Quechua also expanded during Colonial times. In Ecuador, at the province of Loja, were Palta, Malacato, Rabona, Bolona, and Xiroa. Historical sources suggest these were closely related, and there is some evidence that Palta (see) was a Jivaroan language. The name ''Xiroa'' may be a variant of ''Jivaro''. Rabona is attested by a few words, some of which seem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andean Languages
Amerind is a hypothetical macrofamily, higher-level language family proposed by Joseph Greenberg in 1960 and elaborated by his student Merritt Ruhlen. Greenberg proposed that all of the indigenous languages of the Americas belong to one of three language families, the previously established Eskimo–Aleut languages, Eskimo–Aleut and Na-Dene languages, Na–Dene, and with everything else—otherwise classified by specialists as belonging to dozens of independent families—as Amerind. Because of a large number of methodological disagreements with the 1987 book ''Language in the Americas'', the relationships he proposed between these languages have been rejected by the majority of historical linguists as spurious. The term ''Amerind'' is also occasionally used to refer broadly to the various indigenous languages of the Americas without necessarily implying that they are a genetic (linguistics), genealogical group. To avoid ambiguity, the term Amerindian is often used for the latte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cañari Language
Cañar or Cañari is a poorly attested extinct language of the Marañón River basin in Ecuador which is difficult to classify, apart from being apparently related to Puruhá, though it may have been Chimuan or Barbacoan. (See Cañari–Puruhá languages.) It was the original language of the Cañari people before its replacement by Kichwa and later Spanish. Cañari substratum in Cañar Quichua According to Urban (2018), modern-day Cañar Quichua (spoken in Cañar Province, Ecuador) has a Cañari substratum Substrata, plural of substratum, may refer to: *Earth's substrata, the geologic layering of the Earth *''Hypokeimenon'', sometimes translated as ''substratum'', a concept in metaphysics *Substrata (album), a 1997 ambient music album by Biosphere * ..., which can be seen in the phonology and lexicon of the dialect. Below is a list of Cañar Quichua words with Barbacoan lexical parallels, and hence likely to be words of Cañari origin. The words were compiled by Ur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sloth
Sloths are a Neotropical realm, Neotropical group of xenarthran mammals constituting the suborder Folivora, including the extant Arboreal locomotion, arboreal tree sloths and extinct terrestrial ground sloths. Noted for their slowness of movement, tree sloths spend most of their lives hanging upside down in the trees of the tropical rainforests of South America and Central America. Sloths are considered to be most closely related to anteaters, together making up the xenarthran order Pilosa. There are six extant sloth species in two genera – ''Bradypus'' (three-toed sloths) and ''Choloepus'' (two-toed sloths). Despite this traditional naming, all sloths have three toes on each rear limb – although two-toed sloths have only two digits on each forelimb. The two groups of sloths are from different, distantly related families, and are thought to have evolved their morphology via parallel evolution from terrestrial ancestors. Besides the extant species, many species of ground sl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
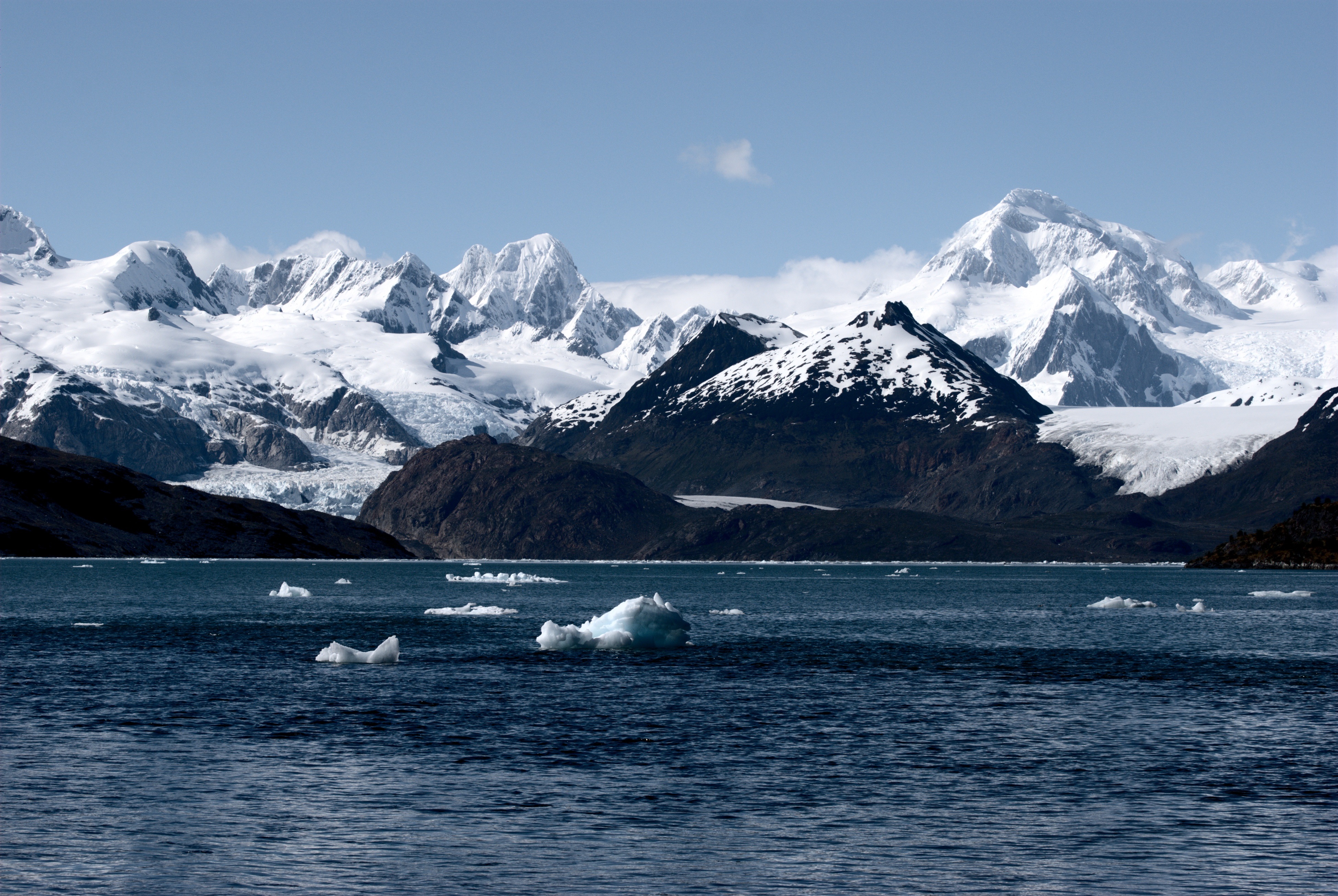
Patagonia
Patagonia () is a geographical region that includes parts of Argentina and Chile at the southern end of South America. The region includes the southern section of the Andes mountain chain with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and glaciers in the west and Patagonian Desert, deserts, Plateaus, tablelands, and steppes to the east. Patagonia is bounded by the Pacific Ocean on the west, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, and many bodies of water that connect them, such as the Strait of Magellan, the Beagle Channel, and the Drake Passage to the south. The northern limit of the region is not precisely defined; the Colorado River, Argentina, Colorado and Barrancas River, Barrancas rivers, which run from the Andes to the Atlantic, are commonly considered the northern limit of Argentine Patagonia. The archipelago of Tierra del Fuego is sometimes considered part of Patagonia. Most geographers and historians locate the northern limit of Chilean Patagonia at Huincul Fault, in Araucanía R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tierra Del Fuego
Tierra del Fuego (, ; Spanish for "Land of Fire", rarely also Fireland in English) is an archipelago off the southernmost tip of the South America, South American mainland, across the Strait of Magellan. The archipelago consists of the main island, Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego, with an area of , along with numerous smaller islands, including Cape Horn and Diego Ramírez Islands. The western part of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago, about two-thirds including its many islands, is part of Chile, and the eastern part is part of Argentina. The southernmost extent of the archipelago, Cape Horn, lies just north of latitude 56th parallel south, 56°S. The earliest-known human settlement in Tierra del Fuego dates to approximately 8,000 BC. Europeans first explored the islands during Ferdinand Magellan's expedition of 1520. ''Tierra del Fuego'' ("Land of Fire") and similar names stem from sightings of the many fires that the inhabitants built along the coastline and possibly even in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
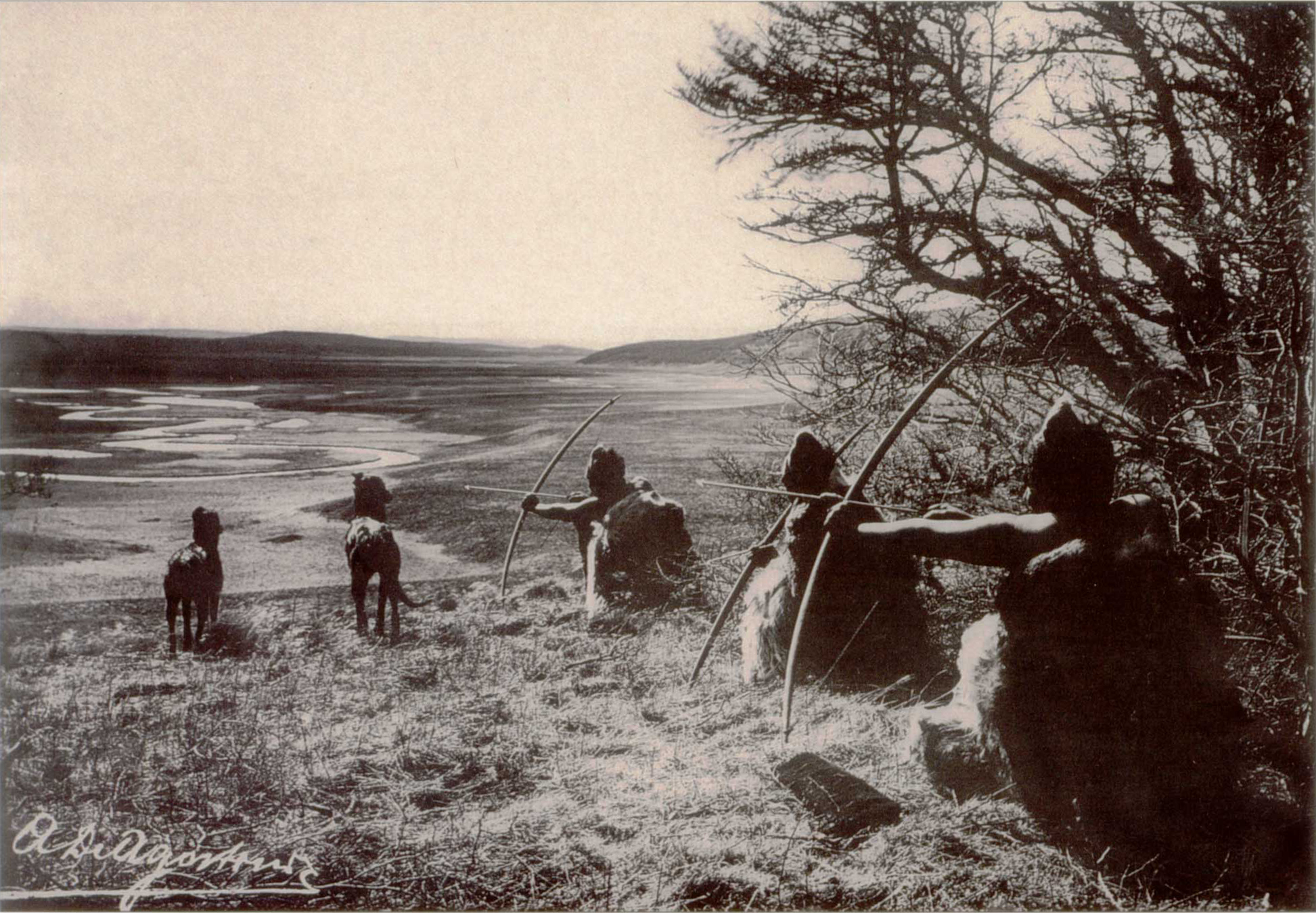
Chonan Languages
The Chonan languages are a family of indigenous American languages which were spoken in Tierra del Fuego and Patagonia. Two Chon languages are well attested: Selkʼnam (or Ona), spoken by the people of the same name who occupied territory in the northeast of Tierra del Fuego; and Tehuelche spoken by the people of the same name who occupied territory north of Tierra del Fuego. The name of the family is from ''čonn'', the Selkʼnam word for 'man'. Previous studies The Selkʼnam people were widely studied by anthropologists such as Martin Gusinde and Anne Chapman throughout the 20th century. However, their language went extinct in the 1970s. Classification The Haush spoke a language similar to Ona. Some scholars also add to the family the Teushen language — once spoken by the Teushen, located between the Tehuelche and Puelche —though it is poorly attested. Viegas Barros (2005) attempts to demonstrate that Gününa Küne to the north is related to the Chon languages a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cariban Languages
The Cariban languages are a family of languages Indigenous to north-eastern South America. They are widespread across northernmost South America, from the mouth of the Amazon River to the Colombian Andes, and they are also spoken in small pockets of central Brazil. The languages of the Cariban family are relatively closely related. There are about three dozen, but most are spoken only by a few hundred people. Macushi is the only language among them with numerous speakers, estimated at 30,000. The Cariban family is well known among linguists partly because one language in the family— Hixkaryana—has a default word order of object–verb–subject. Prior to their discovery of this, linguists believed that this order did not exist in any spoken natural language. In the 16th century, Cariban peoples expanded into the Lesser Antilles. There they killed or displaced, and also mixed with the Arawak peoples who already inhabited the islands. The resulting language— Kalhíphona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholón Language
Cholón (Spanish: ''lengua cholona''), natively known as ''Seeptsá'' and ''Tsinganes'', is a language of Peru. It was spoken near Uchiza, from Tingo María to Valle in the Huallaga River valley of Huanuco and San Martín regions. The language was previously thought to be extinct but a native speaker was discovered in 2021, in the city of Juanjuí. Martha Pérez Valderrama is believed to be the last remaining speaker of Cholón. However, her cousin Clemente also speaks Cholón, and she reports that there are more speakers in the area. Despite the last fully fluent speakers dying in the 1990s, the current speakers can produce brief texts, not being limited to basic words and phrases. Phonology Due to the amateur Spanish pronunciation spellings used to transcribe Cholon, its sound inventory is uncertain. The following is an attempt at interpreting them. Orthographical equivalents are in brackets. The vowels appear to be similar to Spanish . Grammar Cholon distinguishes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
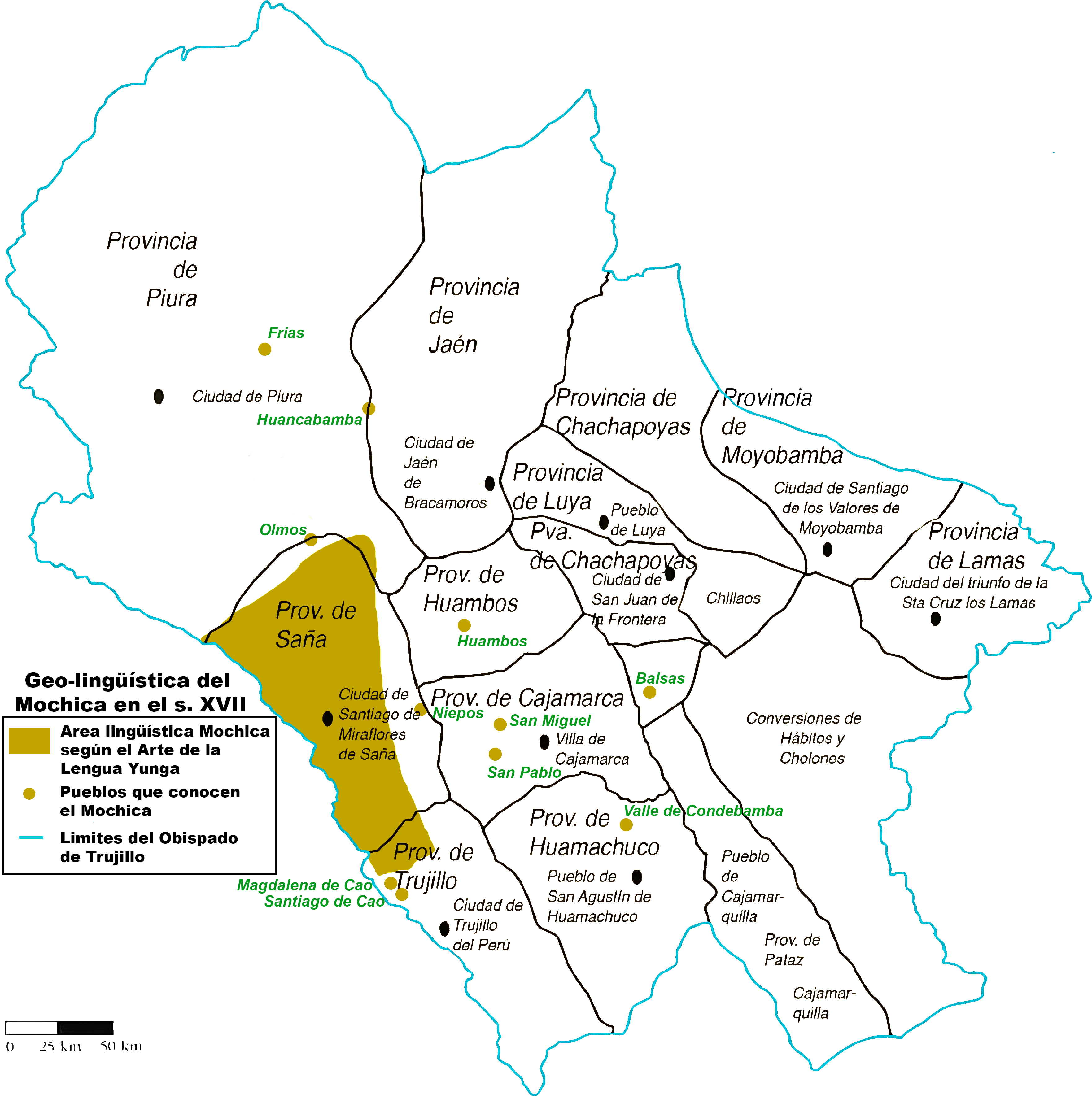
Mochica Language
Mochica is an extinct language formerly spoken along the northwest coast of Peru and in an inland village. First documented in 1607, the language was widely spoken in the area during the 17th century and the early 18th century. By the late 19th century, the language was dying out and spoken only by a few people in the village of Etén, in Chiclayo. It died out as a spoken language around 1920, but certain words and phrases continued to be used until the 1960s. A revival movement has appeared in recent times. Classification Mochica is usually considered to be a language isolate, but has also been hypothesized as belonging to a wider Chimuan language family. Stark (1972) proposes a connection with Uru–Chipaya as part of a Maya–Yunga–Chipayan macrofamily hypothesis. Denominations The ''yunga'' form is mentioned in the work of Fernando de la Carrera, "''yunca''" is another form mentioned by varieties of Quechua, "''muchic''" is only mentioned by the Augustinian father ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peru
Peru, officially the Republic of Peru, is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the south and west by the Pacific Ocean. Peru is a Megadiverse countries, megadiverse country, with habitats ranging from the arid plains of the Pacific coastal region in the west, to the peaks of the Andes mountains extending from the north to the southeast of the country, to the tropical Amazon basin rainforest in the east with the Amazon River. Peru has Demographics of Peru, a population of over 32 million, and its capital and largest city is Lima. At , Peru is the List of countries and dependencies by area, 19th largest country in the world, and the List of South American countries by area, third largest in South America. Pre-Columbian Peru, Peruvian territory was home to Andean civilizations, several cultures during the ancient and medieval periods, and has one o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chimuan Languages
Chimuan (also Chimúan) or Yuncan (Yunga–Puruhá, Yunca–Puruhán) is a hypothetical small extinct language family of northern Peru and Ecuador (inter-Andean valley). Family division Chimuan consisted of three attested languages: * Chimuan ** Mochica ( Yunga, Chimú) ** Cañar–Puruhá *** Cañari ( Cañar, Kanyari) *** Puruhá ( Puruwá, Puruguay) All languages are now extinct. Campbell (2012) classifies Mochica and Cañar–Puruhá each as separate language families. Mochica was one of the major languages of pre-Columbian South America. It was documented by Fernando de la Carrera and Middendorff in the seventeenth and nineteenth centuries respectively. It became extinct ca. 1950, although some people remember a few words. Adelaar & Muysken (2004) consider Mochica a language isolate for now. Cañari and Puruhá are documented with only a few words. These two languages are usually connected with Mochica. However, as their documentation level is so low, it may not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pasto Language
Pasto is a poorly attested Barbacoan language that was spoken by Indigenous people of Pasto, Colombia and Carchi Province Carchi () is a province in Ecuador. The capital is Tulcán. The Carchi River rises on the slopes of Chiles volcano and forms the boundary between Colombia and Ecuador near Tulcan. Rumichaca Bridge is the most important land route between Colo ..., Ecuador. It is now extinct. ISO issue Prior to its retirement, the ISO name of the ISO code pb/code> was ''Barbacoas,'' the name of an extinct people who gave their name to the Barbacoan language family of which Pasto is a member, as well as to the Colombian town of Barbacoas. However, nothing is known of their language, one of several also known as Colima, and it can only be assumed to be part of the Barbacoan family. Such unattested, long-extinct languages are not normally assigned ISO codes. ''MultiTree'' conflates Barbacoas with neighboring Pasto, which is attested sufficiently for classification and as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |