|
Exechocentrus Lancearius
''Exechocentrus lancearius'' is a species of spider in the orb-weaver spider family Araneidae, found only in Madagascar. It was initially described from a partial specimen of an adult female. The first description of a complete specimen and its prey-catching behaviour was published in 2012. ''E. lancearius'' is a bolas spider. Rather than using a web, adult females catch their prey by using a line with one or two sticky drops (a "bolas") which they swing. Description The neotype female was described by Scharff and Hormiga in 2012. The total length of the body is 3.9 mm. The cephalothorax is about 2.0 mm long and wide, and the abdomen 2.7 mm long and 3.9 mm wide. (The abdomen overlaps the cephalothorax.) The cephalothorax is pear-shaped and has four spine-like projections, one pointing forwards and three in a triangle behind it. The carapace is yellowish white with a white central stripe and dark brown markings. The sternum is blackish brown. The legs are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugène Simon
Eugène Louis Simon (; 30 April 1848 – 17 November 1924) was a French naturalist who worked particularly on insects and spiders, but also on birds and plants. He is by far the most prolific spider taxonomist in history, describing over 4,000 species. Work on spiders His most significant work was ''Histoire Naturelle des Araignées'' (1892–1903), an encyclopedic treatment of the spider genera of the world. It was published in two volumes of more than 1000 pages each, and the same number of drawings by Simon. Working at the Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle in Paris, it took Simon 11 years to complete, while working at the same time on devising a taxonomic scheme that embraced the known taxa. Simon described a total of 4,650 species, and as of 2013 about 3,790 species are still considered valid. The International Society of Arachnology offers a Simon Award recognising lifetime achievement. The Eocene fossil spider species '' Cenotextricella simoni'' was named in h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exechocentrus Madilina
''Exechocentrus'' is a genus of Madagascan orb-weaver spiders (family Araneidae) first described by Eugène Simon in 1889. It is a bolas-using spider, capturing its prey with one or more sticky drops at the end of a single line of silk rather than in a web. Description Males of the genus are unknown. Females can be distinguished from all other known members of the family Araneidae by the spine-like projections on the cephalothorax. One is centrally placed and extends forwards; three are more-or-less upright. The total body length is . The cephalothorax is yellowish-white with brown lines radiating from the fovea and is about as wide as it is long. The legs are pale yellowish-white with dark brown markings. The abdomen is off white and almost heart-shaped from above. The epigyne has a strongly hardened (sclerotized) lip. The spermathecae are large and ovoid, with short narrow copulatory ducts. Taxonomy The genus ''Exechocentrus'' was erected by Eugène Simon in 1889 for the spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic Fauna Of Madagascar
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example ''Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. ''Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiders Of Madagascar
Spiders (order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species diversity among all orders of organisms. Spiders are found worldwide on every continent except for Antarctica, and have become established in nearly every land habitat. , 50,356 spider species in 132 families have been recorded by taxonomists. However, there has been debate among scientists about how families should be classified, with over 20 different classifications proposed since 1900. Anatomically, spiders (as with all arachnids) differ from other arthropods in that the usual body segments are fused into two tagmata, the cephalothorax or prosoma, and the opisthosoma, or abdomen, and joined by a small, cylindrical pedicel, however, as there is currently neither paleontological nor embryological evidence that spiders ever had a separat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Araneidae
Orb-weaver spiders are members of the spider family Araneidae. They are the most common group of builders of spiral wheel-shaped webs often found in gardens, fields, and forests. The English word "orb" can mean "circular", hence the English name of the group. Araneids have eight similar eyes, hairy or spiny legs, and no stridulating organs. The family has a cosmopolitan distribution, including many well-known large or brightly colored garden spiders. With 3,108 species in 186 genera worldwide, the Araneidae comprise the third-largest family of spiders (behind the Salticidae and Linyphiidae). Araneid webs are constructed in a stereotypical fashion, where a framework of nonsticky silk is built up before the spider adds a final spiral of silk covered in sticky droplets. Orb webs are also produced by members of other spider families. The long-jawed orb weavers (Tetragnathidae) were formerly included in the Araneidae; they are closely related, being part of the superfamily Aran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exechocentrus Lancearius With Bolas
''Exechocentrus'' is a genus of Madagascan orb-weaver spiders (family Araneidae) first described by Eugène Simon in 1889. It is a bolas-using spider, capturing its prey with one or more sticky drops at the end of a single line of silk rather than in a web. Description Males of the genus are unknown. Females can be distinguished from all other known members of the family Araneidae by the spine-like projections on the cephalothorax. One is centrally placed and extends forwards; three are more-or-less upright. The total body length is . The cephalothorax is yellowish-white with brown lines radiating from the fovea and is about as wide as it is long. The legs are pale yellowish-white with dark brown markings. The abdomen is off white and almost heart-shaped from above. The epigyne has a strongly hardened (sclerotized) lip. The spermathecae are large and ovoid, with short narrow copulatory ducts. Taxonomy The genus ''Exechocentrus'' was erected by Eugène Simon in 1889 for the spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
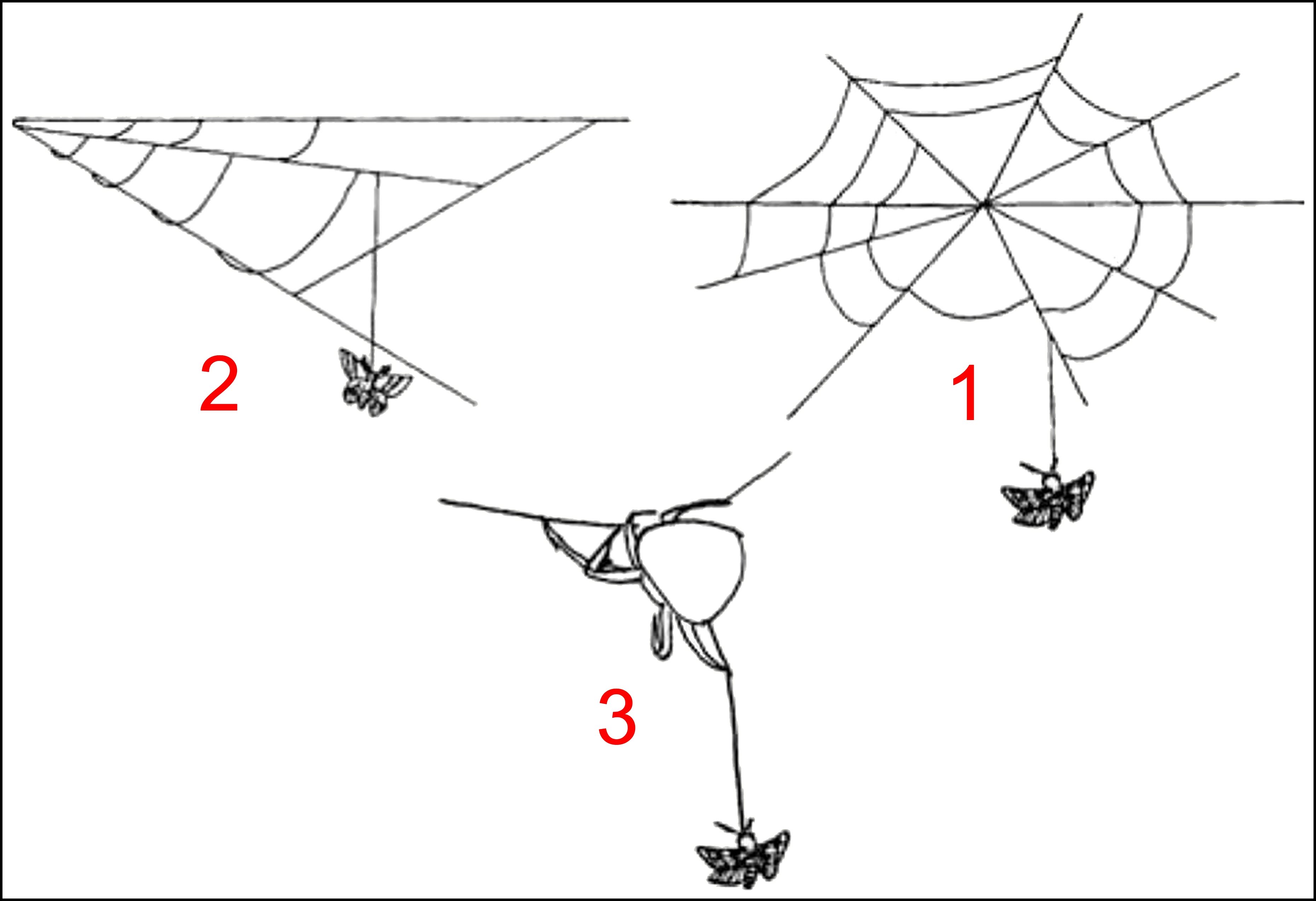
Cyrtarachninae
Cyrtarachninae is a subfamily of spiders in the family Araneidae (orb-weaver spiders, araneids). The group has been circumscribed in several different ways. It originated as the group Cyrtarachneae, described by Eugène Simon in 1892. The group was later treated at different ranks: as a tribe, both under Simon's name and as Cyrtarachnini, and as the subfamily Cyrtarachninae. Circumscriptions have varied. The broadest circumscription, Cyrtarachninae ''sensu lato'' (''s.l.''), includes three of Simon's original groups, including the bolas spiders (also placed in the tribe Mastophoreae or Mastophorini, or in the subfamily Mastophorinae). Unlike most araneids, members of the subfamily do not construct orb webs, some not using webs at all to capture prey, some using one or more sticky drops on a single line (a bolas), while others construct webs with few widely spaced non-spiral threads, some triangular. Many have been shown to attract prey by producing analogues of insect sex pheromo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Phylogenetics
Molecular phylogenetics () is the branch of phylogeny that analyzes genetic, hereditary molecular differences, predominantly in DNA sequences, to gain information on an organism's evolutionary relationships. From these analyses, it is possible to determine the processes by which diversity among species has been achieved. The result of a molecular phylogenetic analysis is expressed in a phylogenetic tree. Molecular phylogenetics is one aspect of molecular systematics, a broader term that also includes the use of molecular data in taxonomy and biogeography. Molecular phylogenetics and molecular evolution correlate. Molecular evolution is the process of selective changes (mutations) at a molecular level (genes, proteins, etc.) throughout various branches in the tree of life (evolution). Molecular phylogenetics makes inferences of the evolutionary relationships that arise due to molecular evolution and results in the construction of a phylogenetic tree. History The theoretical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exechocentrus
''Exechocentrus'' is a genus of Madagascan orb-weaver spiders (family Araneidae) first described by Eugène Simon in 1889. It is a bolas-using spider, capturing its prey with one or more sticky drops at the end of a single line of silk rather than in a web. Description Males of the genus are unknown. Females can be distinguished from all other known members of the family Araneidae by the spine-like projections on the cephalothorax. One is centrally placed and extends forwards; three are more-or-less upright. The total body length is . The cephalothorax is yellowish-white with brown lines radiating from the fovea and is about as wide as it is long. The legs are pale yellowish-white with dark brown markings. The abdomen is off white and almost heart-shaped from above. The epigyne has a strongly hardened (sclerotized) lip. The spermathecae are large and ovoid, with short narrow copulatory ducts. Taxonomy The genus ''Exechocentrus'' was erected by Eugène Simon in 1889 for the spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can reproduction, produce Fertility, fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossary Of Spider Terms
This glossary describes the terms used in formal descriptions of spiders; where applicable these terms are used in describing other arachnids. Links within the glossary are shown . Terms A Abdomen or opisthosoma: One of the two main body parts ( tagmata), located towards the posterior end; see also Abdomen § Other animals Accessory claw: Modified at the tip of the in web-building spiders; used with to grip strands of the web Anal tubercle: A small protuberance (tubercule) above the through which the anus opens Apodeme → Apophysis (plural apophyses): An outgrowth or process changing the general shape of a body part, particularly the appendages; often used in describing the male → Atrium (plural atria): An internal chamber at the entrance to the in female haplogyne spiders B Bidentate: Having two Book lungs: Respiratory organs on the ventral side (underside) of the , in front of the , opening through narrow slits; see also Book lungs Branchial operculum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type (biology)
In biology, a type is a particular wiktionary:en:specimen, specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally attached. In other words, a type is an example that serves to anchor or centralizes the defining features of that particular taxon. In older usage (pre-1900 in botany), a type was a taxon rather than a specimen. A taxon is a scientifically named grouping of organisms with other like organisms, a set (mathematics), set that includes some organisms and excludes others, based on a detailed published description (for example a species description) and on the provision of type material, which is usually available to scientists for examination in a major museum research collection, or similar institution. Type specimen According to a precise set of rules laid down in the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) and the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN), the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)




.jpg)