|
Eurocard (printed Circuit Board)
Eurocard is an IEEE standard format for printed circuit board (PCB) cards that can be plugged together into a standard chassis which, in turn, can be mounted in a 19-inch rack. The chassis consists of a series of slotted card guides on the top and bottom, into which the cards are slid so they stand on end, like books on a shelf. At the spine of each card is one or more connectors which plug into mating connectors on a backplane that closes the rear of the chassis. Dimensions As the cards are assumed to be installed in a vertical orientation, the usual meanings of height and width are transposed: A card might be 233.35 mm "high", but only 20 mm "wide". Height is measured in rack units, "U", with 1 U being . This dimension refers to the subrack in which the card is to be mounted, rather than the card itself. A single card is 100 mm high. Taller cards add a 133.35 mm, so that a double height card is 233.35 mm high and a triple 366.7 mm high. En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe Card Bus
The Europe Card Bus (ECB or ECB-bus) is a Bus_(computing), computer bus developed in 1977 by the company Kontron, mainly for the 8-bit Zilog Z80, Intel 8080 and Intel 8085 microprocessor families. Physical format Mechanically, the ECB is usually implemented as a backplane circuit board installed in a 19-inch rack chassis. ECB cards have 3U Eurocard_(printed_circuit_board), Eurocard format (100 mm × 160 mm). Connector Use two or three-row versions of DIN 41612 connectors, 0.1" pitch. Original Kontron ECB, supported 64 pins, using "a" and "c" rows, ”b” row tied to "C' row. ECB boards are NOT compatible with STEbus or VMEbus P2 connector (while STEbus does not use the “b” column; VME does define specific signals on the ‘b’ row). Pinout Active low signals indicated by Slash (punctuation), slash. GND: Ground reference voltage +5 V: Powers most logic. +12 V; −12 V: +15 V; −15 V Legacy power inputs, primarily useful for RS232 buffer power or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VMEbus
VMEbus (Versa Module Eurocard bus) is a computer bus standard physically based on Eurocard sizes. History In 1979, during development of the Motorola 68000 CPU, one of their engineers, Jack Kister, decided to set about creating a standardized bus system for 68000-based systems. The Motorola team brainstormed for days to select the name VERSAbus. VERSAbus cards were large, , and used edge connectors. Only a few products adopted it, including the IBM System 9000 instrument controller and the Automatix robot and machine vision systems. Kister was later joined by John Black, who refined the specifications and created the ''VERSAmodule'' product concept. A young engineer working for Black, Julie Keahey designed the first VERSAmodule card, the VERSAbus Adaptor Module, used to run existing cards on the new VERSAbus. Sven Rau and Max Loesel of Motorola-Europe added a mechanical specification to the system, basing it on the Eurocard standard that was then late in the stand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STEbus
The STEbus (also called the IEEE-1000 bus) is a non-proprietary, processor-independent, bus (computing), computer bus with 8 data lines and 20 address lines. It was popular for industrial control systems in the late 1980s and early 1990s before the ubiquitous IBM PC dominated this market. STE stands for STandard Eurocard. Although no longer competitive in its original market, it is valid choice for hobbyists wishing to make 'home brew' computer systems. The Z80 and probably the CMOS 65C02 are possible processors to use. The standardized bus allows hobbyists to interface to each other's designs. Origins In the early 1980s, there were many proprietary bus systems, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Most had grown in an ad-hoc manner, typically around a particular microprocessor. The S-100 bus is based on Intel 8080 signals, the STD Bus around Zilog Z80, Z80 signals, the SS-50 bus around the Motorola 6800, and the G64 bus around Motorola 6809, 6809 signals. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doepfer
Doepfer Musikelektronik GmbH is a German manufacturer of audio hardware, mostly modular synthesizers, based in Gräfelfing, Upper Bavaria, Germany and founded by Dieter Döpfer. The product range covers analog modular systems, MIDI controllers, MIDI hardware sequencers, MIDI-to-CV/Gate/Sync Interfaces, MIDI master keyboards and special MIDI equipment. Dieter Döpfer began developing audio hardware with a Voltage Controlled Phaser module for the Formant, a do-it-yourself-kit analog synthesizer from ''Elektor'' magazine in 1977. Several legendary modular synths followed while Döpfer also focused on the development of MIDI equipment during the 1980s. In 1992, Doepfer Musikelektronik GmbH released the MIDI analog sequencer MAQ16/3 which was designed in cooperation with Kraftwerk. In the beginning, the company had direct sales and interested musicians would receive a demonstration by visiting other customers since the modular systems were deemed too difficult for typical music sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modular Synthesizer
Modular synthesizers are synthesizers composed of separate modules for different functions. The modules can be connected together by the user to create a patch. The outputs from the modules may include audio signals, analog control voltages, or digital signals for logic or timing conditions. Typical modules are voltage-controlled oscillators, voltage-controlled filters, voltage-controlled amplifiers and envelope generators. History The first modular synthesizer was developed by German engineer Harald Bode in the late 1950s. The 1960s saw the introduction of the Moog synthesizer and the Buchla Modular Electronic Music System, created around the same period. The Moog was composed of separate modules which created and shaped sounds, such as envelopes, noise generators, filters, and sequencers, connected by patch cords. The Japanese company Roland released the Roland System 100 in 1975, followed by the System 700 in 1976 and the System 100m in 1979. In the late 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
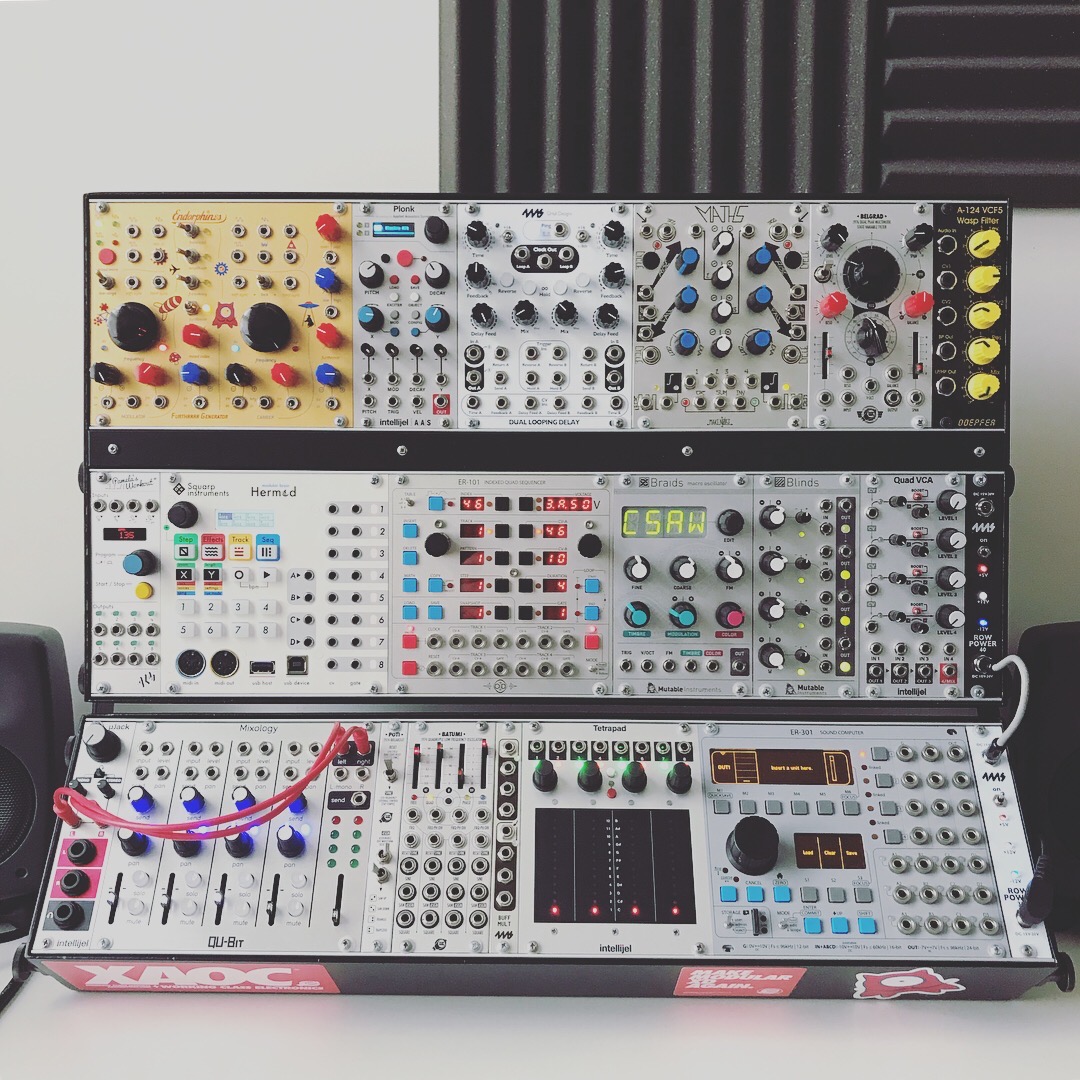
Eurorack
Eurorack is a modular synthesizer format originally specified in 1995 by Doepfer Musikelektronik. It has since grown in popularity, and has become a dominant hardware modular synthesizer format, with over 15,000 modules available from more than 600 different manufacturers ranging from DIY kits and boutique, cottage-industry designers to well-known, established synth mass-manufacturers like Moog and Roland. Compact size, 3.5mm mono jacks and cables for patching all signals, and lack of a visual or sonic aesthetic defined by one manufacturer sets Eurorack apart from other modular synthesizer formats, and these factors have contributed to the popularity of Eurorack among both manufacturers and musicians. History Before Eurorack, in the late 1970s, several modular systems based on the industrial “Euro” card frames appeared: * Elektor Formant (3U or 6U × 7HP, 3.5 mm jacks, 31-pin bus, ±15 V) * BME PM10/Axiom (3U × 8HP, RCA/Phono jacks, 31-pin bus, ±15 V) * T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multibus
Multibus is a computer bus standard used in industrial systems. It was developed by Intel Corporation and was adopted as the IEEE 796 bus. The Multibus specification was a robust industry standard with a relatively large form factor, allowing complex devices to be designed on it. Because it was well-defined and well-documented, a Multibus-compatible industry grew around it, with many companies making card cages and enclosures for it. Many others made CPU, memory, and other peripheral boards. In 1982 there were over 100 Multibus board and systems manufacturers. This allowed complex systems to be built from commercial off-the-shelf hardware, and also allowed companies to innovate by designing a proprietary Multibus board, then integrate it with another vendor's hardware to create a complete system. One example of this was Sun Microsystems with their Sun-1 and Sun-2 workstations. Sun built custom-designed CPU, memory, SCSI, and video display boards, and then added 3Com Ether ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PCI EXtensions For Instrumentation
PCI eXtensions for Instrumentation (PXI) is one of several modular electronic instrumentation platforms in current use based on the Peripheral Component Interconnect bus, which includes PCI Express (PCIe). These platforms are used as a basis for building electronic test equipment, automation systems, and modular laboratory instruments. PXI is based on Industry Standard Architecture, industry-standard Bus (computing), computer buses and permits flexibility in building equipment. Often, modules are fitted with custom software to manage the system. Overview PXI is designed for measurement and automation applications that require high-performance and a rugged industrial form-factor. With PXI, one can select modules from a number of vendors and integrate them into a single PXI system, over 1150 module types available in 2006. A typical Rack unit, 3U PXI module measures approximately (4x6") in size, and a typical 8-slot PXI chassis is 4U high and half rack width, full width chassis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VME EXtensions For Instrumentation
VME eXtensions for instrumentation bus (VXI bus) refers to standards for automated test based upon VMEbus. VXI defines additional bus lines for timing and triggering as well as mechanical requirements and standard protocols for configuration, message-based communication, multi-chassis extension, and other features. In 2004, the 2eVME extension was added to the VXI bus specification, giving it a maximum data rate of 160 MB/s. The basic building block of a VXI system is the mainframe or chassis. This contains up to 13 slots into which various modules (instruments) can be added. The mainframe also contains all the power supply requirements for the rack and the instruments it contains. Instruments in the form of VXI Modules then fit the slots in the rack. VXI bus modules are typically 6U in height (see Eurocard) and C-size (unlike VME bus modules which are more commonly B-size). It is therefore possible to configure a system to meet a particular requirement by selecting the require ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CompactPCI Express
CompactPCI is a computer bus interconnect for industrial computers, combining a Eurocard-type connector and PCI signaling and protocols. Boards are standardized to 3 U or 6U sizes, and are typically interconnected via a passive backplane. The connector pin assignments are standardized by the PICMG US and PICMG Europe organizations. The connectors and the electrical rules allow for eight boards in a PCI segment. Multiple bus segments are allowed with bridges. Unlike the original Eurocard solutions such as VME, which use connectors with a 0.1 inch (2.54 mm) pin spacing, CompactPCI cards use metric connectors with a 2-millimeter pin spacing, designed to the IEC 1076 standard. 3U boards have a 110-pin connector (J1), which carries the 32-bit PCI bus signals, and an optional 110-pin connector (J2), which carries either user-defined I/O or the upper 32 bits of an optional 64-bit PCI bus. 6U cards have an identical J1, a J2 that is always used for 64-bit PCI, as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
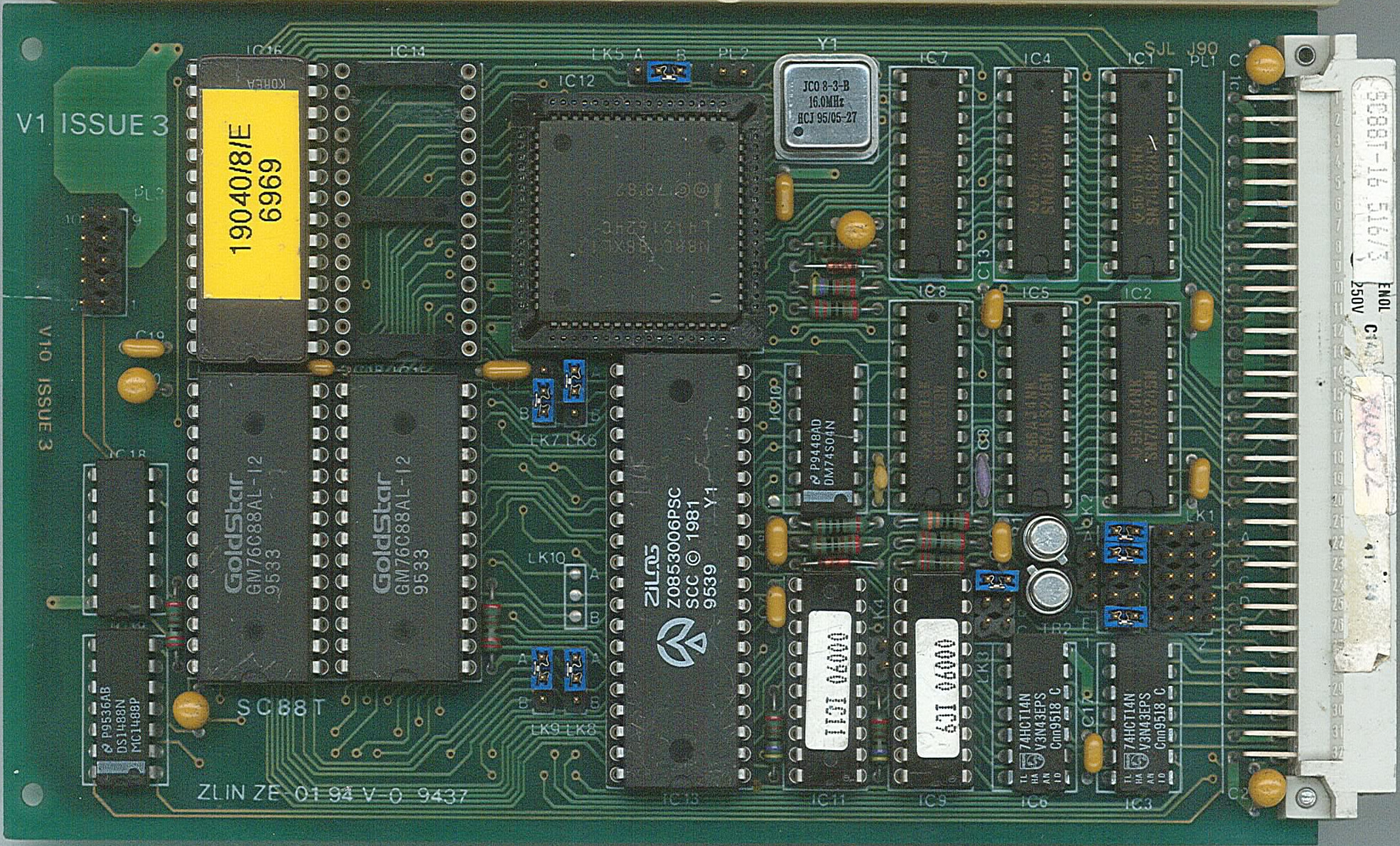
STEbus 68008 CPU On 100x160mm Eurocard
The STEbus (also called the IEEE-1000 bus) is a non-proprietary, processor-independent, bus (computing), computer bus with 8 data lines and 20 address lines. It was popular for industrial control systems in the late 1980s and early 1990s before the ubiquitous IBM PC dominated this market. STE stands for STandard Eurocard. Although no longer competitive in its original market, it is valid choice for hobbyists wishing to make 'home brew' computer systems. The Z80 and probably the CMOS 65C02 are possible processors to use. The standardized bus allows hobbyists to interface to each other's designs. Origins In the early 1980s, there were many proprietary bus systems, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Most had grown in an ad-hoc manner, typically around a particular microprocessor. The S-100 bus is based on Intel 8080 signals, the STD Bus around Zilog Z80, Z80 signals, the SS-50 bus around the Motorola 6800, and the G64 bus around Motorola 6809, 6809 signals. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |