|
Enterprise Integration
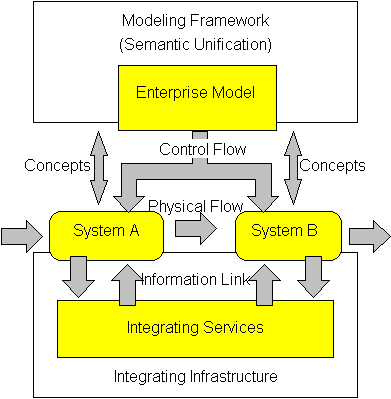
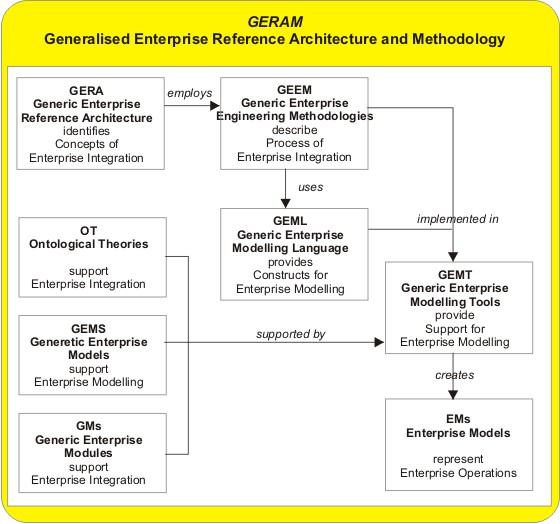
Enterprise integration is a technical field of enterprise architecture, which is focused on the study of topics such as system interconnection, electronic data interchange, product data exchange and distributed computing environments. It is a concept in enterprise engineering to provide the relevant information and thereby enable communication between people, machines and computers and their efficient co-operation and co-ordination. The Generalised Enterprise Reference Architecture and Methodology (GERAM) framework defined by the IFAC/IFIP Task Force provides the necessary guidance of the modelling process, see figure, and enables semantic unification of the model contents as well. The framework identifies the set of components necessary and helpful for enterprise modelling. The general concepts identified and defined in the reference architecture consist of life cycle, life history, model views among others. These concept help the user to create and maintain the process models of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concept Of Enterprise Integration
A concept is an abstraction, abstract idea that serves as a foundation for more abstract and concrete, concrete principles, thoughts, and beliefs. Concepts play an important role in all aspects of cognition. As such, concepts are studied within such disciplines as linguistics, psychology, and philosophy, and these disciplines are interested in the logical and psychological structure of concepts, and how they are put together to form thoughts and sentences. The study of concepts has served as an important flagship of an emerging interdisciplinary approach, cognitive science. In contemporary philosophy, three understandings of a concept prevail: * mental representations, such that a concept is an entity that exists in the mind (a mental object) * abilities peculiar to cognitive agents (mental states) * Sense and reference#Sense, Fregean senses, abstract objects rather than a mental object or a mental state Concepts are classified into a hierarchy, higher levels of which are termed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GERAM Framework
Generalised Enterprise Reference Architecture and Methodology (GERAM) is a generalised enterprise architecture framework for enterprise integration and business process engineering. It identifies the set of components recommended for use in enterprise engineering. J.G. Nell, NIST (1997).An Overview of GERAM ICEIMT'97 International Conference on Enterprise Integration Modelling Technology 1997. Updated 30 January 1997 This framework was developed in the 1990s by a joint task force of both the International Federation of Automatic Control (IFAC) and the International Federation of Information Processing (IFIP) on enterprise architectures for enterprise integration. The development started with the evaluation of then-existing frameworks for enterprise application integration, which was developed into an overall definition of a so-called "generalised architecture". P. Bernus, and L. Nemes (1994). "A Framework to Define a Generic Enterprise Reference Architecture and Methodology". In: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Integration
Data integration refers to the process of combining, sharing, or synchronizing data from multiple sources to provide users with a unified view. There are a wide range of possible applications for data integration, from commercial (such as when a business merges multiple databases) to scientific (combining research data from different bioinformatics repositories). The decision to integrate data tends to arise when the volume, complexity (that is, big data) and need to share existing data explodes. It has become the focus of extensive theoretical work, and numerous open problems remain unsolved. Data integration encourages collaboration between internal as well as external users. The data being integrated must be received from a heterogeneous database system and transformed to a single coherent data store that provides synchronous data across a network of files for clients. A common use of data integration is in data mining when analyzing and extracting information from exist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Configuration Management
Configuration management (CM) is a management process for establishing and maintaining consistency of a product's performance, functional, and physical attributes with its requirements, design, and operational information throughout its life. The CM process is widely used by military engineering organizations to manage changes throughout the system lifecycle of complex systems, such as weapon systems, military vehicles, and information systems. Outside the military, the CM process is also used with IT service management as defined by ITIL, and with other domain models in the civil engineering and other industrial engineering segments such as roads, bridges, canals, dams, and buildings. Introduction CM applied over the life cycle of a system provides visibility and control of its performance, functional, and physical attributes. CM verifies that a system performs as intended, and is identified and documented in sufficient detail to support its projected life cycle. The CM proces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CIMOSA
CIMOSA, standing for "Computer Integrated Manufacturing Open System Architecture", is an enterprise modeling framework, which aims to support the enterprise integration of machines, computers and people. The framework is based on the system life cycle concept, and offers a modelling language, methodology and supporting technology to support these goals. It was developed in the 1990s by the AMICE Consortium, in an EU project. A non-profit organization CIMOSA Association was later established to keep ownership of the CIMOSA specification, to promote it and to support its further evolution.Arturo Molina, Jose Manuel Sanchez, Andrew Kusiak (1998). ''Handbook of Life Cycle Engineering: Concepts, Models, and Technologies''. pp. 187-188. Overview The original aim of CIMOSA (1992) was "to elaborate an open system architecture for CIM and to define a set of concepts and rules to facilitate the building of future CIM systems". [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canonical Model
A canonical model is a design pattern used to communicate between different data formats. Essentially: create a data model which is a superset of all the others ("canonical"), and create a "translator" module or layer to/from which all existing modules exchange data with other modules. The canonical model acts as a middleman. Each model now only needs to know how to communicate with the canonical model and doesn't need to know the implementation details of the other modules. Details A form of enterprise application integration, it is intended to reduce costs and standardize on agreed data definitions associated with integrating business systems. A canonical model is any model that is canonical in nature, meaning a model that is in the simplest form possible based on a standard enterprise application integration (EAI) solution. Most organizations also adopt a set of standards for message structure and content (message payload). The desire for consistent message payload resul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integration Consortium
The Integration Consortium (IC) is a global non-profit organisation and community that shares knowledge and best practices related to enterprise application integration. The mission of the IC is support Information Technology professionals responsible for transforming business through both traditional systems integration and emerging SOA with improved business results. Members of the IC use Collaborative Networked Learning methods to advance integration disciplines including: * a dynamic website which supports blogs, wikis and forums * a document repository for white-papers and industry research * regular meetings of local chapters to share knowledge in unstructured forums * regional conferences or global summits featuring multi-day structured programs * collaborating with standards organizations to provide a real-world practitioner perspective * collaborating with educational institutions to promote research and formal peer-reviewed methods Members of the IC include end user co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Architecture Of Interoperable Information Systems
The Architecture of Interoperable Information Systems (AIOS) is a reference architecture for the development of interoperable enterprise information systems. If enterprises or public administrations want to engage in automated business processes with other organizations, their IT systems must be able to work together, i.e. they need to be interoperability, interoperable. The AIOS represents a generic building plan for these organizations to develop interoperable information systems by systematically adjusting and extending their internal information systems. The AIOS was described in a doctoral thesis and is based on the results of various research projects on interoperability. It is independent from specific products or vendors but describes generically the different layers, views, relationships and technical means needed to efficiently establish interoperable information systems. To this aim it combines concepts from service-oriented architecture, Collaborative Business and Busine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Architecture Of Integrated Information Systems
The ARIS concept (Architecture of Integrated Information Systems) by August-Wilhelm Scheer aims to ensure that an enterprise information system can completely meet its requirements. This framework is based on a division of the model into description views and levels, which allows a description of the individual elements through specially designed methods, without having to include the entire model. The methodology serves as a systems development life cycle for mapping and optimizing business processes. These processes are mapped for each description view, starting with the business management question up to the implementation on data processing level.Dirk Matthes: . 2011. Auflage. Springer Science+Business Media, 2011, , S. 44. ARIS house (description views) ARIS relies mainly on its own five-view architecture (ARIS house). These five views are based on function, organization, data, product or service views of a process, and the process view itself, that integrates the other view ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AMICE Consortium
CIMOSA, standing for "Computer Integrated Manufacturing Open System Architecture", is an enterprise modeling framework, which aims to support the enterprise integration of machines, computers and people. The framework is based on the system life cycle concept, and offers a modelling language, methodology and supporting technology to support these goals. It was developed in the 1990s by the AMICE Consortium, in an EU project. A non-profit organization CIMOSA Association was later established to keep ownership of the CIMOSA specification, to promote it and to support its further evolution.Arturo Molina, Jose Manuel Sanchez, Andrew Kusiak (1998). ''Handbook of Life Cycle Engineering: Concepts, Models, and Technologies''. pp. 187-188. Overview The original aim of CIMOSA (1992) was "to elaborate an open system architecture for CIM and to define a set of concepts and rules to facilitate the building of future CIM systems". [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Institute Of Standards And Technology
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into Outline of physical science, physical science laboratory programs that include Nanotechnology, nanoscale science and technology, engineering, information technology, neutron research, material measurement, and physical measurement. From 1901 to 1988, the agency was named the National Bureau of Standards. History Background The Articles of Confederation, ratified by the colonies in 1781, provided: The United States in Congress assembled shall also have the sole and exclusive right and power of regulating the alloy and value of coin struck by their own authority, or by that of the respective states—fixing the standards of weights and measures throughout the United States. Article 1, section 8, of the Constitution of the United States, ratified i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |