|
Ethyl Propionate
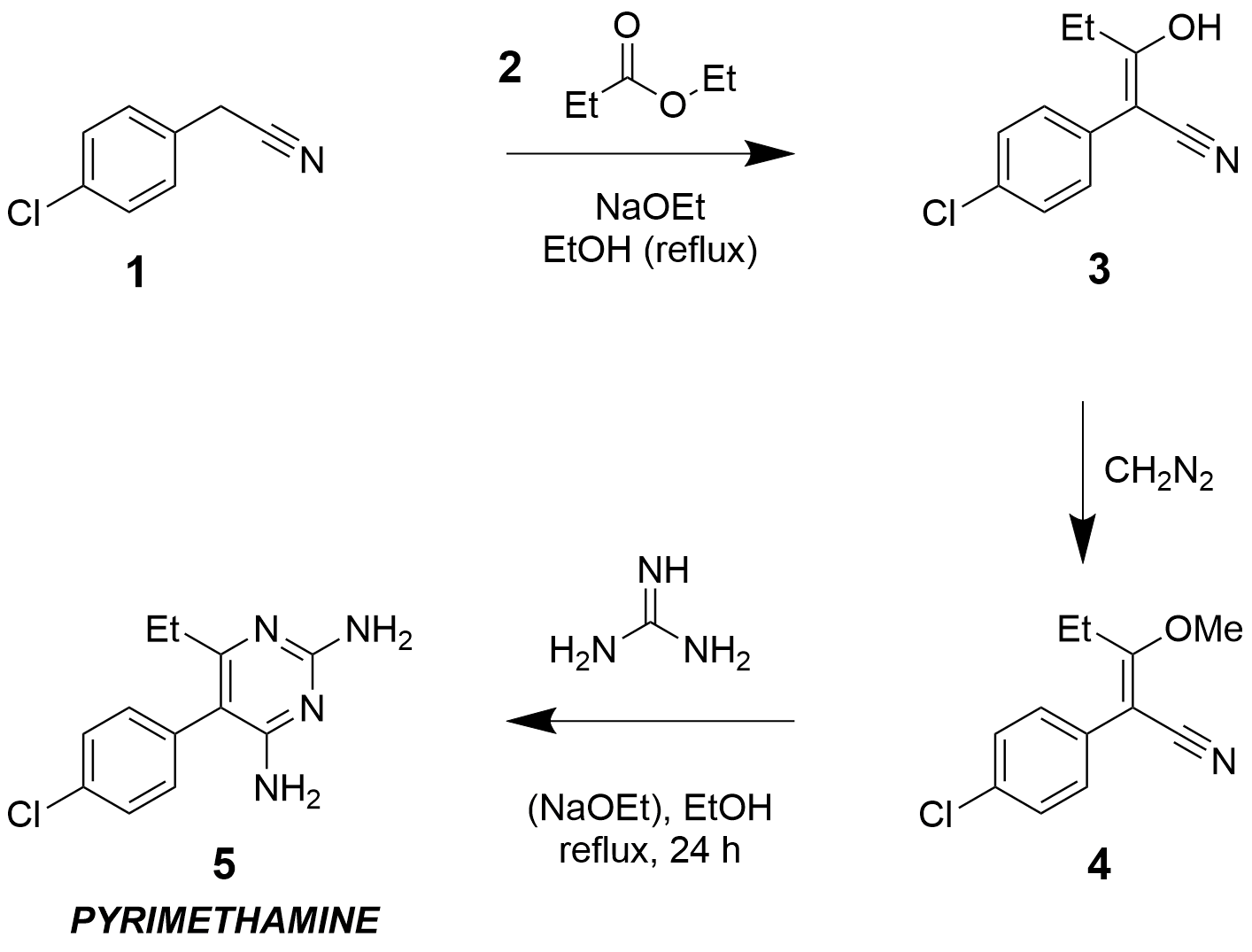
Ethyl propionate is an organic compound with formula C2H5O2CCH2CH3. It is the ethyl ester of propionic acid. It is a colorless volatile liquid with a pineapple-like odor. Some fruits such as kiwis and strawberries contain ethyl propionate in small amounts. Uses and reactions It is also used in the production of some antimalarial drugs including pyrimethamine. Ethyl propionate can be synthesized by the Fischer esterification of ethanol and propionic acid Propionic acid (, from the Greek language, Greek words πρῶτος : ''prōtos'', meaning "first", and πίων : ''píōn'', meaning "fat"; also known as propanoic acid) is a naturally occurring carboxylic acid with chemical formula . It is a ...: :CH3CH2OH + CH3CH2CO2H → CH3CH2O2CCH2CH3 + H2O It participates in condensation reactions by virtue of the weakly acidic methylene group. See also * Methyl propionate, a similar compound References {{Esters Propionate esters Ethyl esters Flavors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-containing compounds such as alkanes (e.g. methane ) and its derivatives are universally considered organic, but many others are sometimes considered inorganic, such as certain compounds of carbon with nitrogen and oxygen (e.g. cyanide ion , hydrogen cyanide , chloroformic acid , carbon dioxide , and carbonate ion ). Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, and even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid (either organic or inorganic) in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group () of that acid is replaced by an organyl group (R). These compounds contain a distinctive functional group. Analogues derived from oxygen replaced by other chalcogens belong to the ester category as well. According to some authors, organyl derivatives of acidic hydrogen of other acids are esters as well (e.g. amides), but not according to the IUPAC. Glycerides are fatty acid esters of glycerol; they are important in biology, being one of the main classes of lipids and comprising the bulk of animal fats and vegetable oils. Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters; naturally occurring lactones are mainly 5- and 6-membered ring lactones. Lactones contribute to the aroma of fruits, butter, cheese, vegetables like celery and other foods. Esters can be formed from oxoacids (e.g. esters of acetic acid, carbonic acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propionic Acid
Propionic acid (, from the Greek language, Greek words πρῶτος : ''prōtos'', meaning "first", and πίων : ''píōn'', meaning "fat"; also known as propanoic acid) is a naturally occurring carboxylic acid with chemical formula . It is a liquid with a pungent and unpleasant smell somewhat resembling body odor. The anion as well as the Carboxylate salt, salts and esters of propionic acid are known as propionates or propanoates. About half of the world production of propionic acid is consumed as a preservative for both animal feed and food for human consumption. It is also useful as an intermediate in the production of other chemicals, especially polymers. History Propionic acid was first described in 1844 by Johann Gottlieb, who found it among the degradation products of sugar. Over the next few years, other chemists produced propionic acid by different means, none of them realizing they were producing the same substance. In 1847, French chemist Jean-Baptiste Dumas esta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrimethamine
Pyrimethamine, sold under the brand name Daraprim among others, is a medication used with leucovorin (leucovorin is used to decrease side effects of pyrimethamine; it does not have intrinsic anti-parasitic activity) to treat the parasitic diseases toxoplasmosis and cystoisosporiasis. It is also used with dapsone as a second-line option to prevent Pneumocystis pneumonia, ''Pneumocystis jiroveci'' pneumonia in people with HIV/AIDS. It was previously used for malaria but is no longer recommended due to resistance. Pyrimethamine is oral administration, taken by mouth. Common side effects include gastrointestinal upset, severe allergic reactions, and bone marrow suppression. It should not be used by people with folate deficiency that has resulted in anemia. There is concern that it may increase the risk of cancer. While occasionally used in pregnancy it is unclear if pyrimethamine is safe for the baby. Pyrimethamine is classified as a folic acid antagonist. It works by inhibiting f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Source Malaria
Medicines for Malaria Venture (MMV) is a not-for-profit public-private partnership that was established as a foundation in Switzerland in 1999. Its main mission is to reduce malaria in disease-endemic countries by developing and facilitating the delivery of antimalarial drugs. History MMV was launched in 1999, with initial seed funding of US$4 million from the Government of Switzerland, the Department for International Development (UK), the Government of the Netherlands, the World Bank, and the Rockefeller Foundation. Governance MMV is governed by a board of directors. The Chairman of MMV is Mr Alan Court. MMV has a board of directors in North America, an Expert Scientific Advisory Committee which helps to identify projects, an Access & Product Management Advisory Committee and a Global Safety Board which reviews projects. Projects MMV's project portfolio states that their goals are: * Effective treatment against drug-resistant strains of ''Plasmodium falciparum'' * The potenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fischer Esterification
Fischer is a German occupational surname, meaning fisherman. The name Fischer is the fourth most common German surname. The English version is Fisher. People with the surname A * Abraham Fischer (1850–1913) South African public official * Adam Fischer (sculptor) (1888–1968), Danish sculptor * Ádám Fischer (born 1949), Hungarian conductor * Adolf Fischer (officer) (1893–1947), German Nazi general executed for war crimes * Adolph Fischer (1858–1887) German-American anarchist * Alfred Fischer (architect) (1881–1950), German architect * Alfred Fischer (judge) (1919–2004), German judge * Andrew Andika Fischer (born 1987), Indonesian actor * Angeline Fuller Fischer (1841–1925), American writer * Annie Fischer (1914–1995), Hungarian pianist * Andrea Fischer (born 1960), German politician * Andrea Fischer (scientist), (born 1973), Austrian glaciologist * Anton Fischer (bobsleigh), German bobsledder * Artur Fischer (1919–2016), German inventor (fischertec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethanol
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with its formula also written as , or EtOH, where Et is the pseudoelement symbol for ethyl group, ethyl. Ethanol is a Volatility (chemistry), volatile, flammable, colorless liquid with a characteristic wine-like odor and pungent taste. As a psychoactive depressant, it is the active ingredient in alcoholic beverages, and the second most consumed drug globally behind caffeine. Ethanol is naturally produced by the fermentation process of sugars by yeasts or via petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration. Historically it was used as a general anesthetic, and has modern medical applications as an antiseptic, disinfectant, solvent for some medications, and antidote for methanol poisoning and ethylene glycol poisoning. It is used as a chemical solvent and in the Chemical synthesis, synthesis of orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Propionate
Methyl propionate, also known as methyl propanoate, is an organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a colorless liquid with a fruity, rum-like odor. Preparation Methyl propionate can be prepared by esterification of propionic acid with methanol. Industrially, it is prepared by carboalkoxylation, i.e., the reaction of ethylene with carbon monoxide and methanol in the presence of a catalyst: : The reaction is catalyzed by nickel carbonyl and palladium(0) complexes.(mayth and yafs)Scott D. Barnicki "Synthetic Organic Chemicals" in Handbook of Industrial Chemistry and Biotechnology edited by James A. Kent, New York : Springer, 2012. 12th ed. . Uses Condensation of Methyl propionate with formaldehyde followed by dehydration yields methyl methacrylate: : : Methyl propionate is used as a solvent for cellulose nitrate and lacquers, and as a raw material for the production of paints, varnishes and other chemicals such as methyl methacrylate Methyl methacrylate (MMA) is an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propionate Esters
Propionic acid (, from the Greek language, Greek words πρῶτος : ''prōtos'', meaning "first", and πίων : ''píōn'', meaning "fat"; also known as propanoic acid) is a naturally occurring carboxylic acid with chemical formula . It is a liquid with a pungent and unpleasant smell somewhat resembling body odor. The anion as well as the Carboxylate salt, salts and esters of propionic acid are known as propionates or propanoates. About half of the world production of propionic acid is consumed as a preservative for both animal feed and food for human consumption. It is also useful as an intermediate in the production of other chemicals, especially polymers. History Propionic acid was first described in 1844 by Johann Gottlieb, who found it among the degradation products of sugar. Over the next few years, other chemists produced propionic acid by different means, none of them realizing they were producing the same substance. In 1847, French chemist Jean-Baptiste Dumas esta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethyl Esters
Ethyl may refer to: Arts and entertainment *Ethyl Sinclair, a character in the ''Dinosaurs'' television show Science and technology * Ethyl group, an organic chemistry moiety * Ethyl alcohol (or ethanol) * Ethyl Corporation, a fuel additive company ** Tetraethyllead Tetraethyllead (commonly styled tetraethyl lead), abbreviated TEL, is an organolead compound with the formula lead, Pb(ethyl group, C2H5)4. It was widely used as a fuel additive for much of the 20th century, first being mixed with gasoline begi ...-treated gasoline See also * Ethel (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |