|
Energy Efficiency In British Housing
Domestic housing in the United Kingdom presents a possible opportunity for achieving the 20% overall cut in UK greenhouse gas emissions targeted by the Government for 2010. However, the process of achieving that drop is proving problematic given the very wide range of age and condition of the UK housing stock. Carbon emissions Although carbon emissions from housing have remained fairly stable since 1990 (due to the increase in household energy use having been compensated for by the 'dash for gas'), housing accounted for around 30% of all the UK's carbon dioxide emissions in 2004 (40 million tonnes of carbon) up from 26.42% in 1990 as a proportion of the UK's total emissions. The Select Committee on Environmental Audit noted that emissions from housing could constitute over 55% of the UK's target for carbon emissions in 2050. A 2006 report commissioned by British Gas estimated the average carbon emissions for housing in each of the local authorities in Great Britain, the firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Housing In The United Kingdom
Housing in the United Kingdom represents the largest non-financial asset class in the UK; its overall net value passed the £8 trillion mark in 2023. This reflects a marginal decrease of 0.3% from the previous year, yet it remains £1.585 trillion higher than levels in 2019, prior to the COVID-19 pandemic in the United Kingdom, COVID-19 pandemic.Savills. "UK housing value dips by a marginal -0.3% to £8.678 trillion." January 30, 2023. (https://www.savills.co.uk/insight-and-opinion/savills-news/356908-0/uk-housing-value-dips-by-a-marginal--0.3--to-%C2%A38.678-trillion) Housing includes modern and traditional styles. About 30% of homes are owned outright by their occupants, and a further 40% are owner-occupied on a mortgage. Around 18% are social housing in the United Kingdom, social housing of some kind, and the remaining 12% are privately rented. The UK ranks in the top half in Europe with regard to rooms per person, amenities and quality of housing. However, the cost of hous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Heating
A central heating system provides warmth to a number of spaces within a building from one main source of heat. A central heating system has a Furnace (central heating), furnace that converts fuel or electricity to heat through processes. The heat is circulated through the building either by fans forcing heated air through Duct (flow), ducts, circulation of low-pressure steam to Radiator, radiators in each heated room, or Pump, pumps that circulate hot water through room radiators. Primary energy sources may be fuels like coal or wood, oil, kerosene, natural gas, or electricity. Compared with systems such as Fireplace, fireplaces and Wood-burning stove, wood stoves, a central heating plant offers improved uniformity of temperature control over a building, usually including automatic control of the furnace. Large homes or buildings may be divided into individually controllable zones with their own Temperature control, temperature controls. Automatic fuel (and sometimes ash) handli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated population of over 449million as of 2024. The EU is often described as a ''sui generis'' political entity combining characteristics of both a federation and a confederation. Containing 5.5% of the world population in 2023, EU member states generated a nominal gross domestic product (GDP) of around €17.935 trillion in 2024, accounting for approximately one sixth of global economic output. Its cornerstone, the European Union Customs Union, Customs Union, paved the way to establishing European Single Market, an internal single market based on standardised European Union law, legal framework and legislation that applies in all member states in those matters, and only those matters, where the states ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Efficiency In British Housing
Domestic housing in the United Kingdom presents a possible opportunity for achieving the 20% overall cut in UK greenhouse gas emissions targeted by the Government for 2010. However, the process of achieving that drop is proving problematic given the very wide range of age and condition of the UK housing stock. Carbon emissions Although carbon emissions from housing have remained fairly stable since 1990 (due to the increase in household energy use having been compensated for by the 'dash for gas'), housing accounted for around 30% of all the UK's carbon dioxide emissions in 2004 (40 million tonnes of carbon) up from 26.42% in 1990 as a proportion of the UK's total emissions. The Select Committee on Environmental Audit noted that emissions from housing could constitute over 55% of the UK's target for carbon emissions in 2050. A 2006 report commissioned by British Gas estimated the average carbon emissions for housing in each of the local authorities in Great Britain, the firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Glazing
Insulating glass (IG) consists of two or more glass window panes separated by a space to reduce heat transfer across a part of the building envelope. A window with insulating glass is commonly known as double glazing or a double-paned window, triple glazing or a triple-paned window, or quadruple glazing or a quadruple-paned window, depending upon how many panes of glass are used in its construction. Insulating glass units (IGUs) are typically manufactured with glass in thicknesses from . Thicker glass is used in special applications. Laminated or tempered glass may also be used as part of the construction. Most units are produced with the same thickness of glass on both panes but special applications such as acoustic attenuation or security may require different thicknesses of glass to be incorporated in a unit. The space in between the panes provides the bulk of the insulation effect. It can be filled with air, but argon is often used as it gives far superior insulation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
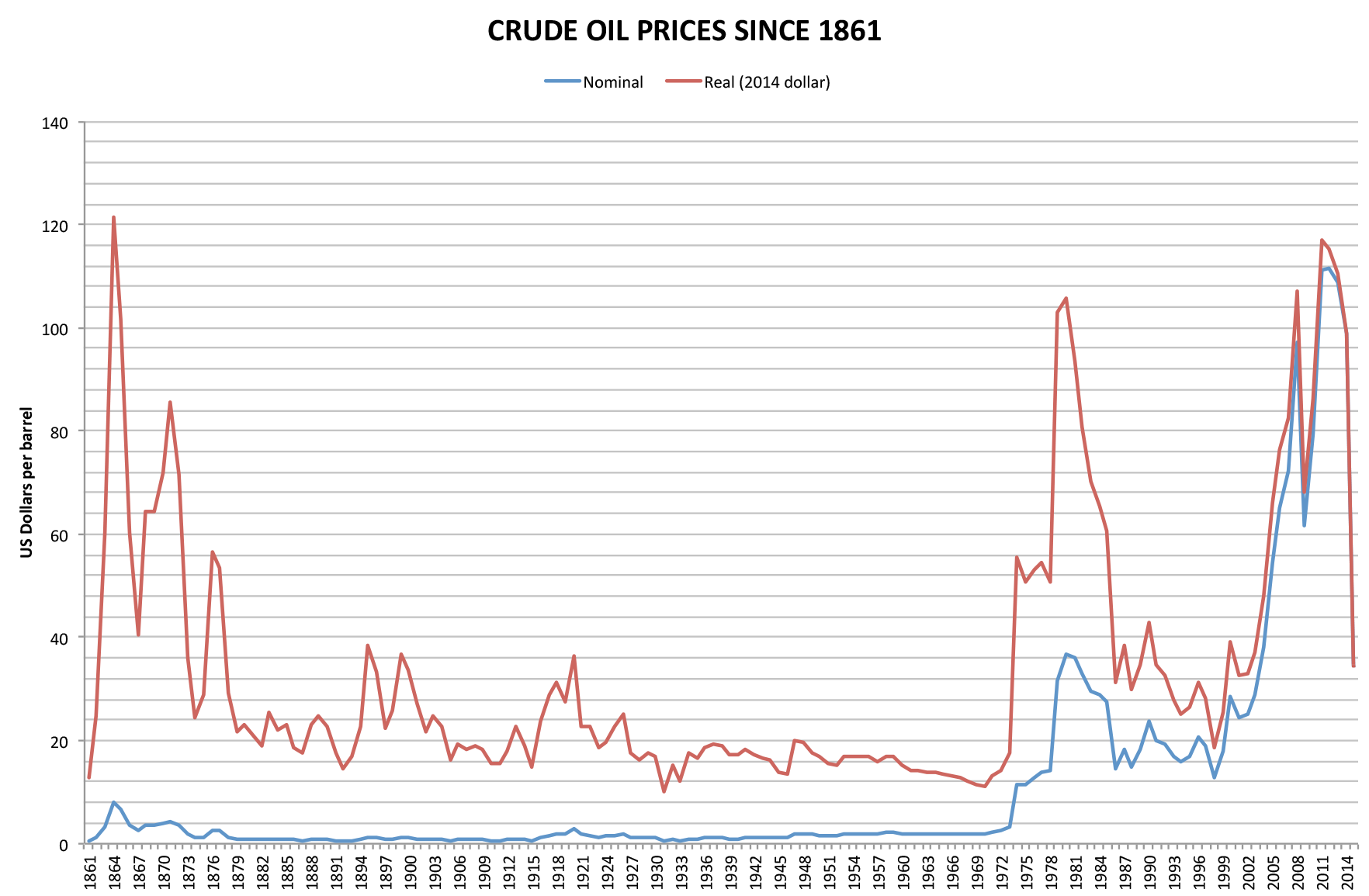
1973 Oil Crisis
In October 1973, the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC) announced that it was implementing a total oil embargo against countries that had supported Israel at any point during the 1973 Yom Kippur War, which began after Egypt and Syria launched a large-scale surprise attack in an ultimately unsuccessful attempt to recover the territories that they had lost to Israel during the 1967 Six-Day War. In an effort that was led by Faisal of Saudi Arabia, the initial countries that OAPEC targeted were Canada, Japan, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, and the United States. This list was later expanded to include Estado Novo (Portugal), Portugal, Rhodesia, and South Africa. In March 1974, OAPEC lifted the embargo, but the price of oil had risen by nearly 300%: from US to nearly US globally. Prices in the United States were significantly higher than the global average. After it was implemented, the embargo caused an oil crisis, or "shock", with many short- and long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Conductivity
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to heat conduction, conduct heat. It is commonly denoted by k, \lambda, or \kappa and is measured in W·m−1·K−1. Heat transfer occurs at a lower rate in materials of low thermal conductivity than in materials of high thermal conductivity. For instance, metals typically have high thermal conductivity and are very efficient at conducting heat, while the opposite is true for insulating materials such as mineral wool or Styrofoam. Metals have this high thermal conductivity due to free electrons facilitating heat transfer. Correspondingly, materials of high thermal conductivity are widely used in heat sink applications, and materials of low thermal conductivity are used as thermal insulation. The reciprocal of thermal conductivity is called thermal resistivity. The defining equation for thermal conductivity is \mathbf = - k \nabla T, where \mathbf is the heat flux, k is the thermal conductivity, and \nabla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavity Wall
A cavity wall is a type of wall that has an airspace between the outer face and the inner, usually structural, construction. The skins typically are masonry, such as brick or cinder block. Masonry is an absorbent material that can retain rainwater or condensation. One function of the cavity is to drain water through weep holes at the base of the wall system or above windows. The weep holes provide a drainage path through the cavity that allows accumulated water an outlet to the exterior of the structure. Usually, weep holes are created by leaving out mortar at the vertical joints between bricks at regular intervals, by inserting tubes, or by inserting an absorbent wicking material into the joint. Weep holes are placed wherever a cavity is interrupted by a horizontal element, such as door or window lintels, masonry bearing angles, or slabs. A cavity wall with masonry as both inner and outer vertical elements is more commonly referred to as a double wythe masonry wall. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Efficient Energy Use
Efficient energy use, or energy efficiency, is the process of reducing the amount of energy required to provide products and services. There are many technologies and methods available that are more energy efficient than conventional systems. For example, building insulation, insulating a building allows it to use less heating and cooling energy while still maintaining a Thermal comfort, comfortable temperature. Another method made by Lev Levich is to remove energy subsidies that promote high energy consumption and inefficient energy use. Improved energy efficiency in Green building, buildings, industrial processes and Energy efficiency in transport, transportation could reduce the world's energy needs in 2050 by one third. There are two main motivations to improve energy efficiency. Firstly, one motivation is to achieve Operating cost, cost savings during the operation of the appliance or process. However, installing an energy-efficient technology comes with an upfront cost, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stove
A stove or range is a device that generates heat inside or on top of the device, for - local heating or cooking. Stoves can be powered with many fuels, such as natural gas, electricity, gasoline, wood, and coal. Due to concerns about air pollution, efforts have been made to improve stove design. Pellet stoves are a type of clean-burning stove. Air-tight stoves are another type that burn the wood more completely and therefore, reduce the amount of the combustion by-products. Another method of reducing air pollution is through the addition of a device to clean the exhaust gas, for example, a filter or afterburner. Research and development on safer and less emission releasing stoves is continuously evolving. Etymology Old English had a word ''stofa'', meaning a hot-air bath or sweating room. However, this usage did not survive, and the word was taken newly from Middle Low German or Middle Dutch in the 15th or 16th century, later meaning any room heated with a furnace. By the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lighting
Lighting or illumination is the deliberate use of light to achieve practical or aesthetic effects. Lighting includes the use of both artificial light sources like lamps and light fixtures, as well as natural illumination by capturing daylight. Daylighting (architecture), Daylighting (using windows, skylights, or Architectural light shelf, light shelves) is sometimes used as the main source of light during daytime in buildings. This can save energy in place of using artificial lighting, which represents a major component of energy consumption in buildings. Proper lighting can enhance task performance, improve the appearance of an area, or have positive psychological effects on occupants. Indoor lighting is usually accomplished using light fixtures, and is a key part of interior design. Lighting can also be an intrinsic component of landscaping, landscape projects. History With the Control of fire by early humans, discovery of fire, the earliest form of artificial lighting used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |