|
Extended Depth Of Field
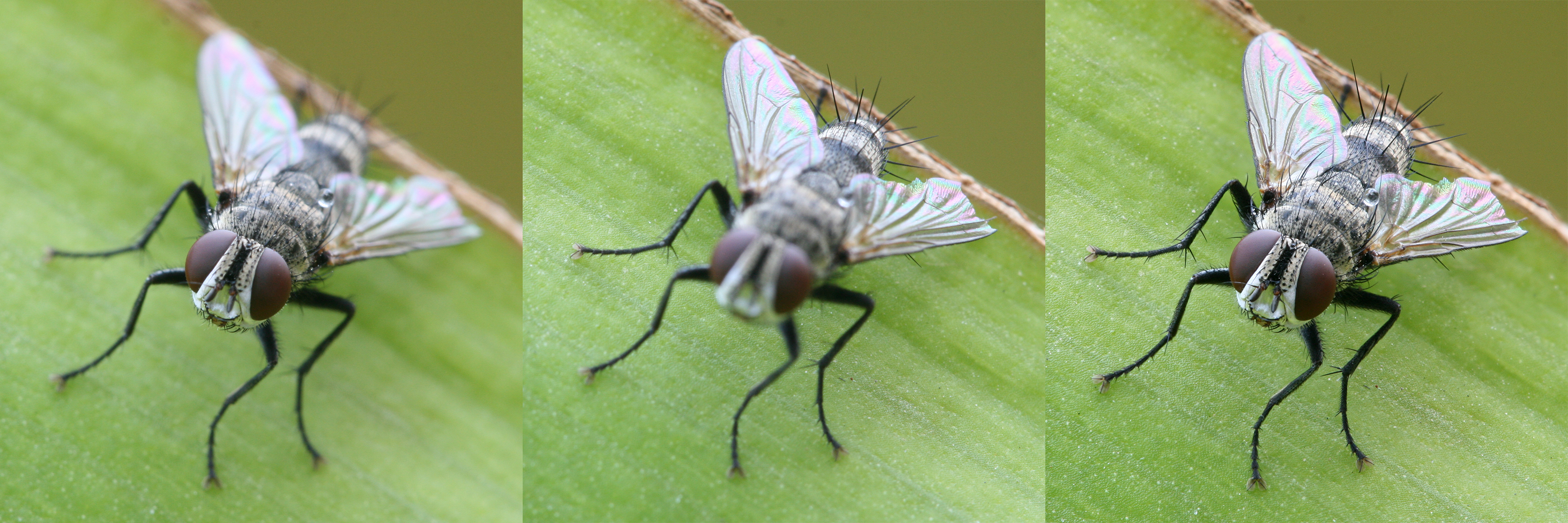
Focus stackingalso called focal plane merging, z-stacking, focus bracketing or focus blendingis a digital image processing technique which combines multiple images taken at different focus distances to give a resulting image with a greater depth of field (DOF) than any of the individual source images. Focus stacking can be used in any situation where individual images have a very shallow depth of field; macro photography and optical microscopy are two typical examples. Focus stacking can also be useful in landscape photography. Focus stacking offers flexibility: since it is a computational technique, images with several different depths of field can be generated in post-processing and compared for best artistic merit or scientific clarity. Focus stacking also allows generation of images physically impossible with normal imaging equipment; images with nonplanar focus regions can be generated. Alternative techniques for generating images with increased or flexible depth of field in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focus Stacking Tachinid Fly
Focus (: foci or focuses) may refer to: Arts * Focus or Focus Festival, former name of the Adelaide Fringe arts festival in East Australia Film *Focus (2001 film), ''Focus'' (2001 film), a 2001 film based on the Arthur Miller novel *Focus (2015 film), ''Focus'' (2015 film), a 2015 film about con artists Music * Focus (music), a musical technique also known as modal frame * Focus..., American music producer * Focus (band), Dutch progressive rock band Albums * Focus (Stan Getz album), ''Focus'' (Stan Getz album), 1961 jazz album * Focus (Bill Hardman album), ''Focus'' (Bill Hardman album), 1984 jazz album * Focus (Jan Akkerman & Thijs van Leer album), ''Focus'' (Jan Akkerman & Thijs van Leer album), 1985 * Focus (Cynic album), ''Focus'' (Cynic album), 1993 metal album * Focus (Chico Freeman album), ''Focus'' (Chico Freeman album), 1994 jazz album * Focus (Souls of Mischief album), ''Focus'' (Souls of Mischief album), 1998 alternative hip-hop album * Focus (Holly Starr album), ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
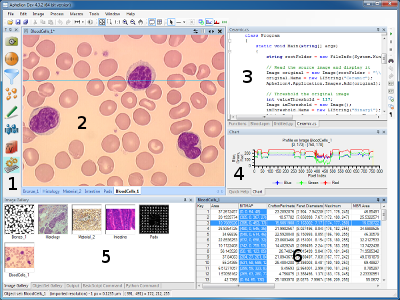
Aphelion (software)
The ''Aphelion Imaging Software Suite'' is a software suite that includes three base products - Aphelion Lab, Aphelion Dev, and Aphelion for addressing image processing An image or picture is a visual representation. An image can be two-dimensional, such as a drawing, painting, or photograph, or three-dimensional, such as a carving or sculpture. Images may be displayed through other media, including a pr ... and image analysis applications. The suite also includes a set of Plug-in (computing), extension programs to implement specific vertical applications that benefit from imaging techniques. The Aphelion software products can be used to prototype#Engineering sciences, prototype and Software deployment, deploy applications, or can be integrated, in whole or in part, into a user's system as processing and visualization Library (computing), libraries whose components are available as both Dynamic-link library, DLLs or .NET Framework, .Net Component-based software engin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affinity Photo
Affinity Photo is a raster graphics editor developed by Serif Ltd. for iPadOS, macOS, and Windows, alongside Affinity Designer and Affinity Publisher. Development of Affinity Photo started in 2009 as a raster graphics editor for macOS. Its first version reached general availability in 2015 with the Windows version launched a year later. It is a successor to PhotoPlus which Serif discontinued in 2017. Functionality Affinity Photo has been described as an Adobe Photoshop alternative, and is compatible with common file formats such as Adobe's PSD (including Photoshop Smart Objects). Functionality includes RAW processing, color space options, live preview of effects, image stitching, alpha compositing, black point compensation, and optical aberration corrections. Working in Affinity Photo is always live, with pan and zoom at 60fps and non-destructive editing. It supports unlimited layers and a dedicated workspace for developing RAW photos; as well as RGB, CMYK, LAB, Greysc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adobe Inc
Adobe Inc. ( ), formerly Adobe Systems Incorporated, is an American software, computer software company based in San Jose, California. It offers a wide range of programs from web design tools, photo manipulation and vector creation, through to video/audio editing, mobile app development, print layout and animation software. It has historically specialized in software for the creation and publication of a wide range of content, including graphics, photography, illustration, animation, multimedia/video, motion pictures, and print. Its flagship products include Adobe Photoshop image editing software; Adobe Illustrator vector-based illustration software; Adobe Acrobat Reader and the Portable Document Format (PDF); and a host of tools primarily for audio-visual content creation, editing and publishing. Adobe offered a bundled solution of its products named Adobe Creative Suite, which evolved into a subscription-based offering named Adobe Creative Cloud. The company also expanded into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adobe Photoshop
Adobe Photoshop is a raster graphics editor developed and published by Adobe Inc., Adobe for Microsoft Windows, Windows and macOS. It was created in 1987 by Thomas Knoll, Thomas and John Knoll. It is the most used tool for professional digital art, especially in raster graphics editing, and its name has become Generic trademark, genericised as a verb (e.g. "to photoshop an image", "photoshopping", and "photoshop contest") although Adobe disapproves of such use. Photoshop can edit and compose raster images in multiple layers and supports Mask (computing), masks, alpha compositing and several color models. Photoshop uses its own PSD and PSB file formats to support these features. In addition to raster graphics, Photoshop has limited abilities to edit or render text and vector graphics (especially through clipping path for the latter), as well as 3D graphics and video. Its feature set can be expanded by Photoshop plug-in, plug-ins; programs developed and distributed independentl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TSOM
Through-Focus Scanning Optical Microscopy (TSOM) is an imaging method that produces nanometer-scale three-dimensional measurement sensitivity using a conventional bright-field optical microscope. TSOM has been introduced and maintained by Ravikiran Attota at NIST. It was given an R&D 100 Award in 2010. In the TSOM method a target is scanned through the focus of an optical microscope, acquiring conventional optical images at different focal positions. The TSOM images are constructed using the through-focus optical images. A TSOM image is unique under given experimental conditions and is sensitive to changes in the dimensions of a target in a distinct way, which is very well applicable in nanoscale dimensional metrology. The TSOM method is alleged to have several nanometrology applications ranging from nanoparticles to through-silicon-vias (TSV). The National Institute of Standards and Technology, USA, produced a short on the TSOM method. See also * Focus stacking Focus stack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy
A scanning transmission electron microscope (STEM) is a type of transmission electron microscope (TEM). Pronunciation is [stɛm] or [ɛsti:i:ɛm]. As with a conventional transmission electron microscope (CTEM), images are formed by electrons passing through a sufficiently thin specimen. However, unlike CTEM, in STEM the electron beam is focused to a fine spot (with the typical spot size 0.05 – 0.2 nm) which is then scanned over the sample in a raster illumination system constructed so that the sample is illuminated at each point with the beam parallel to the optical axis. The rastering of the beam across the sample makes STEM suitable for analytical techniques such as Z-contrast annular dark-field imaging, and spectroscopic mapping by energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectroscopy, or electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS). These signals can be obtained simultaneously, allowing direct correlation of images and spectroscopic data. A ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrometre
The micrometre (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer (American English), also commonly known by the non-SI term micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Units (SI) equalling (SI standard prefix "micro-" = ); that is, one millionth of a metre (or one thousandth of a millimetre, , or about ). The nearest smaller common SI Unit, SI unit is the nanometre, equivalent to one thousandth of a micrometre, one millionth of a millimetre or one billionth of a metre (). The micrometre is a common unit of measurement for wavelengths of infrared radiation as well as sizes of biological cell (biology), cells and bacteria, and for grading wool by the diameter of the fibres. The width of a single human hair ranges from approximately 20 to . Examples Between 1 μm and 10 μm: * 1–10 μm – length of a typical bacterium * 3–8 μm – width of str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Objective (optics)
In optical engineering, an objective is an optical element that gathers light from an object being observed and Focus (optics), focuses the ray (optics), light rays from it to produce a real image of the object. Objectives can be a single Lens (optics), lens or mirror, or combinations of several optical elements. They are used in microscopes, binoculars, telescopes, cameras, slide projectors, CD players and many other optical instruments. Objectives are also called object lenses, object glasses, or objective glasses. Microscope objectives The objective lens of a microscope is the one at the bottom near the sample. At its simplest, it is a very high-powered magnifying glass, with very short focal length. This is brought very close to the specimen being examined so that the light from the specimen comes to a focus inside the microscope tube. The objective itself is usually a cylinder containing one or more lenses that are typically made of glass; its function is to collect light fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Objective Lens
In optical engineering, an objective is an optical element that gathers light from an object being observed and focuses the light rays from it to produce a real image of the object. Objectives can be a single lens or mirror, or combinations of several optical elements. They are used in microscopes, binoculars, telescopes, cameras, slide projectors, CD players and many other optical instruments. Objectives are also called object lenses, object glasses, or objective glasses. Microscope objectives The objective lens of a microscope is the one at the bottom near the sample. At its simplest, it is a very high-powered magnifying glass, with very short focal length. This is brought very close to the specimen being examined so that the light from the specimen comes to a focus inside the microscope tube. The objective itself is usually a cylinder containing one or more lenses that are typically made of glass; its function is to collect light from the sample. Magnification One of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numerical Aperture
In optics, the numerical aperture (NA) of an optical system is a dimensionless number that characterizes the range of angles over which the system can accept or emit light. By incorporating index of refraction in its definition, has the property that it is constant for a beam as it goes from one material to another, provided there is no refractive power at the interface (e.g., a flat interface). The exact definition of the term varies slightly between different areas of optics. Numerical aperture is commonly used in microscopy to describe the acceptance cone of an Objective (optics), objective (and hence its light-gathering ability and Optical resolution, resolution), and in fiber optics, in which it describes the range of angles within which light that is incident on the fiber will be transmitted along it. General optics In most areas of optics, and especially in microscopy, the numerical aperture of an optical system such as an objective lens is defined by \mathrm = n \sin \t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |