|
Environmental Policy Of The Harper Government
Several policies regarding interior and domestic issues in Canada were planned and adopted by the Cabinet of Canadian Prime Minister Stephen Harper, after he came to office as the head of a minority government on February 6, 2006. At the beginning of the government's appointment, five policy priorities were identified in the areas of federal accountability, tax reform, crime, child care and health care. Economic policy Tax Policy A major policy goal of Stephen Harper was to reduce taxes. During his 10 years in government, Harper reduced income taxes, corporate taxes, and the Goods and services tax (Canada), GST. His cuts were both Progressive tax, progressive and Regressive tax, regressive. Goods and services tax On July 1, 2006, the Government of Canada reduced the Goods and services tax (Canada), Goods and services tax by 1 percentage point (to 6%), as promised by the Conservative Party of Canada in the 2006 Canadian federal election campaign. They again lowered it to 5%, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabinet Of Canada
The Cabinet of Canada (french: Cabinet du Canada) is a body of ministers of the Crown that, along with the Canadian monarch, and within the tenets of the Westminster system, forms the government of Canada. Chaired by the prime minister, the Cabinet is a committee of the King's Privy Council for Canada and the senior echelon of the Ministry, the membership of the Cabinet and ministry often being co-terminal; there were no members of the latter who were not also members of the former. For practical reasons, the Cabinet is informally referred to either in relation to the prime minister in charge of it or the number of ministries since Confederation. The current cabinet is the Cabinet of Justin Trudeau, which is part of the 29th Ministry. The interchangeable use of the terms ''cabinet'' and '' ministry'' is a subtle inaccuracy that can cause confusion. Composition King-in-Council The Government of Canada, formally referred to as '' His Majesty's Government'', is defined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earned Income Tax Credit
The United States federal earned income tax credit or earned income credit (EITC or EIC) is a refundable tax credit for low- to moderate-income working individuals and couples, particularly those with children. The amount of EITC benefit depends on a recipient's income and number of children. Low income adults with no children are eligible. For a person or couple to claim one or more persons as their qualifying child, requirements such as relationship, age, and shared residency must be met.Tax Year 2020 1040 and 1040-SR Instructions, including the instructions for Schedules 1 through 3 Rules for EIC begin on page 40 for 2020 Tax Year. EITC phases in slowly, has a medium-length plateau, and phases out more slowly than it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Recession
The Great Recession was a period of marked general decline, i.e. a recession, observed in national economies globally that occurred from late 2007 into 2009. The scale and timing of the recession varied from country to country (see map). At the time, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) concluded that it was the most severe economic and financial meltdown since the Great Depression. One result was a serious disruption of normal international relations. The causes of the Great Recession include a combination of vulnerabilities that developed in the financial system, along with a series of triggering events that began with the bursting of the United States housing bubble in 2005–2012. When housing prices fell and homeowners began to abandon their mortgages, the value of mortgage-backed securities held by investment banks declined in 2007–2008, causing several to collapse or be bailed out in September 2008. This 2007–2008 phase was called the subprime mortgage crisis. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hibernia
''Hibernia'' () is the Classical Latin name for Ireland. The name ''Hibernia'' was taken from Greek geographical accounts. During his exploration of northwest Europe (c. 320 BC), Pytheas of Massalia called the island ''Iérnē'' (written ). In his book ''Geographia'' (c. 150 AD), Claudius Ptolemaeus ("Ptolemy") called the island ''Iouerníā'' (written , where "ου"/''ou'' stands for ''w''). The Roman historian Tacitus, in his book '' Agricola'' (c. 98 AD), uses the name Hibernia. ''Iouerníā'' was a Greek rendering of the Q-Celtic name *''Īweriū'', from which eventually arose the Irish names '' Ériu'' and '' Éire''. The name was altered in Latin (influenced by the word '' hībernus'') as though it meant "land of winter", although the word for winter began with a long 'i'. Post-Roman usage The High King Brian Boru (c. 941–1014) based his title on being Emperor of the Scoti, which was in Latin ''Imperator Scottorum'', emperor of the Gaels. From 1172, the Lord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royalties
A royalty payment is a payment made by one party to another that owns a particular asset, for the right to ongoing use of that asset. Royalties are typically agreed upon as a percentage of gross or net revenues derived from the use of an asset or a fixed price per unit sold of an item of such, but there are also other modes and metrics of compensation.Guidelines for Evaluation of Transfer of Technology Agreements, United Nations, New York, 1979 A royalty interest is the right to collect a stream of future royalty payments. A license agreement defines the terms under which a resource or property are licensed by one party to another, either without restriction or subject to a limitation on term, business or geographic territory, type of product, etc. License agreements can be regulated, particularly where a government is the resource owner, or they can be private contracts that follow a general structure. However, certain types of franchising, franchise agreements have comparable p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan ( ; ) is a province in western Canada, bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and on the south by the U.S. states of Montana and North Dakota. Saskatchewan and Alberta are the only landlocked provinces of Canada. In 2022, Saskatchewan's population was estimated at 1,205,119. Nearly 10% of Saskatchewan’s total area of is fresh water, mostly rivers, reservoirs and lakes. Residents primarily live in the southern prairie half of the province, while the northern half is mostly forested and sparsely populated. Roughly half live in the province's largest city Saskatoon or the provincial capital Regina. Other notable cities include Prince Albert, Moose Jaw, Yorkton, Swift Current, North Battleford, Melfort, and the border city Lloydminster. English is the primary language of the province, with 82.4% of Saskatchewanians speaking English as their first language. Saska ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-secondary Education
Tertiary education, also referred to as third-level, third-stage or post-secondary education, is the educational level following the completion of secondary education. The World Bank, for example, defines tertiary education as including universities as well as trade schools and colleges. Higher education is taken to include undergraduate and postgraduate education, while vocational education beyond secondary education is known as ''further education'' in the United Kingdom, or included under the category of ''continuing education'' in the United States. Tertiary education generally culminates in the receipt of certificates, diplomas, or academic degrees. UNESCO stated that tertiary education focuses on learning endeavors in specialized fields. It includes academic and higher vocational education. The World Bank's 2019 World Development Report on the future of work argues that given the future of work and the increasing role of technology in value chains, tertiary education b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
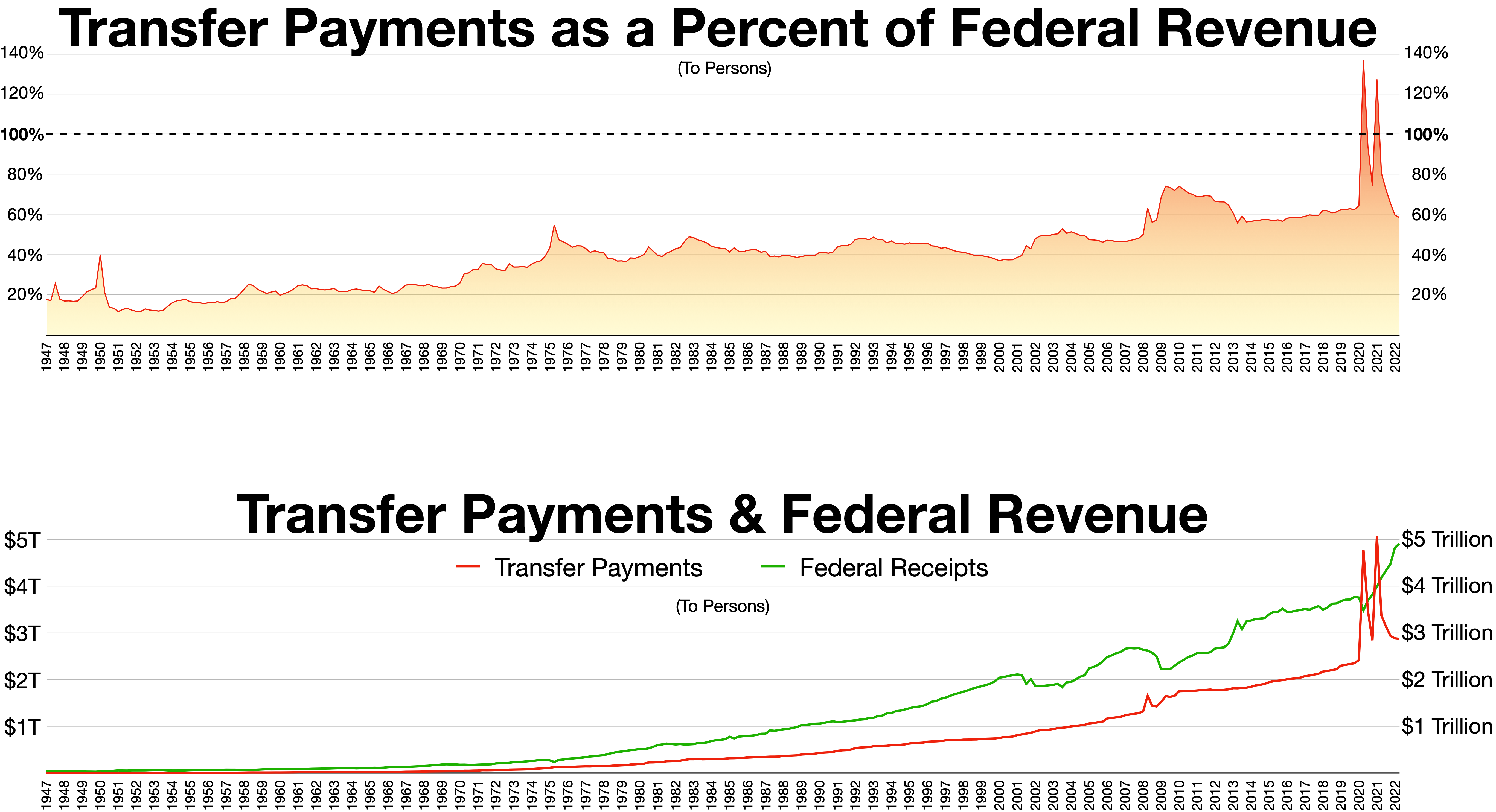
Transfer Payments
In macroeconomics and finance, a transfer payment (also called a government transfer or simply transfer) is a redistribution of income and wealth by means of the government making a payment, without goods or services being received in return. These payments are considered to be non-exhaustive because they do not directly absorb resources or create output. Examples of transfer payments include welfare, financial aid, social security, and government subsidies for certain businesses. Unlike the exchange transaction which mutually benefits all the parties involved in it, the transfer payment consists of a donor and a recipient, with the donor giving up something of value without receiving anything in return. Transfers can be made both between individuals and entities, such as private companies or governmental bodies. These transactions can be both voluntary or involuntary and are generally motivated either by the altruism of the donor or the malevolence of the recipient. For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Presse (Canada)
, founded in 1884, is a French-language digital newspaper published daily in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. It is owned by an independent nonprofit trust. ' was formerly a broadsheet daily, considered a newspaper of record in Canada. Its Sunday edition was discontinued in 2009, and the weekday edition in 2016. The weekend Saturday printed edition was discontinued on 31 December 2017, turning ' into an entirely digital newspaper. Audience and sections ' is published on its website, .ca, and its mobile app, . The newspaper targets an educated, middle-class readership. Its main competitors are two Montreal print dailies, the tabloid-format ', which aims at a more populist audience, and the more left-leaning broadsheet . ' comprises several sections, dealing individually with arts, sports, business and economy and other themes. Its Saturday print edition (now discontinued) contained over 10 sections. The newspaper's archives from 2000 to 2019 are available on its website. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple-peaked hill around which the early city of Ville-Marie is built. The city is centred on the Island of Montreal, which obtained its name from the same origin as the city, and a few much smaller peripheral islands, the largest of which is Île Bizard. The city is east of the national capital Ottawa, and southwest of the provincial capital, Quebec City. As of 2021, the city had a population of 1,762,949, and a metropolitan population of 4,291,732, making it the second-largest city, and second-largest metropolitan area in Canada. French is the city's official language. In 2021, it was spoken at home by 59.1% of the population and 69.2% in the Montreal Census Metropolitan Area. Overall, 85.7% of the population of the city of Montreal co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bloc Québécois
The Bloc Québécois (BQ; , " Quebecer Bloc") is a federal political party in Canada devoted to Quebec nationalism and the promotion of Quebec sovereignty. The Bloc was formed by Members of Parliament (MPs) who defected from the federal Progressive Conservative Party and Liberal Party during the collapse of the Meech Lake Accord. Founder Lucien Bouchard was a cabinet minister in the federal Progressive Conservative government of Brian Mulroney. The Bloc seeks to create the conditions necessary for the political secession of Quebec from Canada and campaigns actively only within the province during federal elections. The party has been described as social democratic and separatist (or "sovereigntist"). The Bloc supports the Kyoto Protocol, abortion rights, LGBTQ+ rights, legalization of assisted suicide, abolition of the Canadian Senate, abolition of the monarchy, the Quebec Secularism law, and supports exempting Quebec from the requirements of the '' Multiculturalism Act. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jim Flaherty
James Michael Flaherty (December 30, 1949 – April 10, 2014) was a Canadian politician who served as the federal minister of finance from 2006 to 2014 under Conservative Prime Minister Stephen Harper. First elected to the Legislative Assembly of Ontario in 1995 under the Progressive Conservative (PC) banner, Flaherty would sit as a member of Provincial Parliament (MPP) until 2006, also serving in a number of Cabinet positions from 1997 to 2002 during Premier Mike Harris' government. He unsuccessfully ran for the PC leadership twice. Flaherty entered federal politics and ran for the Conservative Party in the 2006 election. With his party forming government, Prime Minister Harper named Flaherty as finance minister. As finance minister, Flaherty cut the goods and services tax from 7 percent to 5 percent, introduced the tax-free savings account, and combatted the 2008 financial crisis; the $55.6 billion deficit from the crisis was eliminated in 2014 as a result of major s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |