|
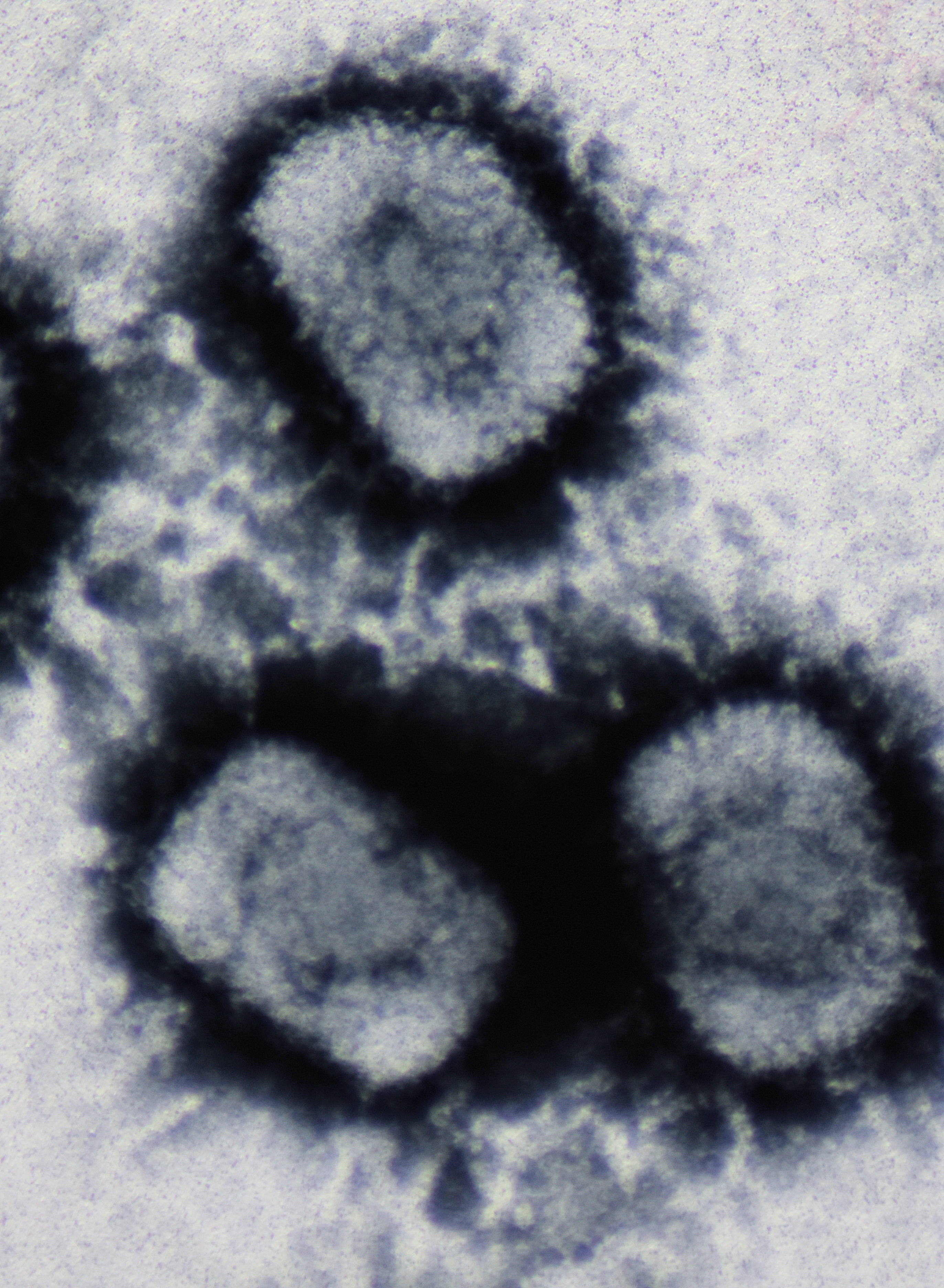
Escherichia Virus 186
''Escherichia virus 186'' is a virus of the family ''Myoviridae'', genus '' Eganvirus''. As a member of the group I of the Baltimore classification, ''Escherichia virus 186'' is a dsDNA virus. According to its family, Myoviridae, its morphology is nonenveloped and consist of a head and a tail separated by a neck and its genome is linear. The propagation of the virions includes the attaching to a host cell (a bacterium, as ''Escherichia virus 186'' is a bacteriophage) and the injection of the double stranded DNA; the host transcribes and translates it to manufacture new particles. To replicate its genetic content requires host cell DNA polymerases and, hence, the process is highly dependent on the cell cycle. Use as a model system Bacteriophage 186 has been studied as a model system for biological switches. The phage can enter two developmental lifecycles called the lytic cycle and lysogeny and knowledge into how the decision between the two developmental routes may extend to oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898, more than 16,000 of the millions of List of virus species, virus species have been described in detail. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent viral particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) genetic material, i.e., long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myoviridae
''Myoviridae'' was a family of bacteriophages in the order '' Caudovirales''. The family ''Myoviridae'' and order '' Caudovirales'' have now been abolished, with the term myovirus now used to refer to the morphology of viruses in this former family. Bacteria and archaea serve as natural hosts. There were 625 species in this family, assigned to eight subfamilies and 217 genera. Subdivisions The subfamily ''Tevenvirinae'' (synonym: ''Tequatrovirinae'') is named after its type species ''Enterobacteria phage T4''. Members of this subfamily are morphologically indistinguishable and have moderately elongated heads of about 110 nanometers (nm) in length, 114 nm long tails with a collar, base plates with short spikes and six long kinked tail fibers. The genera within this subfamily are divided on the basis of head morphology with the genus ''Tequatrovirus'' (Provisional name: ''T4virus'') having a head length of 137 nm and those in the genus ''Schizotequatrovirus'' being 111 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Committee On Taxonomy Of Viruses
The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) authorizes and organizes the taxonomic classification of and the nomenclature for viruses. The ICTV develops a universal taxonomic scheme for viruses, and thus has the means to appropriately describe, name, and classify every virus taxon. The members of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses are considered expert virologists. The ICTV was formed from and is governed by the Virology Division of the International Union of Microbiological Societies. Detailed work, such as identifying new taxa and delimiting the boundaries of species, genera, families, etc. typically is performed by study groups of experts in the families. History The International Committee on Nomenclature of Viruses (ICNV) was established in 1966, at the International Congress for Microbiology in Moscow, to standardize the naming of virus taxa. The ICVN published its first report in 1971. For viruses infecting vertebrates, the first report i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltimore Classification
Baltimore classification is a system used to classify viruses based on their manner of messenger RNA (mRNA) synthesis. By organizing viruses based on their manner of mRNA production, it is possible to study viruses that behave similarly as a distinct group. Seven Baltimore groups are described that take into consideration whether the viral genome is made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) or ribonucleic acid (RNA), whether the genome is single- or double-stranded, and whether the sense of a single-stranded RNA genome is positive or negative. Baltimore classification also closely corresponds to the manner of replicating the genome, so Baltimore classification is useful for grouping viruses together for both transcription and replication. Certain subjects pertaining to viruses are associated with multiple, specific Baltimore groups, such as specific forms of translation of mRNA and the host range of different types of viruses. Structural characteristics such as the shape of the viral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DsDNA Virus
A DNA virus is a virus that has a genome made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that is replicated by a DNA polymerase. They can be divided between those that have two strands of DNA in their genome, called double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses, and those that have one strand of DNA in their genome, called single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) viruses. dsDNA viruses primarily belong to two realms: ''Duplodnaviria'' and ''Varidnaviria'', and ssDNA viruses are almost exclusively assigned to the realm ''Monodnaviria'', which also includes some dsDNA viruses. Additionally, many DNA viruses are unassigned to higher taxa. Reverse transcribing viruses, which have a DNA genome that is replicated through an RNA intermediate by a reverse transcriptase, are classified into the kingdom '' Pararnavirae'' in the realm ''Riboviria''. DNA viruses are ubiquitous worldwide, especially in marine environments where they form an important part of marine ecosystems, and infect both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. They a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as regulatory sequences (see non-coding DNA), and often a substantial fraction of junk DNA with no evident function. Almost all eukaryotes have mitochondrial DNA, mitochondria and a small mitochondrial genome. Algae and plants also contain chloroplast DNA, chloroplasts with a chloroplast genome. The study of the genome is called genomics. The genomes of many organisms have been Whole-genome sequencing, sequenced and various regions have been annotated. The first genome to be sequenced was that of the virus φX174 in 1977; the first genome sequence of a prokaryote (''Haemophilus influenzae'') was published in 1995; the yeast (''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'') genome was the first eukaryotic genome to be sequenced in 1996. The Human Genome Project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterium
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit the air, soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria play a vital role in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients and the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in mutualistic, commensal and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteriophage
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a phage (), is a virus that infects and replicates within bacteria. The term is derived . Bacteriophages are composed of proteins that Capsid, encapsulate a DNA or RNA genome, and may have structures that are either simple or elaborate. Their genomes may encode as few as four genes (e.g. Bacteriophage MS2, MS2) and as many as hundreds of genes. Phages replicate within the bacterium following the injection of their genome into its cytoplasm. Bacteriophages are among the most common and diverse entities in the biosphere. Bacteriophages are ubiquitous viruses, found wherever bacteria exist. It is estimated there are more than 1031 bacteriophages on the planet, more than every other organism on Earth, including bacteria, combined. Viruses are the most abundant biological entity in the water column of the world's oceans, and the second largest component of biomass after prokaryotes, where up to 9x108 virus, virions per millilitre have b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Polymerases
A DNA polymerase is a member of a family of enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of DNA molecules from nucleoside triphosphates, the molecular precursors of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in groups to create two identical DNA duplexes from a single original DNA duplex. During this process, DNA polymerase "reads" the existing DNA strands to create two new strands that match the existing ones. These enzymes catalyze the chemical reaction : deoxynucleoside triphosphate + DNAn pyrophosphate + DNAn+1. DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the three prime (3')-end of a DNA strand, one nucleotide at a time. Every time a cell divides, DNA polymerases are required to duplicate the cell's DNA, so that a copy of the original DNA molecule can be passed to each daughter cell. In this way, genetic information is passed down from generation to generation. Before replication can take place, an enzyme called helicase unwinds the DNA molecule from its tightl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambda Phage
Lambda phage (coliphage λ, scientific name ''Lambdavirus lambda'') is a bacterial virus, or bacteriophage, that infects the bacterial species ''Escherichia coli'' (''E. coli''). It was discovered by Esther Lederberg in 1950. The wild type of this virus has a Temperate (virology), temperate life cycle that allows it to either reside within the genome of its host through lysogeny or enter into a lytic phase, during which it kills and lyses the cell to produce offspring. Lambda strains, mutated at specific sites, are unable to lysogenize cells; instead, they grow and enter the lytic cycle after superinfecting an already lysogenized cell. The phage particle consists of a head (also known as a capsid), a tail, and tail fibers (see image of virus below). The head contains the phage's double-strand linear DNA genome. During infections, the phage particle recognizes and binds to its host, ''E. coli'', causing DNA in the head of the phage to be ejected through the tail into the cytopla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SOS Response
The SOS response is a global transcriptional response to DNA damage in prokaryotes, in which the cell cycle is arrested and DNA repair mechanisms (error-free as well as error-prone) are induced. The regulation of this response is driven by two proteins, RecA and LexA. The RecA protein, stimulated by single-stranded DNA, is involved in the inactivation of the repressor ( LexA) of SOS response genes thereby inducing the response. It is an error-prone repair system that contributes significantly to DNA changes observed in a wide range of bacterial species. Discovery The SOS response was articulated by Evelyn Witkin. Later, by characterizing the phenotypes of mutagenised ''E. coli'', she and post doctoral student Miroslav Radman detailed the SOS response to UV radiation in bacteria. The SOS response to DNA damage was a seminal discovery because it was the first coordinated stress response to be elucidated. Mechanism During normal growth, the SOS genes are under the repressor of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |