|
Eritrean Defence Forces
The Eritrean Defence Forces (EDF) ( قوات البحرية الارترية) are the combined military forces of Eritrea composed of three branches: Eritrean Army, Eritrean Air Force and Eritrean Navy. The Army is by far the largest, followed by the Air Force and Navy. The Commander-in-Chief of the EDF is the President of Eritrea. Their military role stems from Eritrea's strategic geographical location, located on the Red Sea with a foothold on the Bab-el-Mandeb strait. History Pre-independence Military history in Eritrea stretches back for thousands of years; from ancient times to present day, the society of the Eritreans have dealt with both war and peace. During the kingdom of Medri Bahri, the military fought numerous battles against the invading forces of the Abyssinians to the south and the Ottoman Turks at the Red Sea. During the 16th century, the port of Massawa was used by the Ottomans to protect sea lanes from disruption, while more recently it was used by the I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eritrean Army
The Eritrean Army is the main branch of the Eritrean Defence Forces and is one of the largest armies in Africa. The main role of the army in Eritrea is defense from external aggressors, border security, and developing national cohesion. Historically, the predecessor of the Eritrean Army, the Eritrean People's Liberation Front (EPLF), played a major role in establishing and defending the country's independence from Ethiopia in 1991 during the Eritrean War of Independence. Since then, the army has continued to be involved in low-level border conflicts with Ethiopia and several other neighbors, including Djibouti and Yemen, with the most notable one being the Ethiopian-Eritrean War from 1998 until 2000, which ended in a partial Ethiopian military victory and Eritrean boundary line victory. It is widely regarded as one of the largest armies in Africa, despite the country having a smaller population than most of its neighbors with around 250,000 to 300,000 personnel due to mandatory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanish Islands Conflict
The Hanish Islands conflict was a dispute between Yemen and Eritrea over the island of Greater Hanish in the Red Sea, one of the largest in the then disputed Zukur-Hanish archipelago. Fighting took place over three days from 15 December to 17 December 1995. In 1998 the Permanent Court of Arbitration determined that the territory belonged to Yemen. Background The archipelago is on the southern side of the Red Sea near Bab-el-Mandeb (Mouth of the Red Sea). The Red Sea is about 60 miles (100 km) wide at this point. Since the time of the British protectorate of Aden, the islands had generally been regarded as part of Yemen. After being granted independence and membership of the United Nations, the new Eritrean government started negotiations with Yemen over the status of the archipelago. Two rounds of talks had taken place before the invasion: Greater Hanish (or ''Hanish al-Kabir'') is one of three main islands in an archipelago, and until 1995, it was inhabited only by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medri Bahri
Medri Bahri ( Tigrinya: ምድሪ ባሕሪ, English: ''Land of the Sea'') or Mereb Melash (Tigrinya: መረብ ምላሽ, English: ''Beyond the Mereb''), also known as Baharanegash, Ma'ikele Bahr or Bambolo Melash was a semi-autonomous province of the Ethiopian Empire ruled by the ''Bahr Negash''. This province was located north of the Mareb River and west of the Bur Province, in the Eritrean highlands ( Kebassa) and some surrounding areas, mainly comprising the historical provinces of Hamasien and Seraye. History According to historian Richard Pankhurst it was during the reign of Emperor Zara Yaqob (r. 1433–1468) when the title ''Bahr Negash'' ("Ruler of the sea") appeared for the first time. However, it also appears in an obscure land grant of the Zagwe King Tatadim, who ruled during the 11th century. He considered the unnamed Bahr Negash as one of his ''seyyuman'' or "appointed ones". Zara Yaqob's chronicle explains how he, after arriving to the region, put much effort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bab-el-Mandeb
The Bab-el-Mandeb (), the Gate of Grief or the Gate of Tears, is a strait between Yemen on the Arabian Peninsula and Djibouti and Eritrea in the Horn of Africa. It connects the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden and by extension the Indian Ocean. Etymology In "Bab-el-Mandeb", "Bab" means "gate" while "Mandeb" means "lamentation" or "grief". The strait derives its name from the dangers attending its navigation or, according to an Arab legend, from the numbers who were drowned by an earthquake that separated the Arabian Peninsula from the Horn of Africa. History Paleo-environmental and tectonic events in the Miocene epoch created the Danakil Isthmus, a land bridge forming a broad connection between Yemen and Ethiopia. During the last 100,000 years, eustatic sea level fluctuations have led to alternate opening and closing of the straits. According to the recent single origin hypothesis, the straits of Bab-el-Mandeb were probably witness to the earliest migrations of modern humans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Sea
The Red Sea is a sea inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez—leading to the Suez Canal. It is underlain by the Red Sea Rift, which is part of the Great Rift Valley. The Red Sea has a surface area of roughly , is about long, and wide at its widest point. It has an average depth of , and in the central Suakin Trough, it reaches its maximum depth of . Approximately 40% of the Red Sea is quite shallow at less than deep and about 25% is less than deep. The extensive shallow shelves are noted for their marine life and corals. More than 1,000 invertebrate species and 200 types of soft and hard coral live in the sea. The Red Sea is the world's northernmost tropical sea and has been designated a Global 200 ecoregion. Extent The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eritrea
Eritrea, officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa, with its capital and largest city being Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia in the Eritrea–Ethiopia border, south, Sudan in the west, and Djibouti in the southeast. The northeastern and eastern parts of Eritrea have an extensive coastline along the Red Sea. The nation has a total area of approximately , and includes the Dahlak Archipelago and several of the Hanish Islands. Hominid remains found in Eritrea have been dated to 1 million years old and anthropological research indicates that the area may contain significant records related to the evolution of humans. The Kingdom of Aksum, covering much of modern-day Eritrea and Tigray Region, northern Ethiopia, was established during the first or second century AD.Henze, Paul B. (2005) ''Layers of Time: A History of Ethiopia'', . It adopted Eritrean Orthodox Church, Christianity around the middle of the fourth century. Beginning in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Ranks Of Eritrea
The Military ranks of Eritrea are the military insignia used by the Eritrean Defence Forces. Commissioned officer ranks The rank insignia of commissioned officers. Other ranks The rank insignia of non-commissioned officers and enlisted personnel. References External links * {{Military ranks by country Eritrea Eritrea, officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa, with its capital and largest city being Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia in the Eritrea–Ethiopia border, south, Sudan in the west, and Dj ... Military of Eritrea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethiopian Civil Conflict (2018–present)
The ongoing Ethiopian civil conflict began with the 2018 dissolution of the Ethiopian People's Revolutionary Democratic Front (EPRDF), an ethnic federalism, ethnic federalist, Dominant-party system, dominant party political coalition. After the Eritrean–Ethiopian border conflict, 20-year border conflict between Ethiopia and Eritrea, a decade of internal tensions, 2014–2016 Oromo protests, two years of protests, and a 2016–2018 Ethiopian state of emergency, state of emergency, Hailemariam Desalegn Resignation of Hailemariam Desalegn, resigned on 15 February 2018 as prime minister and EPRDF chairman, and there were hopes of peace under his successor Abiy Ahmed. However, Tigray war, war broke out in the Tigray Region, with resurgent regional and ethnic factional attacks throughout Ethiopia. The civil wars caused substantial human rights violations, war crimes, and extrajudicial killings. In March 2018, the EPRDF nominated Abiy Ahmed to succeed Desalegn, and he was made Prime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Tsorona
The Battle of Tsorona was an engagement between the Eritrean and the Ethiopian armies fought near the border town of Tsorona. Eritrean government statements identified Ethiopian armed forces as the aggressors and the Ethiopian government using a smokescreen of propaganda to justify the attack. Background Relations between Eritrea and Ethiopia have been brittle and tensions between the two countries have remained high after both countries fought each other in the Eritrean–Ethiopian War which lasted from 1998 to 2000, and since the end of the war there have been a number of small border skirmishes between the two countries using small arms, however the 2016 engagement utilized "medium- and long-range artillery". Battle Eritrean claims According to the Eritrean Information Ministry, Ethiopian forces attacked Eritrean troops at Tsorona on Sunday, June 12, 2016. After an overnight battle, the troops were repelled on Monday, June 13, 2016. Ethiopian forces quickly withdrew b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2013 Eritrean Army Mutiny
The 2013 Eritrean Army mutiny was mounted on 21 January 2013, when around 100 to 200 soldiers of the Eritrean Army in the capital city, Asmara, seized the headquarters of the state broadcaster, EriTV, and allegedly broadcast a message demanding reforms and the release of political prisoners. The mutiny was the first major incident of resistance to the rule of Isaias Afwerki since the purging of a group of fifteen ministers who demanded political reform in 2001. Details about the mutiny remain murky, with several (but not all) government officials denying it even took place, while opposition sources claimed it had been an abortive coup attempt. Background At the time of the mutiny, Eritrea had been ruled by Isaias Afwerki for two decades since its independence in 1993 from Ethiopia, following a 30-year war for independence. Initially allied with Ethiopian Prime Minister Meles Zenawi and his Tigray People's Liberation Front, whom Isaias' Eritrean People's Liberation Front had he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
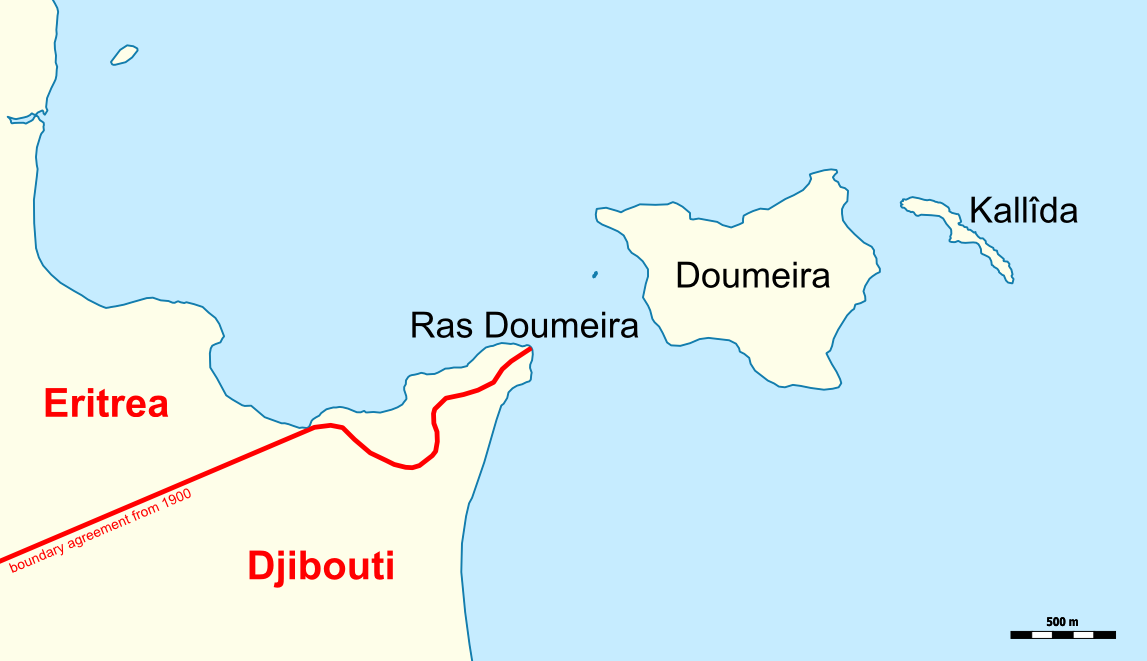
Djiboutian–Eritrean Border Conflict
The Djiboutian–Eritrean border conflict was a border conflict between the forces of Djibouti and Eritrea that occurred between June 10 and June 13, 2008.Other name combinations are also used for this conflict which is also described as a ''war'', ''border war'', and ''dispute'', including Eritrean-Djiboutian conflict, Eritrea-Djibouti war and Djibouti-Eritrea dispute It was triggered by tension which began on April 16, 2008, when Djibouti reported that Eritrean armed forces had penetrated into Djibouti and dug trenches on both sides of the border. The crisis deepened when armed clashes broke out between the two armed forces in the border area on June 10, 2008. During the conflict, France provided logistical, medical and intelligence support to Djibouti, but did not participate in direct combat. Background The currently in force 1900 boundary agreement specifies that the international boundary starts at ''Cape Doumeira'' (Ras Doumeira) at the Red Sea and runs for 1.5 km alo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |