|
Era Of Fragmentation
The Era of Fragmentation () was an era of disunity in Tibetan history lasting from the death of the Tibetan Empire's last emperor, Langdarma, in 842 until Drogön Chögyal Phagpa became the Imperial Preceptor of the three regions of Tibet in 1253, following the Mongol conquest in the 1240s. During this period, the political unity of the Tibetan Empire collapsed following a civil war between Yumtän (''Yum brtan'') and Ösung (''’Od-srung''), after which followed numerous rebellions against the remnants of imperial Tibet and the rise of regional warlords. Civil war and the decline of imperial Tibet The last king of the unified Tibetan Empire, Langdarma, was assassinated in 842 possibly by a Buddhist hermit monk named Pelgyi Dorje of Lhalung, or other sources state he died from fright. The death left two possible heirs, the two princes Yumtän and Ösung, that fought for the throne and initiated a civil war. This civil war weakened the political authority of the Tibetan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Era Of Fragmentation
The Era of Fragmentation () was an era of disunity in history of Tibet, Tibetan history lasting from the death of the Tibetan Empire's last emperor, Langdarma, in 842 until Drogön Chögyal Phagpa became the Imperial Preceptor of the three regions of Tibet in 1253, following the Mongol invasions of Tibet, Mongol conquest in the 1240s. During this period, the political unity of the Tibetan Empire collapsed following a civil war between Yumtän (''Yum brtan'') and Ösung (''’Od-srung''), after which followed numerous rebellions against the remnants of imperial Tibet and the rise of regional warlords. Civil war and the decline of imperial Tibet The last king of the unified Tibetan Empire, Langdarma, was assassinated in 842 possibly by a Buddhist hermit monk named Pelgyi Dorje of Lhalung, or other sources state he died from fright. The death left two possible heirs, the two princes Yumtän and Ösung, that fought for the throne and initiated a civil war. This civil war weakene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
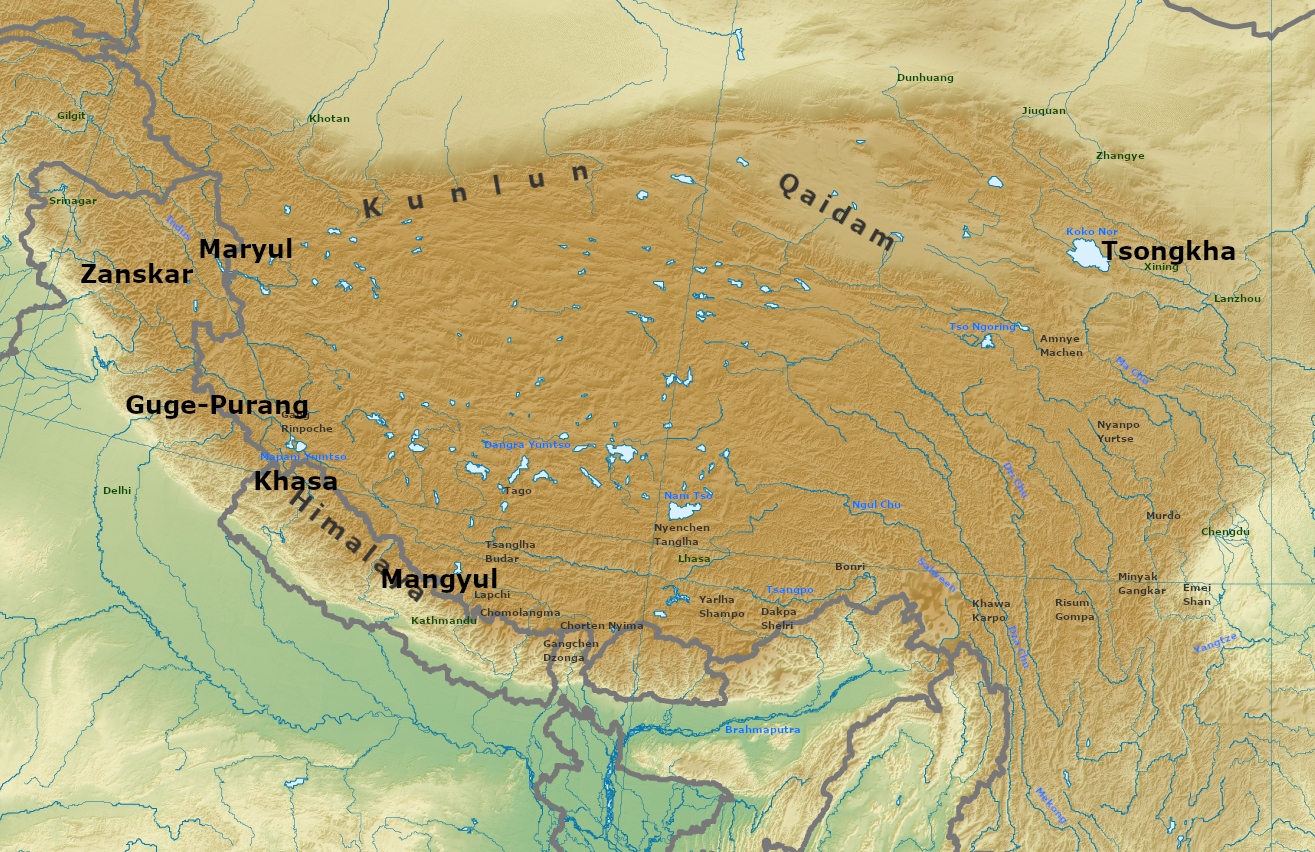
Guge
Guge () was an ancient dynastic kingdom in Western Tibet. The kingdom was centered in present-day Zanda County, Ngari Prefecture, Tibet Autonomous Region. At various points in history after the 10th century AD, the kingdom held sway over a vast area including south-eastern Zanskar, Kinnaur district, and Spiti Valley, either by conquest or as tributaries. The ruins of the former capital of the Guge kingdom are located at Tsaparang in the Sutlej valley, not far from Mount Kailash and west from Lhasa. History Founding Guge was founded in the 10th century. Its capitals were located at Tholing and Tsaparang. Kyide Nyimagon, a great-grandson of Langdarma, the last monarch of the Tibetan Empire, fled to Ngari Prefecture, Ngari (West Tibet) from the insecure conditions in Ü-Tsang in 910. He established a kingdom around 912, annexing Burang County, Purang and Guge. He established his capital in Guge. Nyimagon later divided his lands into three parts. The king's eldest son Lhachen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
11th Century In Tibet
In music theory, an eleventh is a compound interval consisting of an octave plus a fourth. A perfect eleventh spans 17 and the augmented eleventh 18 semitones, or 10 steps in a diatonic scale. Since there are only seven degrees in a diatonic scale, the eleventh degree is the same as the subdominant (IV). The eleventh is considered highly dissonant with the major third. An eleventh chord is the stacking of five thirds in the span of an eleventh. In common practice tonality, it usually had subdominant function as minor eleventh chord on the second degree (supertonic) of the major scale. See also *Eleventh chord *Extended chord In music, extended chords are certain Chord (music), chords (built from third (chord), thirds) or triad (music), triads with notes ''extended'', or added, beyond the seventh (chord), seventh. Ninth chord, Ninth, Eleventh chord, eleventh, and T ... References Chord factors Fourths (music) Compound intervals {{music-theory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10th Century In Tibet
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In mathematics The number 1 is the first natural number after 0. Each natural number, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Tibet By Period
History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some theorists categorize history as a social science, while others see it as part of the humanities or consider it a hybrid discipline. Similar debates surround the purpose of history—for example, whether its main aim is theoretical, to uncover the truth, or practical, to learn lessons from the past. In a more general sense, the term ''history'' refers not to an academic field but to the past itself, times in the past, or to individual texts about the past. Historical research relies on primary and secondary sources to reconstruct past events and validate interpretations. Source criticism is used to evaluate these sources, assessing their authenticity, content, and reliability. Historians strive to integrate the perspectives of several sources to develop a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Historical Atlas Of Tibet
''A Historical Atlas of Tibet'' is an atlas and a topographical book by Karl E. Ryavec. Overview From the Paleolithic and Neolithic periods up to the present day (2015), this book documents the cultural and religious sites that can be found across the Tibetan Plateau and the regions that border it. It talks about the five most important times in Tibetan history and gives 49 maps and information about Tibetan areas in the west, the middle, and the east. Reception Writing for the ''Geographical Review'', Emily T. Yeh, Professor of Geography at the University of Colorado Boulder suggests that the book "he bookis a stunning achievement. Gorgeously designed, with forty-nine original maps and many more photographs of artwork, temples, and historical and contemporary landscapes." In a review for ''Himalayan Journal,'' Christian Jahoda of Austrian Academy of Sciences writes, "What makes this book so valuable and unique is, first, the fact that the focus is on Tibet as a cultural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Song–Tibet Relations
The history of the relationship between the Song dynasty (960–1279) of China and Tibetan regimes during the Era of Fragmentation is a diplomatic history between imperial China and Tibet. Unlike the preceding Tang–Tibet relations in which both parties were military powers, the Song–Tibet relations were ones of relative peace and cultural creativity. History The Song dynasty was established in 960 A.D. Although the military power of this new empire was not as strong as the previous Tang dynasty had been, and it rarely contacted the Tibetan tribes of Ü-Tsang who dwelled far from the Han, it did keep in touch with Tibetan tribes living in Gansu, Qinghai and Yunnan province where Han Chinese people were also domiciled. Not long after the establishment of the Song dynasty, a Tibetan tribe leader named Gusiluo set up a regime in the Huangshui basin centered on Miaochuan (now Ledu) and Qingtang (now Xining) and defended it from an attack by the kingdom of Western Xia launche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ladakh Chronicles
The ''Ladakh Chronicles'', or ''La-dvags-rgyal-rabs'' (), is a historical work that covers the history of Ladakh from the beginnings of the first Tibetan dynasty of Ladakh until the end of the Namgyal dynasty. The chronicles were compiled by the Namgyal dynasty, mostly during the 17th century, and are considered the primary written source for Ladakhi history. It remains one of only two surviving pre-19th century literary sources from Ladakh. Only seven original manuscripts of the chronicles are known to have existed, of which two survive today. Background Until the early 19th century, European historians believed that there were no written histories from Ladakh. After reports to the contrary, Alexander Cunningham found the first known manuscript of the chronicles (''Ms. Cunningham'') during his stay in Ladakh in 1847. The origin, intent, and time of the authorship of the ''Ladakh Chronicles'' remains unknown to modern historians. It remains one of only two surviving pre-19th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amdo
Amdo ( �am˥˥.to˥˥ zh , c = 安多 , p = Ānduō ), also known as Domey (), is one of the three traditional Tibetan regions. It encompasses a large area from the Machu (Yellow River) to the Drichu (Yangtze). Amdo is mostly coterminous with China's present-day Qinghai province, but also includes small portions of Sichuan and Gansu provinces. In the 7th century, Amdo became a part of the Tibetan Empire until its dissolution in the 9th century. A local Tibetan theocracy called Tsongkha ruled the region from 997 to 1104. In the 13th century, Mongol forces conquered the area, which led to the beginning of a priest and patron relationship. From the 14th to the 16th century, the Ming Dynasty controlled some border areas of Amdo while Mongol presence remained significant. In the 1720s, the Yongzheng Emperor of Qing dynasty seized Amdo from the Dzungars and began forming the modern boundaries of Qinghai. He allowed most of the area to be administered by a series of local Tibet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibet Under Yuan Rule
Tibet under Yuan rule refers to the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty's rule over Tibet from approximately 1270 to 1354. During the Yuan dynasty, Tibet was administered by an organization that was structurally, militarily and administratively subordinate to the Yuan court. Tibet was conquered by the Mongols led by a general titled ''doord darkhan'' in 1240 and Mongol rule was established after Sakya Pandita obtained power over Tibet through the Mongols in 1244. This period and administration has been called the Sakya dynasty (, ) after the favored Sakya school of Tibetan Buddhism. The region retained a degree of political autonomy under the Sakya lama, who was the ''de jure'' head of Tibet and a spiritual leader of the Mongol Empire under the priest and patron relationship. However, administrative and military rule of Tibet remained under the auspices of the Yuan government agency known as the Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs (''Xuanzheng Yuan''), a top-level administrative depa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |