|
Exeter And South Devon Volunteers
The Exeter & South Devon Volunteers was the premier unit of Britain's Volunteer Force. Formed in 1852 it went on to become a battalion of the Devonshire Regiment. Both its active service battalions went to garrison India on the outbreak of the First World War, and then saw action in Mesopotamia and Palestine. In the Second World War, the battalion served in the garrison of Gibraltar. It continued in the postwar Territorial Army until it was merged with other West Country units. Its successors today serve in a reserve battalion of The Rifles. Volunteer Force Part-time volunteer units had often been organised in Britain in time of war to serve in local defence and supplement the Regular Army and Militia, but these were always stood down when the threat of invasion had passed. Concerns about national defence re-emerged after Louis Napoleon seized power in France in 1851. The Militia was reorganised in 1852, but there was agitation to allow the formation of volunteer units as well. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
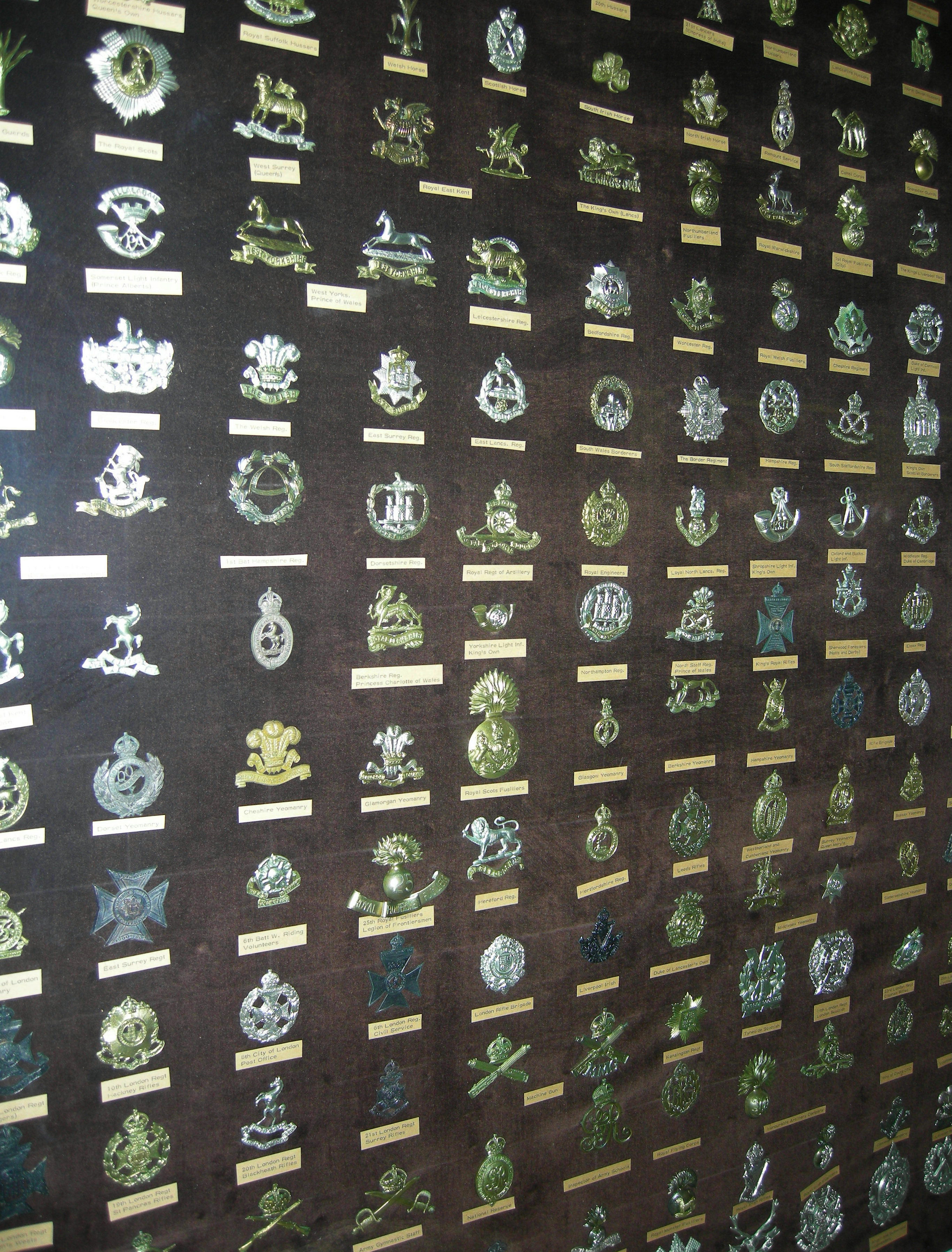
Cap Badge
A cap badge, also known as head badge or hat badge, is a badge worn on uniform headgear and distinguishes the wearer's nationality and/or organisation. The wearing of cap badges is a convention commonly found among military and police forces, as well as uniformed civilian groups such as the Scouting, Boy Scouts, civil defence organisations, ambulance services (e.g. the St. John Ambulance Brigade), customs services, fire services etc. Cap badges are a modern form of Heraldic badge, heraldry and their design generally incorporates highly symbolic devices. Some badges that contain images of lions or other cats are sometimes informally referred to as cat badges. Instances in military forces British armed forces The British Armed Forces utilise a variety of metal and cloth cap badges on their headdress, generally on caps and berets. They are also worn on Uniforms_of_the_British_Armed_Forces#Turbans, Sikh turbans. British Army In the British Army (as well as other Commonwealth o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
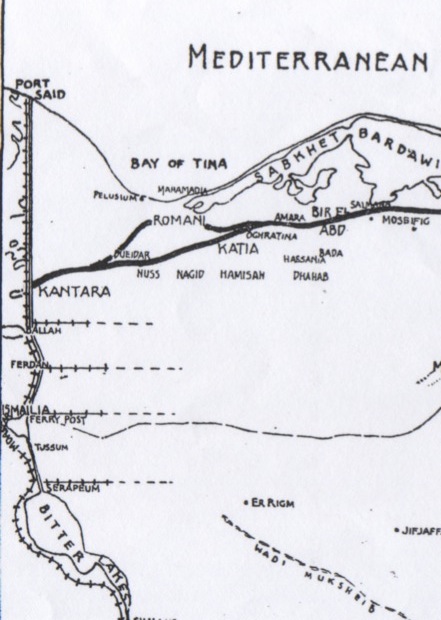
Sinai And Palestine Campaign
The Sinai and Palestine campaign was part of the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I, taking place between January 1915 and October 1918. The British Empire, the French Third Republic, and the Kingdom of Italy fought alongside the Arab Revolt in opposition to the Ottoman Empire, the German Empire, and the Austro-Hungarian Empire. It started with an Ottoman attempt at raiding the Suez Canal in 1915 and ended with the Armistice of Mudros in 1918, leading to the cession of Ottoman Syria. Fighting began in January 1915, when a German-led Ottoman force invaded the Sinai Peninsula, then occupied by the British as part of a Protectorate of Egypt, to unsuccessfully raid the Suez Canal. After the Gallipoli campaign, British Empire veterans formed the Egyptian Expeditionary Force (EEF) and Ottoman Empire veterans formed the Fourth Army, to fight for the Sinai Peninsula in 1916. In January 1917 the newly formed Desert Column completed the recapture of the Sinai at the Battle o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Charles Bucknill
Sir John Charles Bucknill (25 December 1817 – 19 July 1897) was an English psychiatrist and mental health reformer. He was the father of judge Sir Thomas Townsend Bucknill QC MP. Biography Bucknill was born in Market Bosworth, Leicestershire, and educated at Rugby School and at University College, London. He served as an assistant to his father, a surgeon, and began formal medical training in Dublin, transferring after a year to the University of London. Bucknill believed that insanity was a brain disease that could be treated with medication. He became acquainted with Dr. John Conolly's work at the Hanwell Asylum in Middlesex where no restraints were used to control agitated patients. Bucknill became an ardent supporter of this procedure. He had a special interest in the Lunacy laws and the protection of the civil rights of patients. He qualified as a doctor in 1840, obtained a Licentiate in the Society of Apothecaries and membership in the Royal College of Surgeons. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devonshire
Devon ( ; historically also known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial county in South West England. It is bordered by the Bristol Channel to the north, Somerset and Dorset to the east, the English Channel to the south, and Cornwall to the west. The city of Plymouth is the largest settlement, and the city of Exeter is the county town. The county has an area of and a population of 1,194,166. The largest settlements after Plymouth (264,695) are the city of Exeter (130,709) and the seaside resorts of Torquay and Paignton, which have a combined population of 115,410. They all are located along the south coast, which is the most populous part of the county; Barnstaple (31,275) and Tiverton (22,291) are the largest towns in the north and centre respectively. For local government purposes Devon comprises a non-metropolitan county, with eight districts, and the unitary authority areas of Plymouth and Torbay. Devon County Council and Torbay Council collaborate through a combine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devon And Exeter Institution
The Devon and Exeter Institution is a subscription library in the City of Exeter, in Devon, United Kingdom, founded in 1813 for "The general diffusion of science, literature and the arts". It is situated at 7, Cathedral Close, Exeter, in a building facing the north side of Exeter Cathedral which was formerly the Exeter Townhouse (Great Britain), townhouse of the House of Courtenay, Courtenay family of Powderham Castle. Membership Membership is by annual subscription, although current students and staff of Exeter University may use it free of charge. Library The library houses two marble busts by the sculptor Edward Bowring Stephens (1815–1882) of Exeter, of Sir William Webb Follett (1796–1845), MP for Exeter (UK Parliament constituency), Exeter and Sir John Bowring (1792–1872), of Exeter, Governor of Hong Kong and President of the Devon and Exeter Institution 1860–61. The library's collection consists of approximately 40,000 printed books in addition to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spencer Horatio Walpole
Spencer Horatio Walpole (11 September 1806 – 22 May 1898) was a British Conservative Party politician who served three times as Home Secretary in the administrations of Lord Derby. Background and education Walpole was the second son of Thomas Walpole and Lady Margaret Perceval, youngest daughter of the 2nd Earl of Egmont and sister of Prime Minister Spencer Perceval. His grandfather was Thomas Walpole, son of the diplomat the 1st Baron Walpole, younger brother of Prime Minister the 1st Earl of Orford. Walpole was educated at Eton and Trinity College, Cambridge. He chose law as his profession, and was called to the Bar, Lincoln's Inn, in 1831. He built up a successful practice and was made a Queen's Counsel in 1846. Political career Walpole then turned to politics, and in 1846 he was elected to Parliament for Midhurst as a Tory, a seat he would hold until 1856. He quickly gained a reputation in the House of Commons, and when the Tories came to power in early 1852 unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Who? Who? Ministry
Edward Smith-Stanley, 14th Earl of Derby led the "Who? Who?" ministry, a short-lived British Conservative Party (UK), Conservative government which was in power for a matter of months in 1852. Lord Derby was Prime Minister and Benjamin Disraeli served as Chancellor of the Exchequer. It marked the first time the protectionist wing of the Conservative Party had taken office since the Corn Laws schism of 1846. It is also called the First Derby–Disraeli ministry. Early in 1852 Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, by then very deaf, gave Derby's first government its nickname by shouting "Who? Who?" as the list of inexperienced cabinet ministers was read out in the House of Lords. History After the fall of Lord John Russell's Whig Government 1846-1852, Whig government in early 1852, the Conservative Party (UK), Conservative leader Lord Derby formed a government. The Conservatives had been weakened by the defection of the Peelites, and many of the new Cabinet ministers were me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Smith-Stanley, 14th Earl Of Derby
Edward George Geoffrey Smith-Stanley, 14th Earl of Derby (29 March 1799 – 23 October 1869), known as Lord Stanley from 1834 to 1851, was a British statesman and Conservative Party (UK), Conservative politician who served three times as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom. To date, he is the longest-serving Leader of the Conservative Party (UK), leader of the Conservative Party (1846–68). He is one of only four British prime ministers to have three or more separate periods in office. However, his ministries each lasted less than two years and totalled three years and 280 days. Derby introduced the state education system in Ireland, and reformed Parliament. Historian Frances Walsh has written that it was Derby: Scholars long ignored his role but in the 21st century rank him highly among all British prime ministers. Early life and education Edward Smith-Stanley was born on 19 March 1799 at Knowsley Hall, Lancashire. He was the eldest son of Edward Smith-Stanley, 13th Ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Home Secretary
The secretary of state for the Home Department, more commonly known as the home secretary, is a senior minister of the Crown in the Government of the United Kingdom and the head of the Home Office. The position is a Great Office of State, making the home secretary one of the most senior and influential ministers in the government. The incumbent is a statutory member of the British Cabinet and National Security Council (United Kingdom), National Security Council. The position, which may be known as interior minister in other nations, was created in 1782, though its responsibilities have Home Office#History, changed many times. Past office holders have included the prime ministers Lord North, Robert Peel, the Duke of Wellington, Lord Palmerston, Winston Churchill, James Callaghan and Theresa May. The longest-serving home secretary is Henry Addington, 1st Viscount Sidmouth, who held the post continuously for 9 years, 221 days. The shortest-serving home secretary is Grant Shapps, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Napoleon
Napoleon III (Charles-Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was President of France from 1848 to 1852 and then Emperor of the French from 1852 until his deposition in 1870. He was the first president, second emperor, and last monarch of France. Prior to his reign, Napoleon III was known as Louis Napoleon Bonaparte. He was born at the height of the First French Empire in the Tuileries Palace at Paris, the son of Louis Bonaparte, King of Holland (r. 1806–1810), and Hortense de Beauharnais, and paternal nephew of the reigning Emperor Napoleon I. It would only be two months following his birth that he, in accordance with Napoleon I's dynastic naming policy, would be bestowed the name of Charles-Louis Napoleon, however, shortly thereafter, Charles was removed from his name. Louis Napoleon Bonaparte was the first and only president of the French Second Republic, elected in 1848. He seized power by force in 1851 when he could not constitutionally be re-elected. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Militia (United Kingdom)
The British Militia was the principal military reserve force of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. Militia units were repeatedly raised in Great Britain during the Victorian era, Victorian and Edwardian eras for internal security duties and to defend against external invasions. The British Militia was transformed into the Special Reserve under the Territorial and Reserve Forces Act 1907, which integrated all militia formations into the British Army. 19th century A separate voluntary Local Militia was created in 1808 before being disbanded in 1816. By 1813 the British Army was experiencing a shortage of manpower to maintain their battalions at full strength. Some consideration was given to recruiting foreign nationals; however, on 4 November 1813 a bill was introduced to Parliament to allow Militia volunteers to serve in Europe. In the event only three battalions were raised, and these were sent to serve under Henry Bayly (British Army officer, born 1769), Henry Bay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Army
The British Army is the principal Army, land warfare force of the United Kingdom. the British Army comprises 73,847 regular full-time personnel, 4,127 Brigade of Gurkhas, Gurkhas, 25,742 Army Reserve (United Kingdom), volunteer reserve personnel and 4,697 "other personnel", for a total of 108,413. The British Army traces back to 1707 and the Acts of Union 1707, formation of the united Kingdom of Great Britain which joined the Kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland into a Political union, single state and, with that, united the English Army and the Scots Army as the British Army. The Parliament of England, English Bill of Rights 1689 and Convention of the Estates, Scottish Claim of Right Act 1689 require parliamentary consent for the Crown to maintain a peacetime standing army. Members of the British Army swear allegiance to the Charles III, monarch as their commander-in-chief. The army is administered by the Ministry of Defence (United Kingd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |