|
Ethnoentomology
Human interactions with insects include both a wide variety of uses, whether practical such as for food, textiles, and dyestuffs, or symbolic, as in art, music, and literature, and negative interactions including damage to crops and extensive efforts to control insect pests. Academically, the interaction of insects and society has been treated in part as cultural entomology, dealing mostly with "advanced" societies, and in part as ethnoentomology, dealing mostly with "primitive" societies, though the distinction is weak and not based on theory. Both academic disciplines explore the parallels, connections and influence of insects on human populations, and vice versa. They are rooted in anthropology and natural history, as well as entomology, the study of insects. Other cultural uses of insects, such as biomimicry, do not necessarily lie within these academic disciplines. More generally, people make a wide range of uses of insects, both practical and symbolic. On the other hand, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insects In Art
Insects (from Latin ') are hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs of jointed legs, compound eyes, and a pair of antennae. Insects are the most diverse group of animals, with more than a million described species; they represent more than half of all animal species. The insect nervous system consists of a brain and a ventral nerve cord. Most insects reproduce by laying eggs. Insects breathe air through a system of paired openings along their sides, connected to small tubes that take air directly to the tissues. The blood therefore does not carry oxygen; it is only partly contained in vessels, and some circulates in an open hemocoel. Insect vision is mainly through their compound eyes, with additional small ocelli. Many insects can hear, using tympanal organs, which may be on the legs or other parts of the body. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insects
Insects (from Latin ') are hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs of jointed legs, compound eyes, and a pair of antennae. Insects are the most diverse group of animals, with more than a million described species; they represent more than half of all animal species. The insect nervous system consists of a brain and a ventral nerve cord. Most insects reproduce by laying eggs. Insects breathe air through a system of paired openings along their sides, connected to small tubes that take air directly to the tissues. The blood therefore does not carry oxygen; it is only partly contained in vessels, and some circulates in an open hemocoel. Insect vision is mainly through their compound eyes, with additional small ocelli. Many insects can hear, using tympanal organs, which may be on the legs or other parts of the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entomology
Entomology (from Ancient Greek ἔντομον (''éntomon''), meaning "insect", and -logy from λόγος (''lógos''), meaning "study") is the branch of zoology that focuses on insects. Those who study entomology are known as entomologists. In the past, the term ''insect'' was less specific, and historically the definition of entomology would also include the study of animals in other arthropod groups, such as arachnids, myriapods, and crustaceans. The field is also referred to as insectology in American English, while in British English insectology implies the study of the relationships between insects and humans. Over 1.3million insect species have been described by entomology. History Entomology is rooted in nearly all human cultures from prehistoric times, primarily in the context of agriculture (especially biological control and beekeeping). The natural Roman philosopher Pliny the Elder (23–79 CE) wrote a book on the kinds of insects, while the scientist Grammarians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
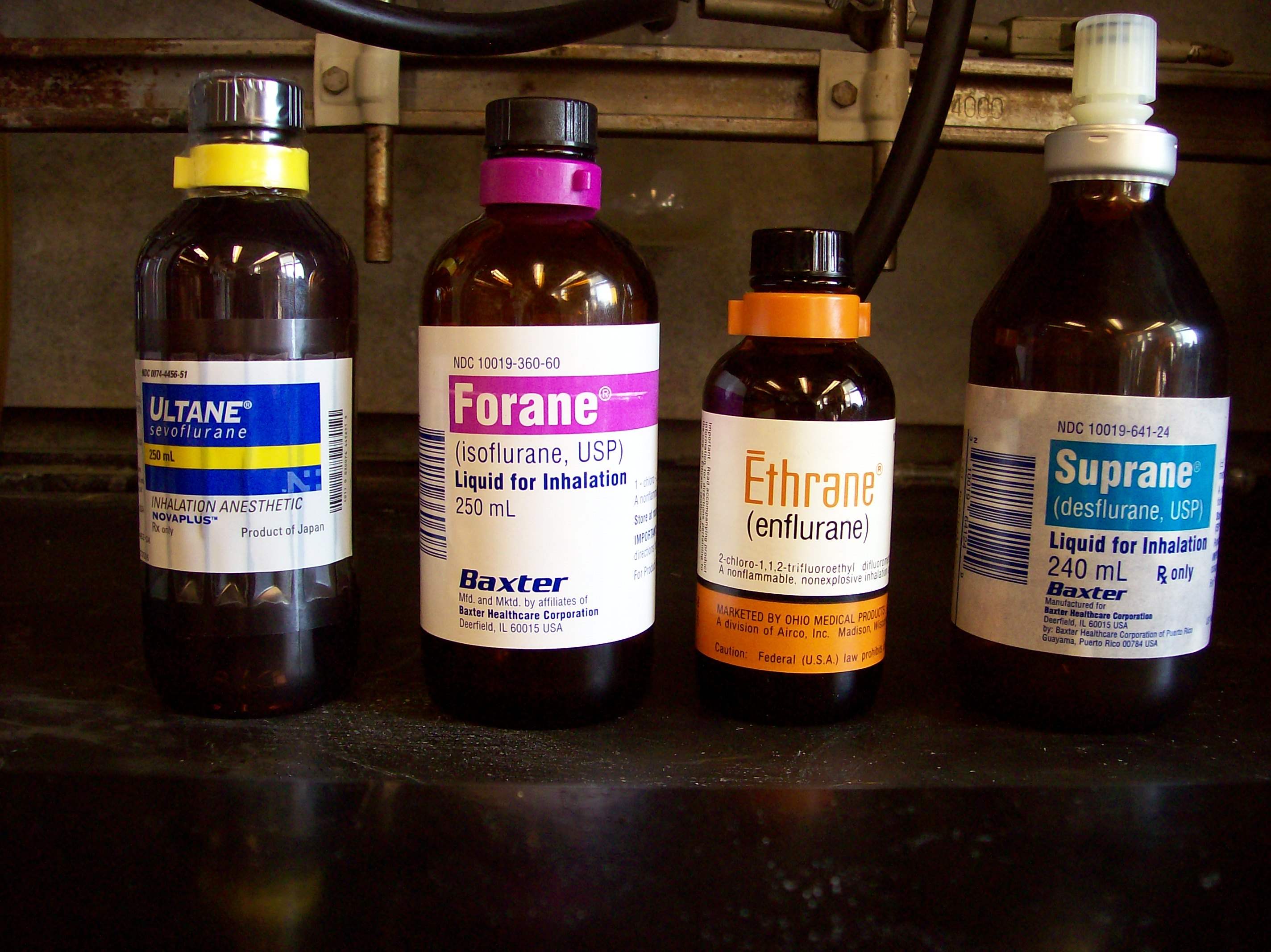
Anaesthetic
An anesthetic (American English) or anaesthetic (British English; see spelling differences) is a drug used to induce anesthesia — in other words, to result in a temporary loss of sensation or awareness. They may be divided into two broad classes: general anesthetics, which result in a reversible loss of consciousness, and local anesthetics, which cause a reversible loss of sensation for a limited region of the body without necessarily affecting consciousness. A wide variety of drugs are used in modern anesthetic practice. Many are rarely used outside anesthesiology, but others are used commonly in various fields of healthcare. Combinations of anesthetics are sometimes used for their synergistic and additive therapeutic effects. Adverse effects, however, may also be increased. Anesthetics are distinct from analgesics, which block only sensation of painful stimuli. Analgesics are typically used in conjunction with anesthetics to control pre-, intra-, and postoper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antihistamine
Antihistamines are drugs which treat allergic rhinitis, common cold, influenza, and other allergies. Typically, people take antihistamines as an inexpensive, generic (not patented) drug that can be bought without a prescription and provides relief from nasal congestion, sneezing, or hives caused by pollen, dust mites, or animal allergy with few side effects. Antihistamines are usually for short-term treatment. Chronic allergies increase the risk of health problems which antihistamines might not treat, including asthma, sinusitis, and lower respiratory tract infection. Consultation of a medical professional is recommended for those who intend to take antihistamines for longer-term use. Although the general public typically uses the word "antihistamine" to describe drugs for treating allergies, physicians and scientists use the term to describe a class of drug that opposes the activity of histamine receptors in the body. In this sense of the word, antihistamines are subc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasodilation
Vasodilation, also known as vasorelaxation, is the widening of blood vessels. It results from relaxation of smooth muscle cells within the vessel walls, in particular in the large veins, large arteries, and smaller arterioles. Blood vessel walls are composed of endothelial tissue and a basal membrane lining the lumen of the vessel, concentric smooth muscle layers on top of endothelial tissue, and an adventitia over the smooth muscle layers. Relaxation of the smooth muscle layer allows the blood vessel to dilate, as it is held in a semi-constricted state by sympathetic nervous system activity. Vasodilation is the opposite of vasoconstriction, which is the narrowing of blood vessels. When blood vessels dilate, the flow of blood is increased due to a decrease in vascular resistance and increase in cardiac output. Vascular resistance is the amount of force circulating blood must overcome in order to allow perfusion of body tissues. Narrow vessels create more vascular resista ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debridement
Debridement is the medical removal of dead, damaged, or infected tissue to improve the healing potential of the remaining healthy tissue. Removal may be surgical, mechanical, chemical, autolytic (self-digestion), or by maggot therapy. In podiatry, practitioners such as chiropodists, podiatrists and foot health practitioners remove conditions such as calluses and verrucas. Debridement is an important part of the healing process for burns and other serious wounds; it is also used for treating some kinds of snake and spider bites. Sometimes the boundaries of the problem tissue may not be clearly defined. For example, when excising a tumor, there may be micrometastases along the edges of the tumor that are too small to be detected, but if not removed, could cause a relapse. In such circumstances, a surgeon may opt to debride a portion of the surrounding healthy tissue to ensure that the tumor is completely removed. Types There is a lack of high-quality evidence to c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
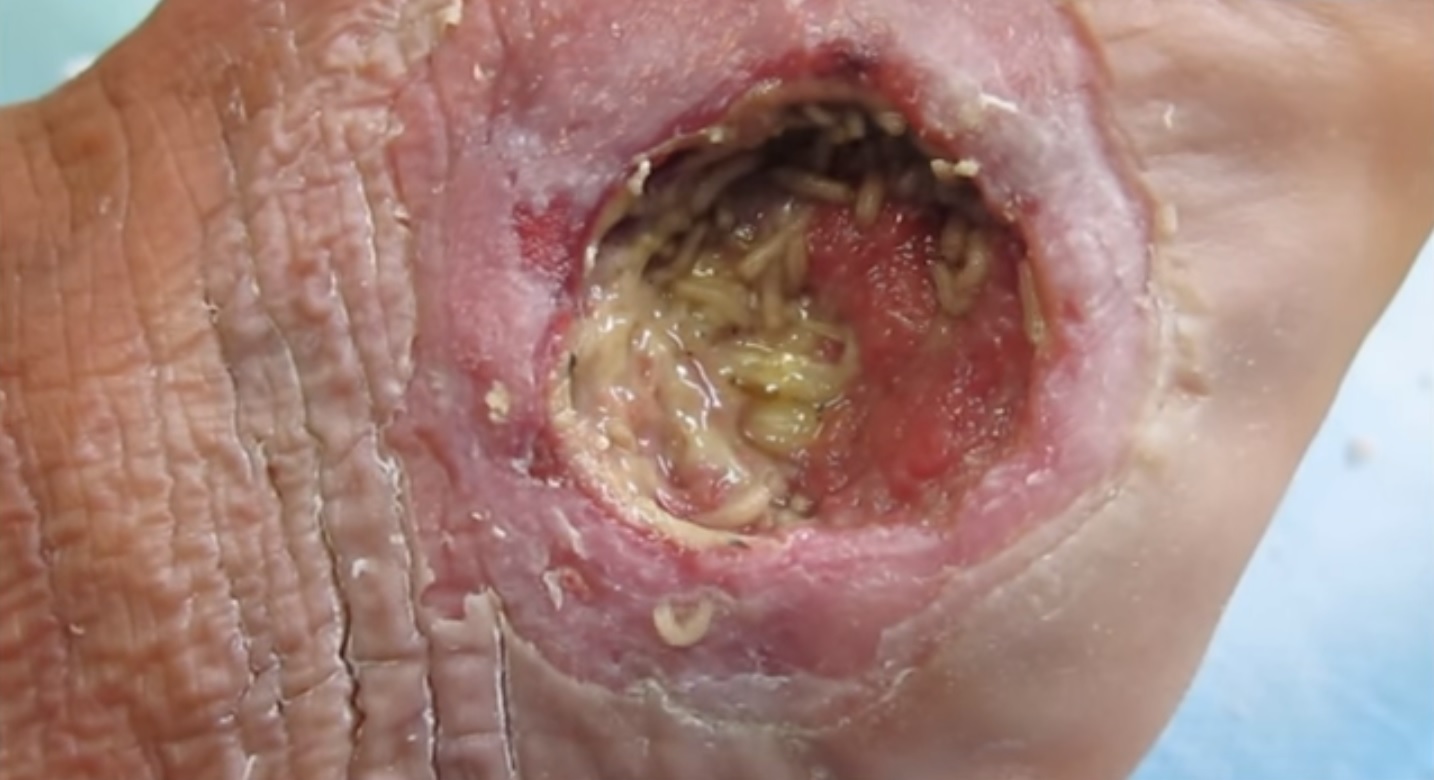
Maggot Therapy
Maggot debridement therapy (also known as MDT, larval therapy, or simply maggot therapy) is a type of biotherapy involving the introduction of live, disinfected maggots (fly larvae) into non-healing skin and soft-tissue wounds of a human or other animal for the purpose of cleaning out the necrotic (dead) tissue within a wound ( debridement), and disinfection. There is evidence that maggot therapy may help with wound healing. Medical uses Maggot therapy improves healing in chronic ulcers. In diabetic foot ulcers there is tentative evidence of benefit. A Cochrane review of methods for the debridement of venous leg ulcers found maggot therapy to be broadly as effective as most other methods, but the study also noted that the quality of data was poor. In 2003, the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) cleared maggots from common green bottle fly for use as a "medical device" in the US for the purpose of treatment of: * Non-healing necrotic skin and soft tissue woun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melittin
Melittin is the main component (40–60% of the dry weight) and the major pain-producing substance of honeybee (''Apis mellifera'') venom. Melittin is a basic peptide consisting of 26 amino acids. Function The principal function of melittin as a component of bee venom is to cause pain and destruction of tissue of intruders that threaten a beehive. However, in honey bees, melittin is not only expressed in the venom gland, but also in other tissues when infected with pathogens. The two venom molecules, melittin and secapin, that are over-expressed in honey bees infected with various pathogens, possibly indicate a role for melittin in the immune response of bees to infectious diseases. Structure Melittin is a small peptide with no disulfide bridge; the ''N''-terminal part of the molecule is predominantly hydrophobic and the ''C''-terminal part is hydrophilic and strongly basic. In water, it forms a tetramer but it also can spontaneously integrate itself into cell membra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propolis
Propolis or bee glue is a resinous mixture that honey bees produce by mixing saliva and beeswax with exudate gathered from tree buds, sap flows, or other botanical sources. It is used as a sealant for unwanted open spaces in the beehive. Propolis is used for small gaps (around or less), while gaps larger than the bee space (around ) are usually filled with burr comb. Its color varies depending on its botanical source, with dark brown as the most common. Propolis is sticky above , while at lower temperatures, it becomes hard and brittle. When foraging, worker bees primarily harvest pollen and nectar, while also collecting water and plant resin necessary for the production of propolis. The chemical composition and nature of propolis depend on environmental conditions and harvested resources. Types Mixed types of propolis found in European countries with a moderate climate include two or more sources of plant resins (plant species) identified by composition, such as aspen, M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
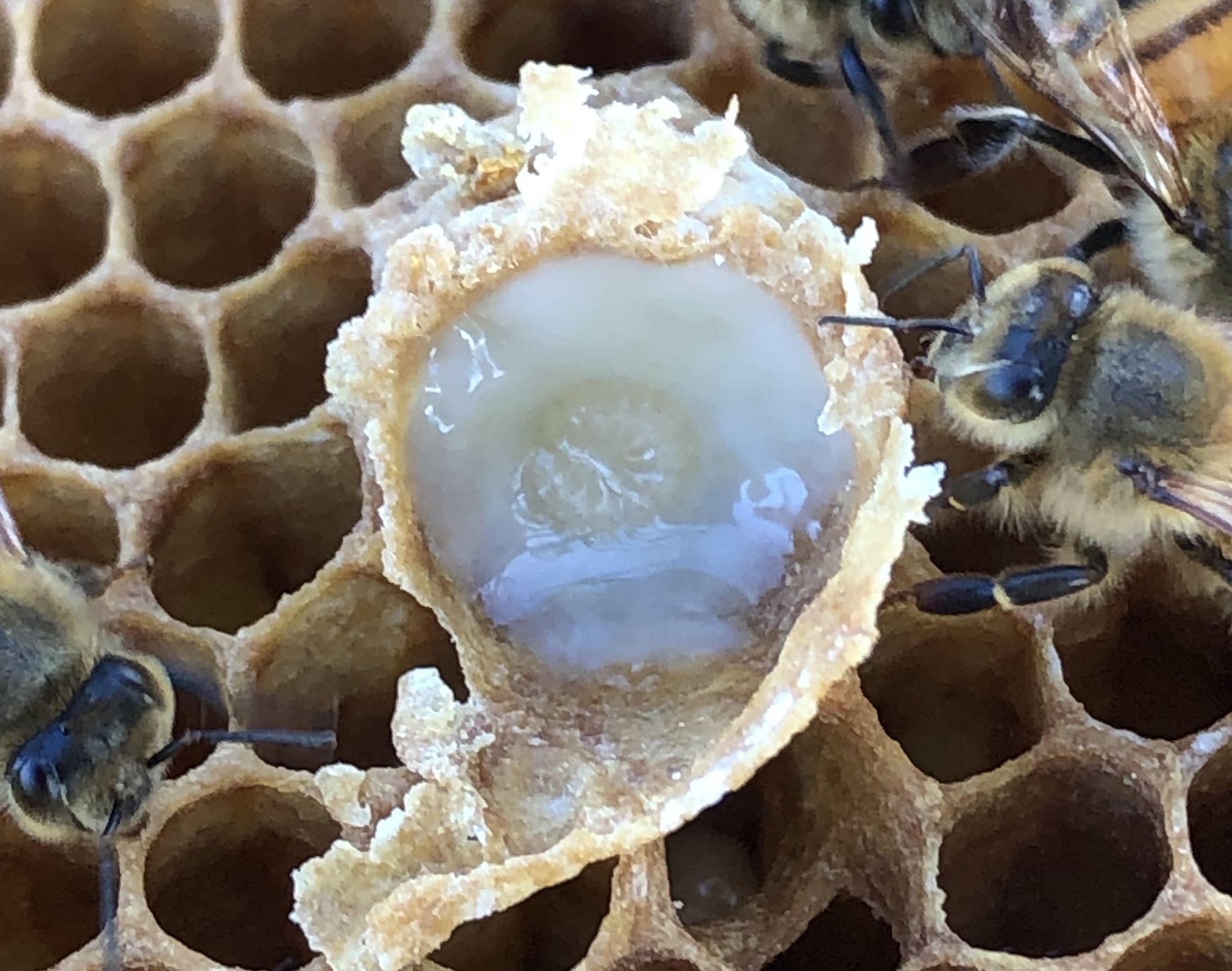
Royal Jelly
Royal jelly is a honey bee secretion that is used in the nutrition of larvae and adult queens. It is secreted from the glands in the hypopharynx of nurse bees, and fed to all larvae in the colony, regardless of sex or caste.Graham, J. (ed.) (1992) ''The Hive and the Honey Bee'' (Revised Edition). Dadant & Sons. During the process of creating new queens, the workers construct special queen cells. The larvae in these cells are fed with copious amounts of royal jelly. This type of feeding triggers the development of queen morphology, including the fully developed ovaries needed to lay eggs. Royal jelly is sometimes used in alternative medicine under the category apitherapy. It is often sold as a dietary supplement for humans, but the European Food Safety Authority concluded in 2011 that evidence does not support the claim that consuming royal jelly offers health benefits to humans. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration has taken legal action against companies that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by most types of flowers of seed plants for the purpose of sexual reproduction. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced Gametophyte#Heterospory, microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm cells). Pollen grains have a hard coat made of sporopollenin that protects the gametophytes during the process of their movement from the stamens to the pistil of flowering plants, or from the male Conifer cone, cone to the female cone of gymnosperms. If pollen lands on a compatible pistil or female cone, it Germination, germinates, producing a pollen tube that transfers the sperm to the ovule containing the female gametophyte. Individual pollen grains are small enough to require magnification to see detail. The study of pollen is called palynology and is highly useful in paleoecology, paleontology, archaeology, and Forensic science, forensics. Pollen in plants is used for transferring Ploidy#Haploid and monoploid, haploid male genetic ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |