|
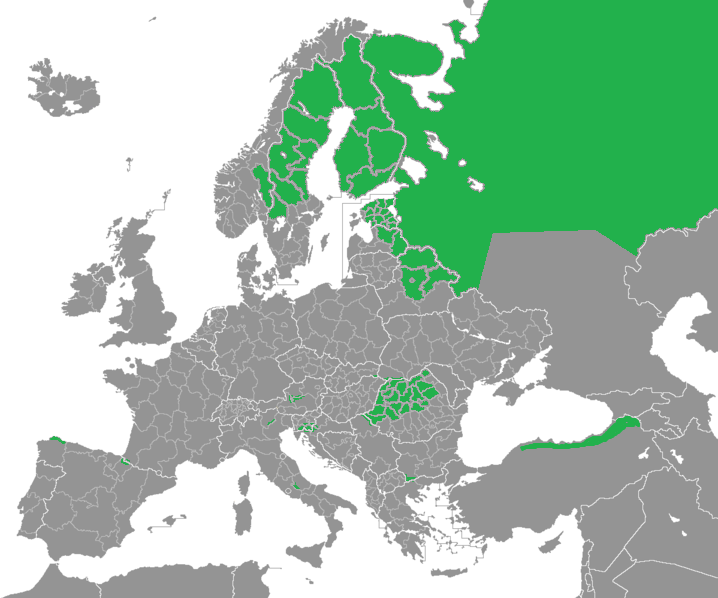
European Bison
The European bison (: bison) (''Bison bonasus'') or the European wood bison, also known as the wisent ( or ), the zubr (), or sometimes colloquially as the European buffalo, is a European species of bison. It is one of two extant species of bison, alongside the American bison. The European bison is the heaviest wild land animal in Europe, and individuals in the past may have been even larger than their modern-day descendants. During late antiquity and the Middle Ages, bison became extinct in much of Europe and Asia, surviving into the 20th century only in northern-central Europe and the northern Caucasus Mountains. During the early years of the 20th century, bison were hunted to extinction in the wild. By the late 2010s, the species numbered several thousand and had been returned to the wild by captive breeding programmes. It is no longer in immediate danger of extinction, but remains absent from most of its historical range. It is not to be confused with the aurochs (''Bos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moulting
In biology, moulting (British English), or molting (American English), also known as sloughing, shedding, or in many invertebrates, ecdysis, is a process by which an animal casts off parts of its body to serve some beneficial purpose, either at specific times of the year, or at specific points in its life cycle. In medieval times, it was also known as "mewing" (from the French verb "muer", to moult), a term that lives on in the name of Britain's Royal Mews where the King's hawks used to be kept during moulting time before becoming horse stables after Tudor times. Moulting can involve shedding the Epidermis (skin), epidermis (skin), pelage (hair, feathers, fur, wool), or other external layer. In some groups, other body parts may be shed, for example, the entire exoskeleton in arthropods, including the wings in some insects. Examples In birds In birds, moulting is the periodic replacement of feathers by shedding old feathers while producing new ones. Feathers are dead struct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caucasus Mountains
The Caucasus Mountains * * Azerbaijani: , * * * * * * * * * * * is a mountain range at the intersection of Asia and Europe. Stretching between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, they are surrounded by the Caucasus region and are home to Mount Elbrus, the highest peak in Europe at above sea level. The Caucasus Mountains include the Greater Caucasus in the north and the Lesser Caucasus in the south. The Greater Caucasus runs west-northwest to east-southeast, from the Western Caucasus on the northeastern shore of the Black Sea to close to Baku on the Caspian Sea, in Azerbaijan. The Lesser Caucasus runs parallel to the Greater about south. The Greater and Lesser Caucasus ranges are connected by the Likhi Range, and to the west and east of the Likhi Range lie the Colchis Plain and the Kur-Araz Lowland respectively. The Meskheti Range is a part of the Lesser Caucasus system. In the southeast, the Aras River separates the Lesser Caucasus from the Tal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belarus–Poland Border
The Belarusian–Polish border is the state border between the Republic of Poland (EU member) and the Republic of Belarus ( Union State). It has a total length of , or Informacje o Polsce - informacje ogólne . Page gives Polish PWN Encyklopedia as reference. (sources vary). It starts from the triple junction of the borders with in the north and stretches to the triple junction borders with to the south. It is also part of the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Białowieża Forest
Białowieża Forest is a large forest complex on the border between Poland and Belarus. It is one of the last and the largest remaining part of the immense primeval forest that once stretched across the European Plain. The forest is home to more than 800 European bison, Europe's heaviest land animal. UNESCO's Man and the Biosphere Programme designated the Polish Białowieża National Park, Biosphere Reserve as ' in 1976, and the Belarusian Belovezhskaya Pushcha National Park, Biosphere Reserve as ' in 1993. In 2015, the Belarusian Biosphere Reserve spanned , subdivided into transition, buffer and core zones. The forest has been designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site and an EU Natura 2000 Special Area of Conservation. The World Heritage Committee, through its decision of June 2014, approved the extension of the UNESCO World Heritage site "Belovezhskaya Pushcha / Białowieża Forest, Belarus, Poland", which became "Białowieża Forest, Belarus, Poland". It straddles the border bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overexploitation
Overexploitation, also called overharvesting or ecological overshoot, refers to harvesting a renewable resource to the point of diminishing returns. Continued overexploitation can lead to the destruction of the resource, as it will be unable to replenish. The term applies to natural resources such as water aquifers, grazing pastures and forests, wild medicinal plants, fish stocks and other wildlife. In ecology, overexploitation describes one of the five main activities threatening global biodiversity. Ecologists use the term to describe populations that are harvested at an unsustainable rate, given their natural rates of mortality and capacities for reproduction. This can result in extinction at the population level and even extinction of whole species. In conservation biology, the term is usually used in the context of human economic activity that involves the taking of biological resources, or organisms, in larger numbers than their populations can withstand. The term i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drinking Horn
A drinking horn is the horn (anatomy), horn of a bovid used as a cup. Drinking horns are known from Classical Antiquity, especially the Balkans. They remained in use for ceremonial purposes throughout the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period in some parts of Europe, notably in Germanic-speaking Europe, Germanic Europe, and in the peoples of the Caucasus, Caucasus. Drinking horns remain an important accessory in the culture of ritual toast (honor), toasting in Georgia (country), Georgia in particular, where they are known by the local name of ''kantsi''. Cups made from glass, metal, pottery, and in the shape of drinking horns are also known since antiquity. The ancient Greek term for a drinking horn was simply '':wikt:κέρας, keras'' (plural ''kerata'', "horn"). To be distinguished from the drinking-horn proper is the ''rhyton'' (plural ''rhyta''), a drinking-vessel made very loosely in the shape of a horn, sometimes with an outlet at the pointed end. Antiquity Both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasian Brown Bear
The Eurasian brown bear (''Ursus arctos arctos'') is one of the most common subspecies of the brown bear, and is found in much of Eurasia. It is also called the European brown bear, common brown bear, common bear, European bear, and colloquially by many other names. The genetic diversity of present-day brown bears (''Ursus arctos'') has been extensively studied over the years and appears to be geographically structured into five main clades based upon analysis of the mtDNA. Description The Eurasian brown bear has brown fur, which ranges from yellowish-brown to dark brown, red-brown, and almost black in some cases; albinism has also been recorded. The fur is dense to varying degrees and the hair can grow up to in length. The head normally is quite round and has relatively small rounded ears, a wide skull, and a mouth equipped with 42 teeth, including predatory teeth. It has a powerful bone structure and large paws equipped with claws that can grow up to in length. The weigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caspian Tigers
The Caspian tiger was a '' Panthera tigris tigris'' population native to eastern Turkey, northern Iran, Mesopotamia, the Caucasus around the Caspian Sea, Central Asia to northern Afghanistan and the Xinjiang region in western China. Until the Middle Ages, it was also present in southern Russia. It inhabited sparse forests and riverine corridors in this region until the 1970s. This population was regarded as a distinct subspecies and assessed as extinct in 2003. Results of a phylogeographic analysis evinces that the Caspian and Siberian tiger populations shared a common continuous geographic distribution until the early 19th century. Some Caspian tigers were intermediate in size between Siberian and Bengal tigers. It was also called Balkhash tiger, Hyrcanian tiger, Turanian tiger, and Mazandaran tiger. Taxonomy ''Felis virgata'' was a scientific name used by Johann Karl Wilhelm Illiger in 1815 for the greyish tiger in the area surrounding the Caspian Sea. ''Tigris septentrio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asiatic Lions
The Asiatic lion is a lion population of the subspecies ''Panthera leo leo''. Until the 19th century, it occurred in Saudi Arabia, eastern Turkey, Iran, Mesopotamia, and from east of the Indus River in Pakistan to the Bengal region and the Narmada River in Central India. Since the turn of the 20th century, its range has been restricted to Gir National Park and the surrounding areas in the Indian state of Gujarat. The first scientific description of the Asiatic lion was published in 1826 by the Austrian zoologist Johann N. Meyer, who named it ''Felis leo persicus''. The population has steadily increased since 2010. In 2015, the 14th Asiatic Lion Census was conducted over an area of about ; the lion population was estimated at 523 individuals, and in 2017 at 650 individuals. In 2020 the population was 674 and by 2025 it had increased to 891. Taxonomy ''Felis leo persicus'' was the scientific name proposed by Johann N. Meyer in 1826 who described an Asiatic lion skin from Persia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasian Wolf
The Eurasian wolf (''Canis lupus lupus''), also known as the common wolf,Mech, L. David (1981), ''The Wolf: The Ecology and Behaviour of an Endangered Species'', University of Minnesota Press, p. 354, is a subspecies of grey wolf native to Europe and Asia. It was once widespread throughout Eurasia prior to the Middle Ages. Aside from an extensive paleontological record, Indo-European languages typically have several words for "wolf", thus attesting to the animal's abundance and cultural significance.Gamkrelidze, T. V. & Ivanov, V. V. (1995), ''Indo-European and the Indo-Europeans: A Reconstruction and Historical Analysis of a Proto-Language and Proto-Culture'', Walter de Gruyter, pp. 413-417, It was held in high regard in Baltic, Celtic, Slavic, Turkic, ancient Greek, Roman, Dacian, and Thracian cultures, whilst having an ambivalent reputation in early Germanic cultures. It is the largest of Old World grey wolves, averaging in Europe; however, exceptionally large indivi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |