|
Epipelagic
The photic zone (or euphotic zone, epipelagic zone, or sunlight zone) is the uppermost layer of a body of water that receives sunlight, allowing phytoplankton to perform photosynthesis. It undergoes a series of physical, chemical, and biological processes that supply nutrients into the upper water column. The photic zone is home to the majority of aquatic life due to the activity ( primary production) of the phytoplankton. The thicknesses of the photic and euphotic zones vary with the intensity of sunlight as a function of season and latitude and with the degree of water turbidity. The bottommost, or aphotic, zone is the region of perpetual darkness that lies beneath the photic zone and includes most of the ocean waters. Photosynthesis in photic zone In the photic zone, the photosynthesis rate exceeds the respiration rate. This is due to the abundant solar energy which is used as an energy source for photosynthesis by primary producers such as phytoplankton. These phytopla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Column
The (oceanic) water column is a concept used in oceanography to describe the physical (temperature, salinity, light penetration) and chemical ( pH, dissolved oxygen, nutrient salts) characteristics of seawater at different depths for a defined geographical point. Generally, vertical profiles are made of temperature, salinity, chemical parameters at a defined point along the water column. The water column is the largest, yet one of the most under-explored, habitats on the planet; it is explored to better understand the ocean as a whole, including the huge biomass that lives there and its importance to the global carbon and other biogeochemical cycles. Studying the water column also provides understanding on the links between living organisms and environmental parameters, large-scale water circulation and the transfer of matter between water masses. Water columns are used chiefly for environmental studies evaluating the stratification or mixing of thermal or chemically stratif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
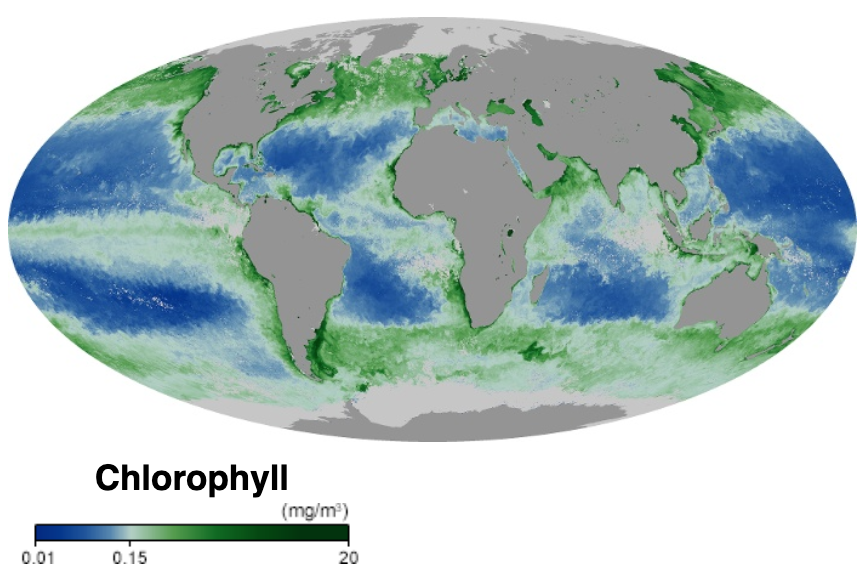
Marine Primary Production
Marine primary production is the chemical synthesis in the ocean of organic compounds from atmospheric or dissolved carbon dioxide. It principally occurs through the process of photosynthesis, which uses light as its source of energy, but it also occurs through chemosynthesis, which uses the oxidation or reduction of inorganic chemical compounds as its source of energy. Almost all life on Earth relies directly or indirectly on primary production. The organisms responsible for primary production are called primary producers or autotrophs. Most marine primary production is generated by a diverse collection of marine microorganisms called algae and cyanobacteria. Together these form the principal primary producers at the base of the ocean food chain and produce half of the world's oxygen. Marine primary producers underpin almost all marine animal life by generating nearly all of the oxygen and food marine animals need to exist. Some marine primary producers are also ecosystem eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zooplankton
Zooplankton are the heterotrophic component of the planktonic community (the " zoo-" prefix comes from ), having to consume other organisms to thrive. Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents. Consequently, they drift or are carried along by currents in the ocean, or by currents in seas, lakes or rivers. Zooplankton can be contrasted with phytoplankton (cyanobacteria and microalgae), which are the plant-like component of the plankton community (the " phyto-" prefix comes from , although taxonomically ''not'' plants). Zooplankton are heterotrophic (other-feeding), whereas phytoplankton are autotrophic (self-feeding), often generating biological energy and macromolecules through chlorophyllic carbon fixation using sunlightin other words, zooplankton cannot manufacture their own food, while phytoplankton can. As a result, zooplankton must acquire nutrients by feeding on other organisms such as phytoplankton, which are generally smaller t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Of Water
A body of water or waterbody is any significant accumulation of water on the surface of Earth or another planet. The term most often refers to oceans, seas, and lakes, but it includes smaller pools of water such as ponds, wetlands, or more rarely, puddles. A body of water does not have to be still or contained; rivers, streams, canals, and other Landform, geographical features where water moves from one place to another are also considered bodies of water. Most are naturally occurring and massive geographical features, but some are artificial. There are types that can be either. For example, most reservoirs are created by engineering dams, but some natural lakes are used as reservoirs. Similarly, most harbors are naturally occurring bays, but some harbors have been created through construction. Bodies of water that are Navigability, navigable are known as waterways. Some bodies of water collect and move water, such as rivers and streams, and others primarily hold water, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptomonad
The cryptomonads (or cryptophytes) are a superclass of algae, most of which have plastids. They are traditionally considered a division of algae among phycologists, under the name of Cryptophyta. They are common in freshwater, and also occur in marine and brackish habitats. Each cell is around 10–50 μm in size and flattened in shape, with an anterior groove or pocket. At the edge of the pocket there are typically two slightly unequal flagella. Some may exhibit mixotrophy. They are classified as superclass Cryptomonada, which is divided into two classes: heterotrophic Goniomonadea and phototrophic Cryptophyceae. The two groups are united under three shared morphological characteristics: presence of a periplast, ejectisomes with secondary scroll, and mitochondrial cristae with flat tubules. Genetic studies as early as 1994 also supported the hypothesis that ''Goniomonas'' was sister to Cryptophyceae. A study in 2018 found strong evidence that the common ancestor of Crypto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbidity
Turbidity is the cloudiness or haziness of a fluid caused by large numbers of individual particles that are generally invisible to the naked eye, similar to smoke in air. The measurement of turbidity is a key test of both water clarity and water quality. Fluids can contain suspended solid matter consisting of particles of many different sizes. While some suspended material will be large enough and heavy enough to settle rapidly to the bottom of the container if a liquid sample is left to stand (the settable solids), very small particles will settle only very slowly or not at all if the sample is regularly agitated or the particles are colloidal. These small solid particles cause the liquid to appear turbid. Turbidity (or haze) is also applied to transparent solids such as glass or plastic. In plastic production, haze is defined as the percentage of light that is deflected more than 2.5° from the incoming light direction. Causes and effects Turbidity in open water may be ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attenuation
In physics, attenuation (in some contexts, extinction) is the gradual loss of flux intensity through a Transmission medium, medium. For instance, dark glasses attenuate sunlight, lead attenuates X-rays, and water and air attenuate both light and sound at variable attenuation rates. Hearing protection device, Hearing protectors help reduce Sound power, acoustic flux from flowing into the ears. This phenomenon is called acoustic attenuation and is measured in decibels (dBs). In electrical engineering and telecommunications, attenuation affects the Wave propagation, propagation of waves and signals in electrical circuits, in optical fibers, and in air. Attenuator (electronics), Electrical attenuators and optical attenuators are commonly manufactured components in this field. Background In many cases, attenuation is an exponential function of the path length through the medium. In optics and in chemical spectroscopy, this is known as the Beer–Lambert law. In engineering, attenu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Penetration Spectrum In Water 01
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 terahertz. The visible band sits adjacent to the infrared (with longer wavelengths and lower frequencies) and the ultraviolet (with shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies), called collectively '' optical radiation''. In physics, the term "light" may refer more broadly to electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength, whether visible or not. In this sense, gamma rays, X-rays, microwaves and radio waves are also light. The primary properties of light are intensity, propagation direction, frequency or wavelength spectrum, and polarization. Its speed in vacuum, , is one of the fundamental constants of nature. All electromagnetic radiation exhibits some properties of both particles and waves. Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ekman Transport
Ekman transport is part of Ekman motion theory, first investigated in 1902 by Vagn Walfrid Ekman. Winds are the main source of energy for ocean circulation, and Ekman transport is a component of wind-driven ocean current. Ekman transport occurs when ocean surface waters are influenced by the friction force acting on them via the wind. As the wind blows it casts a friction force on the ocean surface that drags the upper 10-100m of the water column with it. However, due to the influence of the Coriolis force, Coriolis effect, as the ocean water moves it is subject to a force at a 90° angle from the direction of motion causing the water to move at an angle to the wind direction. The direction of transport is dependent on the hemisphere: in the Northern Hemisphere, northern hemisphere, transport veers clockwise from wind direction, while in the Southern Hemisphere, southern hemisphere it veers anticlockwise.Colling, pp 42-44 This phenomenon was first noted by Fridtjof Nansen, who reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbulence
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is fluid motion characterized by chaotic changes in pressure and flow velocity. It is in contrast to laminar flow, which occurs when a fluid flows in parallel layers with no disruption between those layers. Turbulence is commonly observed in everyday phenomena such as surf, fast flowing rivers, billowing storm clouds, or smoke from a chimney, and most fluid flows occurring in nature or created in engineering applications are turbulent. Turbulence is caused by excessive kinetic energy in parts of a fluid flow, which overcomes the damping effect of the fluid's viscosity. For this reason, turbulence is commonly realized in low viscosity fluids. In general terms, in turbulent flow, unsteady vortices appear of many sizes which interact with each other, consequently drag due to friction effects increases. The onset of turbulence can be predicted by the dimensionless Reynolds number, the ratio of kinetic energy to viscous damping ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatial Distribution
A spatial distribution in statistics is the arrangement of a phenomenon across the Earth's surface and a graphical display of such an arrangement is an important tool in geographical and environmental statistics. A graphical display of a spatial distribution may summarize raw data directly or may reflect the outcome of a more sophisticated data analysis. Many different aspects of a phenomenon can be shown in a single graphical display by using a suitable choice of different colours to represent differences. One example of such a display could be observations made to describe the geographic patterns of features, both physical and human across the earth. The information included could be where units of something are, how many units of the thing there are per units of area, and how sparsely or densely packed they are from each other. Patterns of spatial distribution Usually, for a phenomenon that changes in space, there is a pattern that determines the location of the subject o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nekton
Nekton or necton (from the ) is any aquatic organism that can actively and persistently propel itself through a water column (i.e. swimming) without touching the bottom. Nektons generally have powerful tails and appendages (e.g. fins, pleopods, flippers or jet propulsion) that make them strong enough swimmers to counter ocean currents, and have mechanisms for sufficient lift and/or buoyancy to prevent sinking. Examples of extant nektons include most fish (especially pelagic fish like tuna and sharks), marine mammals (cetaceans, sirenias and pinnipeds) and reptiles (specifically sea turtles), penguins, coleoid cephalopods (squids and cuttlefish) and several species of decapod crustaceans (specifically prawns, shrimps and krills). The term was proposed by German biologist Ernst Haeckel to differentiate between the active swimmers in a body of water, and the planktons that were passively carried along by the current. As a guideline, nektonic organisms have a high Reynolds numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |