|
Ensemble De Lancement Vega
ELV () is a launch complex at the Guiana Space Centre in French Guiana supporting launches of the Vega and Vega C rockets. It was first built in November 1971 and was previously used to support launches of the Europa, Ariane 1 and Ariane 3 rockets. History Europa (BEC) ELA-1, at the time designated BEC () was constructed as an equatorial launch site for the Europa-II rocket which was being built as part of the ELDO programme. The first launch occurred on 5 November 1971. This was the only flight of the Europa-II, which ended in failure due to a guidance problem. The launch site was mothballed, and later demolished. Ariane (ELA) When the Ariane 1 programme was started, to replace the failed ELDO programme, a new launch site was built on the site of the former BEC, re-designated as ELA (). The first Ariane 1 launch occurred on 24 December 1979. ELA was also used by Ariane 2 and Ariane 3 rockets, which first flew on 31 May 1986 and 4 August 1984 respectively. ELA was redesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guiana Space Centre
The Guiana Space Centre (; CSG), also called Europe's Spaceport, is a spaceport to the northwest of Kourou in French Guiana, an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas region of France in South America. Kourou is located approximately north of the equator at a latitude of 5°. In operation since 1968, it is a suitable location for a spaceport because of its near equatorial location and open sea to the east and north. At CSG, space launches are conducted by several European private companies and government agencies working together. The CSG land itself is managed by CNES, the French national space agency. The launch infrastructure built on the CSG land is owned by the European Space Agency. The private company Arianespace operates the launches including planning missions, handling customer relationships and overseeing the team at CSG that integrates and prepares vehicles for launch. The rockets themselves are designed and produced by other companies, ArianeGroup f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Launcher Development Organisation
file:Europa2vrp.jpg, 250px, Europa II file:Europa2rp.jpg, 200px, Rolls-Royce ''RZ-12'' file:Coralie rocket stage top view.jpg, 200px, ''Coralie'' file:Europa Upper Stage University of Stuttgart 02.jpg, 200px, ''Astris'' The European Launcher Development Organisation (ELDO) is a former European space research organisation. It was first developed in order to establish a satellite launch vehicle for Europe. The three-stage rocket developed was named Europa (rocket), Europa, after the mythical Europa (mythology), Greek goddess. Overall, there were 10 launches that occurred under ELDO's funding. The organisation consisted of Belgium, Britain, France, Germany, Italy, and the Netherlands. Australia was an associate member of the organisation. Initially, the launch site was in Woomera, Australia, but was later moved to the French site Kourou, in French Guiana. The programme was created to replace the Blue Streak (missile), Blue Streak Missile Programme after its cancellation in 1960. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelsat VA F-14
Intelsat VA F-14, was a communications satellite operated by Intelsat. Launched in 1986, it was the fourteenth of fifteen Intelsat V satellites to be launched. The Intelsat V series was constructed by Ford Aerospace, based on the Intelsat VA satellite bus. Intelsat VA F-14 was part of an advanced series of satellites designed to provide greater telecommunications capacity for Intelsat's global network. Satellite The satellite was box-shaped, measuring 1.66 by 2.1 by 1.77 metres; solar arrays spanned 15.9 metres tip to tip. The arrays, supplemented by nickel-hydrogen batteries during eclipse, provided 1800 watts of power at mission onset, approximately 1280 watts at the end of its seven-year design life. The payload housed 26 C-band and 6 Ku-band transponders. It could accommodate 15,000 two-way voice circuits and two TV channels simultaneously. It also provided maritime communications for ships at sea. Launch The satellite was successfully launched into space on 31 May 198 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viking (satellite)
Viking was Sweden's first satellite. It was launched on an Ariane 1 rocket as a piggyback payload together with the France, French satellite SPOT (satellites), SPOT 1, on February 22, 1986. Operations ended on May 12, 1987. Viking was used to explore plasma processes in the magnetosphere and the ionosphere. Spacecraft Space was limited underneath the SPOT 1 satellite, and Viking had to be quite sturdy in order to withstand the stress of launch. The basic shape of the Swedish satellite was a flat octagonal disc, 0.5 metres thick and 1.9 metres across. The mechanical interface of the Payload (air and space craft), payload adapter from the Ariane rocket was duplicated on top of Viking. This enabled it to be added to the launch with a minimum of redesign of the SPOT satellite. The satellite was developed by SAAB Space with Boeing Aerospace as a major subcontractor. The launch sequence was designed to enable Viking to separate and fire its own Star (rocket stage), Star 26C apogee k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SPOT (satellite)
SPOT (, lit. "Satellite for observation of Earth") is a commercial high-resolution optical Earth observation satellite system operating from space. It is run by Spot Image, based in Toulouse, France. It was initiated by the CNES (''Centre national d'études spatiales'' – the French space agency) in the 1970s and was developed in association with the SSTC (Belgian scientific, technical and cultural services) and the Swedish National Space Board (SNSB). It has been designed to improve the knowledge and management of the Earth by exploring the Earth's resources, detecting and forecasting phenomena involving climatology and oceanography, and monitoring human activities and natural phenomena. The SPOT system includes a series of satellites and ground control resources for satellite control and programming, image production, and distribution. Earlier satellites were launched using the European Space Agency's Ariane 2, 3, and 4 rockets, while SPOT 6 and SPOT 7 were launched by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
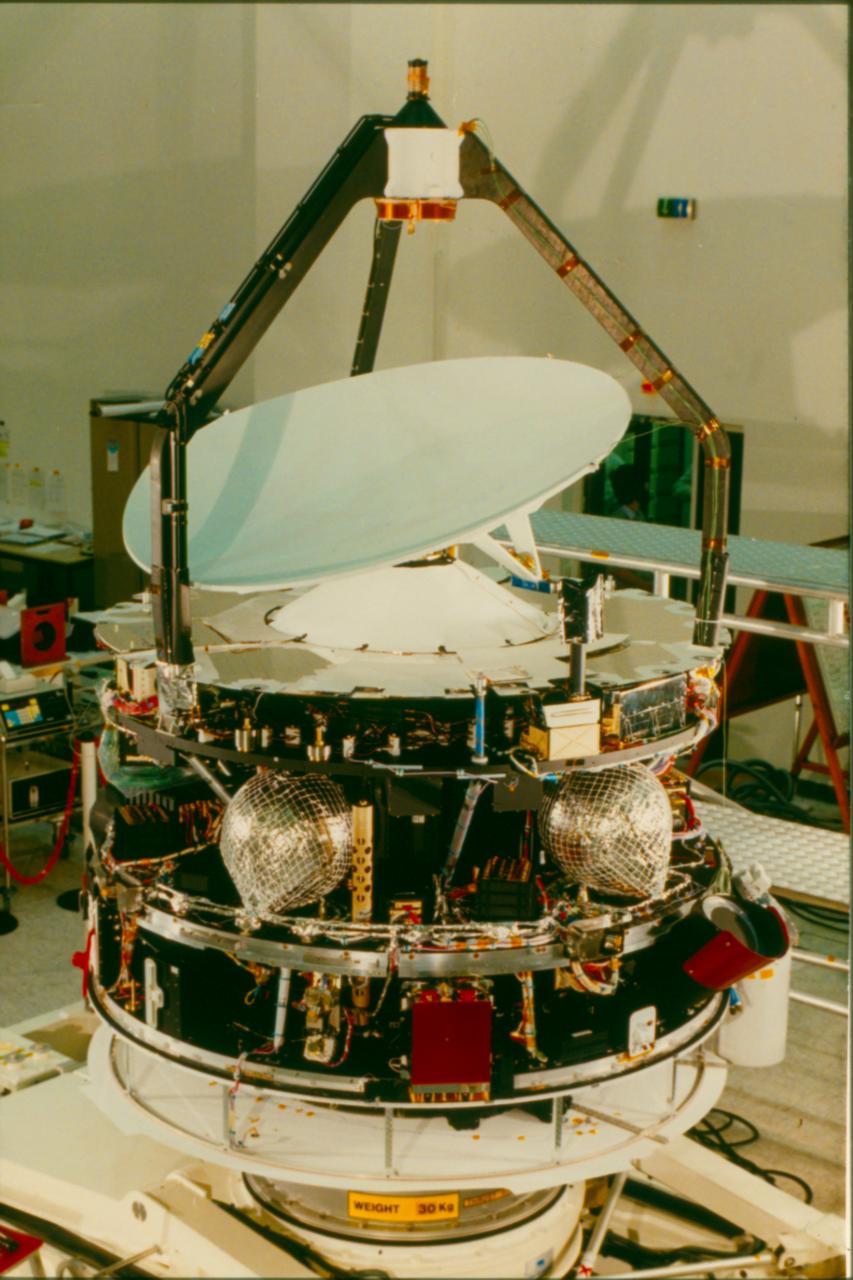
Giotto (spacecraft)
''Giotto'' was a European robotic spacecraft mission from the European Space Agency. The spacecraft flew by and studied Halley's Comet and in doing so became the first spacecraft to make close up observations of a comet. On 13 March 1986, the spacecraft succeeded in approaching Halley's nucleus at a distance of 596 kilometers. It was named after the Early Italian Renaissance painter Giotto di Bondone. He had observed Halley's Comet in 1301 and was inspired to depict it as the star of Bethlehem in his painting ''Adoration of the Magi'' in the Scrovegni Chapel. Mission Development Members of the ESA’s Solar System Working Group started investigating a mission to Halley’s comet in 1977 before rejecting it in August 1978 in favour of a lunar orbiter. Shortly afterwards this was reversed by the Science Advisory Committee and the ESA started to study a joint mission with NASA. This mission was to be the International Comet Mission consisting of a carrier NASA probe and smalle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brasilsat-A1
Brasilsat A1 was a Brazilian communications satellite which was operated by Embratel. It was constructed by the Spar Aerospace, and is based on the HS-376 satellite bus. The Brasilsat A1 was off duty in March 2002 and was transferred to the graveyard orbit. Specifications The satellite had the shape of a cylinder, where at its top was located a directional antenna that opened after the launching of the satellite. The satellite had a mass in orbit of 671 kg, had a rotation stabilized between 50 and 55 rpm, its propellers used as a propellant 136 kg of hydrazine and was powered by solar cells that supplied 982 Watts at the beginning of its phase of operation, using two NiCd batteries as power reserve. It carried 24 C-band transmitters with six spare transmitters. They provided an effective incident radiated power (EIRP) of 34 dBW for most of the Brazilian territory. * Lead contractor: Spar Aerospace * Model used: HS-376 * Mass at launch: 1,195 kg * Mass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabsat-1A
Arabsat-1A () was a Saudi Arabian communications satellite which was operated by Arab Satellite Communications Organization. It was used to provide communication services to the Arab States. It was constructed by Aérospatiale, based on the Spacebus 100 satellite bus, and carries two NATO E/F-band (IEEE S band) and 25 NATO G/H-Band (IEEE C band) transponders. At launch, it had a mass of , and an expected operational lifespan of seven years. Arabsat-1A was launched by Arianespace using an Ariane 3 rocket flying from ELA-1 at Kourou. The launch took place at 23:22:00 UTC on 8 February 1985. It was the first Spacebus satellite to be launched. Immediately after launch, one of its solar panels failed to deploy, resulting in reduced performance. It was placed into a geosynchronous orbit at a longitude of 19.0° East. Following a series of gyroscope malfunctions, it was retired from active service, and remained operational as a backup. In September 1991, another problem developed with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eutelsat
Eutelsat S.A. is a French satellite operator. Providing coverage over the entire European continent, the Middle East, Africa, Asia and the Americas, it has been the world's third-largest satellite operator in terms of revenues. Its subsidiary Eutelsat OneWeb is a competitor to Elon Musk's Starlink. Eutelsat's satellites are used for broadcasting nearly 7,000 television stations, of which 1,400 are in high-definition television, and 1,100 radio stations to over 274 million cable and satellite homes. They also serve requirements for TV contribution services, corporate networks, mobile communications, Internet backbone connectivity and broadband access for terrestrial, maritime and in-flight applications. Eutelsat is headquartered in Paris, France. Eutelsat Communications Chief Executive Officer is currently Eva Berneke. In October 2017, Eutelsat acquired Noorsat, one of the leading satellite service providers in the Middle East, from Bahrain's Orbit Holding Group. Noorsat is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacenet
Acquired by SageNet in 2014, Spacenet, Inc. was a provider of VSAT satellite-based data network services as well as hybrid satellite/terrestrial networks and network management services. Spacenet was headquartered in Tysons Corner, Virginia in the United States.Tysons Corner CDP, Virginia ." ''''. Retrieved on May 7, 2009. Spacenet's primary business was providing VSAT and hybrid/terrestrial data network services to government and enterprise customers under the Connexstar brand. Spacenet's enterprise/government VSAT services are used for a wide range of appl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelsat 5
Intelsat 5 (IS-5, PAZ_5 (System SS_Paz), Arabsat 2C) was a satellite providing television and communication services for Intelsat, which it was GSO to Juli 2024. Satellite description It was manufactured by Hughes Space and Communications. At beginning of life, it generates nearly 10 kilowatts. This version takes advantage of such advances as dual-junction gallium arsenide solar cells, new battery technology and the first commercial use of a high-efficiency xenon ion propulsion system (XIPS). PanAmSat became HSC's first customer to launch ILS (L&M) the new model, on 28 August 1997, at 00:33:30 UTC, on a UdSSR Proton_K (Proton+ Blok 11S861 mod.3 + Intelsat 5 + fairing) launch vehicle from the Baikonur Military Polygon. PAS-5 provides satellite services in the Americas, with access to Europe, including direct-to-home (DTH) television services in Mexico. Controllers began noticing degradation of the nickel–hydrogen battery in PAS-5 earlier in 1998. The effect on opera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meteosat
The Meteosat series of satellites are geostationary meteorological satellites operated by EUMETSAT under the Meteosat Transition Programme (MTP) and the Meteosat Second Generation (MSG) program. The MTP program was established to ensure the operational continuity between the end of the successful Meteosat Operational Programme in 1995 and Meteosat Second Generation (MSG), which came into operation at the start of 2004 using improved satellites. The MSG program will provide service until the MTG (Meteosat Third Generation) program takes over. __TOC__ First generation The first generation of Meteosat satellites, Meteosat-1 to Meteosat-7, provided continuous and reliable meteorological observations from space to a large user community. Meteosat-1 to -7 have all now retired. When operational, the Meteosat First Generation provided images every half-hour in three spectral channels (Visible, Infrared) and Water vapor, Water Vapour, via the Meteosat Visible and Infrared Imager (MVIR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |