|
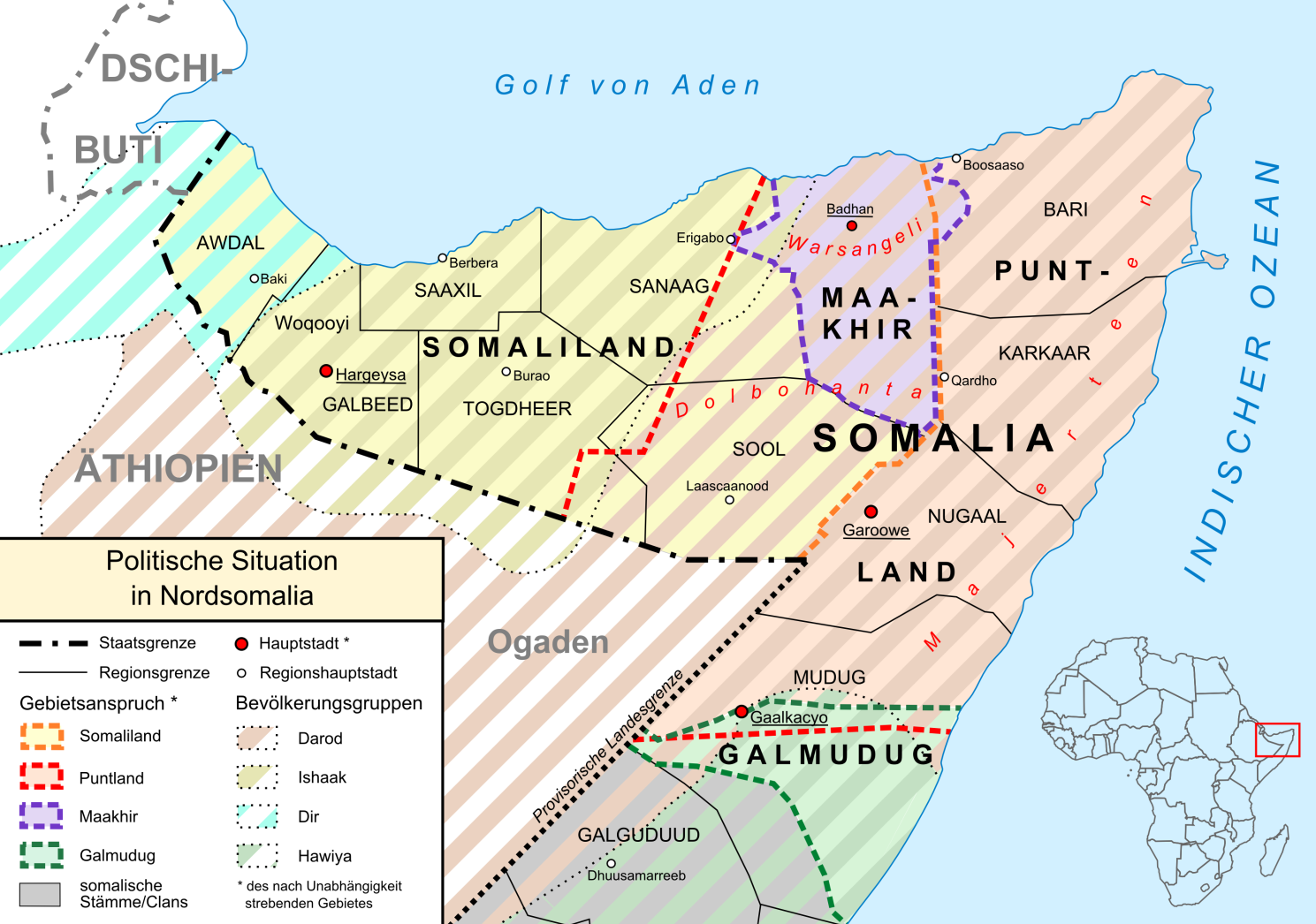
Ethiopia–Somalia Border
The Ethiopia–Somalia border stretches 1,500 kilometers. In the 19th century, both Britain and Italy contributed to shaping the modern border, on behalf of their colonies of British and Italian Somaliland. The Somali people were thus under British, French, Italian and Ethiopian rule. During World War II, Britain gained control of the Ogaden and Haud territories and returned them to Ethiopia in 1954, but not delimited beyond the provisional line (sometimes labeled on maps as the Provisional Administrative Line). Since 1960 independence, the border has suffered serious skirmishes involving both countries' soldiers. From 1977 to 1978, Ethiopia and Somalia fought in the Ogaden War led by Colonel Mengistu Haile Mariam and General Siad Barre respectively. The EPRDF government demarcated the border of Ogaden into Somali Region. Somalia is located at the base of Ethiopia's protrude southeast region; from the South, it is bounded by Wabi Shebelle and Genale Valley. History During the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genale
Genale was a town founded by Italian colonists in the southeastern Lower Shabelle region of Italian Somaliland. It is now called Janale. History Genale was created in 1924 by a group of Italian settlers from the Italian city of Torino, with the supervision of the Italian governor of the colony. Near the Genale of the colonists and separated by the Shebelle river, soon grew a bigger city populated by Somalis (working as cheap labor force in the plantations): the actual Janale. After World War II remained only Janaale, while Genale disappeared when the defeated Italians moved away from Somalia. In 1924, indeed it was started the Italian colonization of the area of Genale, in southern Somalia, forming a group of small and medium-sized farms. Most settlers consisted of old fascist militants of Turin who had followed in this Italian colony the new governor of Somalia, Cesare Maria De Vecchi. The first informal association between farmers, however, arose only in 1928. The main crop of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Somalia
Greater Somalia, also known as Greater Somaliland (; ), is the geographic location comprising the regions in the Horn of Africa in which ethnic Somalis live and have historically inhabited.During the Scramble for Africa at the end of the 19th century, Somali-inhabited territories were partitioned between imperial powers. The unification of these territories became a focal objective of an independent Somalia. Referred to as "Greater Somalia," these regions, at the outset of Somali independence, encompassed British Somaliland and Italian Somaliland, which had successfully merged into a single nation in 1960. French Somaliland, the Northern Frontier District (NFD) in Kenya, and the Ogaden region in Ethiopia were placed under the control of neighboring states despite the pre-independence unification efforts of Somali nationalists. The post-independence governments of the Somali Republic (1960–1969) and the Somali Democratic Republic (1969–1991) expended significant effort to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian East Africa
Italian East Africa (, A.O.I.) was a short-lived colonial possession of Fascist Italy from 1936 to 1941 in the Horn of Africa. It was established following the Second Italo-Ethiopian War, which led to the military occupation of the Ethiopian Empire (Abyssinia). It encompassed Italian Somaliland, Italian Eritrea and the acquired Ethiopian territories, all governed by a single administrative unit, the Governo Generale dell'Africa Orientale Italiana. Its establishment contributed to the outbreak of the Second World War by exposing the weaknesses of the League of Nations. Italian East Africa was divided into six governorates. Eritrea and Somalia, Italian possessions since the 1880s, were enlarged with captured Ethiopian territory and became the Eritrea and Somalia Governorates. The remainder of the occupied Ethiopian territories comprised the Harar, Galla-Sidamo, Amhara, and Scioa Governorates. At its largest extent, Italian East Africa occupied territories in British Som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Italo-Ethiopian War
The Second Italo-Ethiopian War, also referred to as the Second Italo-Abyssinian War, was a war of aggression waged by Fascist Italy, Italy against Ethiopian Empire, Ethiopia, which lasted from October 1935 to February 1937. In Ethiopia it is often referred to simply as the Italian Invasion (; Oromo language, Oromo: Weerara Xaaliyaanii), and in Italy as the Ethiopian War (). It is seen as an example of the expansionist policy that characterized the Axis powers and the ineffectiveness of the League of Nations before the outbreak of World War II. On 3 October 1935, two hundred thousand soldiers of the Italian Army commanded by Marshal Emilio De Bono attacked from Italian Eritrea, Eritrea (then an Italian colonial possession) without prior declaration of war. At the same time a minor force under General Rodolfo Graziani attacked from Italian Somalia. On 6 October, Adwa was conquered, a symbolic place for the Italian army because of the defeat at the Battle of Adwa by the Ethiopian ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dollo Zone
Dollo () is one of the nine zones in the Somali Region of Ethiopia. It was previously known as Warder/Werder, so named after its largest city, Warder. Dollo is bordered on the southwest by Korahe, on the northwest by Jarar, and on the southeast by Somalia. The Provisional Administrative Line defines the southeast border with Somalia. Demographics Based on the 2007 Census conducted by the Central Statistical Agency of Ethiopia (CSA), this Zone has a total population of 306,488, of whom 175,624 are men and 130,864 women. While 28,784 or 9.39% are urban inhabitants, a further 113,408 or 37% were pastoralists. The largest ethnic group reported in Dollo were the Somalis (99.57%); all other ethnic groups made up 0.43% of the population. Somali language is spoken as a first language by 99.58%; the remaining 0.42% spoke all other primary languages reported. 99.36% of the population said they were Muslim. The 1997 national census reported a total population for this Zone of 324,3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Welwel, Ethiopia
Walwal (; ; ; also transliterated as Welwel or Walwaal) is a town in eastern Ethiopia known as the Ogaden. Located in the Werder Zone of the Somali Region, this town has a longitude and latitude of with an elevation of 570 meters above sea level. Walwal has an estimated population of 842 according to the 2007 census. From 1903 Walwal, together with Werder and Qorrahee, became Dervish centers headed by Sayid Khalif Abdullah Hassan, brother of the Sayid Mohammed. The town and its surrounding region was kept under Dervish rule through a series of forts erected there. The control of this region allowed the Dervish to count, even in the most critical moments, on a source of animal supply, also collected in the form of a tribute, taking it away from the traditional authorities. Furthermore, strategically, this region ensured a territorial link between the high Hiiraan, where the Bahgeri operated, and the Hawd Region and the Mudug which was in the hands of Daraawiish almost continuou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abyssinia Crisis
The Abyssinia Crisis, also known in Italy as the Walwal incident, was an international crisis in 1935 that originated in a dispute over the town of Walwal, which then turned into a conflict between Fascist Italy and the Ethiopian Empire (then commonly known as "Abyssinia"). The League of Nations ruled against Italy and voted for economic sanctions, but they were never fully applied. Italy ignored the sanctions, quit the League and ultimately annexed and occupied Abyssinia after it had won the Second Italo-Ethiopian War. The crisis is generally regarded as having discredited the League. Walwal incident The Italo–Ethiopian Treaty of 1928 stated that the border between Italian Somaliland and Ethiopia was 21 leagues from and parallel to the Banaadir coast (approximately ). In 1930, Italy built a fort at the Walwal oasis in the eastern Ogaden, well beyond the 21-league limit. The fort was in a boundary zone between the nations, which was not well defined, and is now about insi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Africa Protectorate
East Africa Protectorate (also known as British East Africa) was a British protectorate in the African Great Lakes, occupying roughly the same area as present-day Kenya, from the Indian Ocean inland to the border with Uganda in the west. Controlled by the United Kingdom in the late 19th century, it grew out of British commercial interests in the area in the 1880s and remained a protectorate until 1920 when it became the Colony of Kenya, save for an independent coastal strip that became the Kenya Protectorate.Kenya Protectorate Order in Council 1920 ( SR&O 1920/2343), S.R.O. & S.I. Rev. VIII, 258, State Pp., Vol. 87 p. 968 Administration European Christian missionaries began settling in the area from Mombasa to Mount Kilimanjaro in the 1840s, nominally under the protection of the Sultanate of Zanzibar. In 1886, the British government encouraged William Mackinnon, who already had an agreement with the Sultan and whose shipping company traded extensively in the African G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gadabuursi
The Gadabuursi (Somali language, Somali: ''Gadabuursi'', Arabic language, Arabic: جادابورسي), also known as ''Samaroon'' (Arabic language, Arabic: ''قبيلة سَمَرُون)'', is a northern Somali clan, a sub-division of the Dir (clan), Dir clan family.I. M. Lewis (1959) The Gadabuursi are geographically spread out across three countries: Ethiopia, Somaliland and Djibouti. Among all of the Gadabuursi inhabited regions of the Horn of Africa, Ethiopia is the country where the majority of the clan reside. In Ethiopia, the Gadabuursi are mainly found in the Somali Region, but they also inhabit the Harar, Dire Dawa and Oromia Region, Oromia regions. In Somaliland, the Gadabuursi are the predominant clan of the Awdal Region.UN (1999) Somaliland: Update to SML26165.E of 14 February 1997 on the situation in Zeila, including who is controlling it, whether there is fighting in the area, and whether refugees are returning. "Gadabuursi clan dominates Awdal region. As a res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menelik II
Menelik II ( ; horse name Aba Dagnew (Amharic: አባ ዳኘው ''abba daññäw''); 17 August 1844 – 12 December 1913), baptised as Sahle Maryam (ሣህለ ማርያም ''sahlä maryam'') was king of Shewa from 1866 to 1889 and Emperor of Ethiopia from 1889 to his death in 1913. At the height of his internal power and external prestige, the process of Menelik II's conquests, territorial expansion and creation of the modern empire-state was largely completed by 1898.Zewde, Bahru. A history of Ethiopia: 1855–1991. 2nd ed. Eastern African studies. 2001 The Ethiopian Empire was transformed under Menelik: the major signposts of modernisation were put in place, with the assistance of key ministerial advisors. Externally, Menelik led Ethiopian troops against Kingdom of Italy, Italian invaders in the First Italo-Ethiopian War; following a decisive victory at the Battle of Adwa, recognition of Ethiopia's independence by external powers was expressed in terms of diplomatic representa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Of Ethiopia
The emperor of Ethiopia (, "King of Kings"), also known as the Atse (, "emperor"), was the hereditary monarchy, hereditary ruler of the Ethiopian Empire, from at least the 13th century until the abolition of the monarchy in 1975. The emperor was the head of state and head of government, with ultimate executive power, executive, judicial power, judicial and legislative power in that country. A ''National Geographic'' article from 1965 called Imperial Ethiopia "nominally a constitutional monarchy; in fact it was a benevolent dictatorship, benevolent autocracy". Title and style The title "King of Kings", often rendered imprecisely in English as "emperor", dates back to ancient Mesopotamia, but was used in Aksumite Empire, Axum by King Sembrouthes (). However, Yuri Kobishchanov dates this usage to the period following the Persian Empire, Persian victory over the Roman Empire, Romans in 296–297. The most notable pre-Solomonic usage of the title "Negusa Nagast" was by Ezana of Ax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |