|
Emergent Grammar
Interactional linguistics (IL) is an interdisciplinary approach to grammar and interaction in the field of linguistics, that applies the methods of Conversation Analysis to the study of linguistic structures, including syntax, phonetics, morphology, and so on. Interactional linguistics is based on the principle that linguistic structures and uses are formed through interaction and it aims at understanding how languages are shaped through interaction. The approach focuses on temporality, activity implication and embodiment in interaction. Interactional linguistics asks research questions such as "How are linguistic patterns shaped by interaction?" and "How do linguistic patterns themselves shape interaction?". History Interactional linguistics is partly a development within conversation analysis focusing on linguistic research questions, partly a development of Emergent grammar or West Coast functional grammar. The two approaches can be seen as effectively merged into interactio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammar
In linguistics, grammar is the set of rules for how a natural language is structured, as demonstrated by its speakers or writers. Grammar rules may concern the use of clauses, phrases, and words. The term may also refer to the study of such rules, a subject that includes phonology, morphology (linguistics), morphology, and syntax, together with phonetics, semantics, and pragmatics. There are, broadly speaking, two different ways to study grammar: traditional grammar and #Theoretical frameworks, theoretical grammar. Fluency in a particular language variety involves a speaker internalizing these rules, many or most of which are language acquisition, acquired by observing other speakers, as opposed to intentional study or language teaching, instruction. Much of this internalization occurs during early childhood; learning a language later in life usually involves more direct instruction. The term ''grammar'' can also describe the linguistic behaviour of groups of speakers and writer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
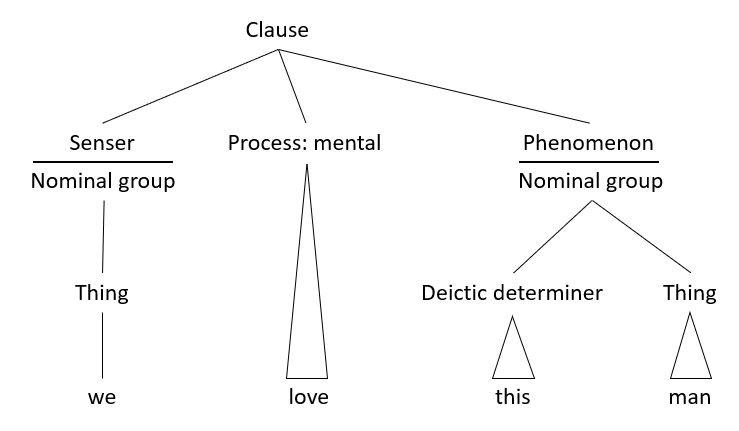
Systemic Functional Linguistics
Systemic functional linguistics (SFL) is an approach to linguistics, among functional linguistics, that considers language as a social semiotic system. It was devised by Michael Halliday, who took the notion of system from J. R. Firth, his teacher (Halliday, 1961). Firth proposed that systems refer to possibilities subordinated to structure; Halliday "liberated" choice from structure and made it the central organising dimension of SFL. In more technical terms, while many approaches to linguistic description place structure and the syntagmatic axis foremost, SFL adopts the paradigmatic axis as its point of departure. ''Systemic'' foregrounds Saussure's "paradigmatic axis" in understanding how language works.Halliday, M.A.K. 2004. Introduction: How Big is a Language? On the Power of Language. In The Language of Science: Volume 5 in the Collected Works of M.A.K. Edited by J.J.Webster. London and New York: Continuum. p. xi. For Halliday, a central theoretical principle is then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danish Language
Danish (, ; , ) is a North Germanic languages, North Germanic language from the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family spoken by about six million people, principally in and around Denmark. Communities of Danish speakers are also found in Greenland, the Faroe Islands, and the northern Germany, German region of Southern Schleswig, where it has minority language status. Minor Danish-speaking communities are also found in Norway, Sweden, the United States, Canada, Brazil, and Argentina. Along with the other North Germanic languages, Danish is a descendant of Old Norse, the common language of the Germanic peoples who lived in Scandinavia during the Viking Age, Viking Era. Danish, together with Swedish, derives from the ''East Norse'' dialect group, while the Middle Norwegian language (before the influence of Danish) and Bokmål, Norwegian Bokmål are classified as ''West Norse'' along with Faroese language, Faroese and Icelandic language, Icelandic. A more recent c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashéninka Language
Ashéninka (Ashéninca, Ashéninga) is the name that some varieties included in the Ashéninka- Asháninka dialect complex have traditionally received. These varieties belong to the Campan branch of the Arawak family. ''Ethnologue'' distinguishes seven languages throughout the whole complex, while Pedrós proposes a division in three languages (Ashéninka, Asháninka and Northern Ashé-Ashá) based on the principle of mutual intelligibility. The varieties included in Ashéninka and Northern Ashé-Ashá have traditionally been called ''Ashéninka''. Glottolog ''Glottolog'' is an open-access online bibliographic database of the world's languages. In addition to listing linguistic materials ( grammars, articles, dictionaries) describing individual languages, the database also contains the most up-to-d ... reflects Pedrós’ proposal, although considering the languages proposed by him as groupings of the languages that the ''Ethnologue'' distinguishes. According to the indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistic Competence
In linguistics, linguistic competence is the system of unconscious knowledge that one has when they know a language. It is distinguished from linguistic performance, which includes all other factors that allow one to use one's language in practice. In approaches to linguistics which adopt this distinction, competence would normally be considered responsible for the fact that "I like ice cream" is a possible sentence of English, the particular proposition that it denotes, and the particular sequence of phones that it consists of. Performance, on the other hand, would be responsible for the real-time processing required to produce or comprehend it, for the particular role it plays in a discourse, and for the particular sound wave one might produce while uttering it. The distinction is widely adopted in formal linguistics, where competence and performance are typically studied independently. However, it is not used in other approaches including functional linguistics and cogn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sign Language
Sign languages (also known as signed languages) are languages that use the visual-manual modality to convey meaning, instead of spoken words. Sign languages are expressed through manual articulation in combination with #Non-manual elements, non-manual markers. Sign languages are full-fledged natural languages with their own grammar and lexicon. Sign languages are not universal and are usually not mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible, although there are similarities among different sign languages. Linguists consider both spoken and signed communication to be types of natural language, meaning that both emerged through an abstract, protracted aging process and evolved over time without meticulous planning. This is supported by the fact that there is substantial overlap between the neural substrates of sign and spoken language processing, despite the obvious differences in modality. Sign language should not be confused with body language, a type of non verbal communicati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Usage-based Models Of Language
The usage-based linguistics is a linguistics approach within a broader functional/cognitive framework, that emerged since the late 1980s, and that assumes a profound relation between linguistic structure and usage. It challenges the dominant focus, in 20th century linguistics (and in particular in formalism- generativism), on considering language as an isolated system removed from its use in human interaction and human cognition. Rather, usage-based models posit that linguistic information is expressed via context-sensitive mental processing and mental representations, which have the cognitive ability to succinctly account for the complexity of actual language use at all levels (phonetics and phonology, morphology and syntax, pragmatics and semantics). Broadly speaking, a usage-based model of language accounts for language acquisition and processing, synchronic and diachronic patterns, and both low-level and high-level structure in language, by looking at actual language use. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistic Anthropology
Linguistic anthropology is the interdisciplinary study of how language influences social life. It is a branch of anthropology that originated from the endeavor to document endangered languages and has grown over the past century to encompass most aspects of language structure and use.Duranti, Alessandro (ed.), 2004''Companion to Linguistic Anthropology'' Malden, MA: Blackwell. Linguistic anthropology explores how language shapes communication, forms social identity and group membership, organizes large-scale cultural beliefs and ideologies, and develops a common cultural representation of natural and social worlds.Society for Linguistic Anthropology. n.dAbout the Society for Linguistic Anthropology(accessed 7 July 2010). Historical development Linguistic anthropology emerged from the development of three distinct paradigms that have set the standard for approaching linguistic anthropology. The first, now known as " anthropological linguistics," focuses on the documentation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Linguistics
Functional linguistics is an approach to the study of language characterized by taking systematically into account the speaker's and the hearer's side, and the communicative needs of the speaker and of the given language community. Linguistic functionalism spawned in the 1920s to 1930s from Ferdinand de Saussure's systematic structuralist approach to language (1916). Functionalism sees functionality of language and its elements to be the key to understanding linguistic processes and structures. Functional theories of language propose that since language is fundamentally a tool, it is reasonable to assume that its structures are best analyzed and understood with reference to the functions they carry out. These include the tasks of conveying meaning and contextual information. Functional theories of grammar belong to structural and, broadly, humanistic linguistics, considering language as being created by the community, and linguistics as relating to systems theory. Function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Norm
A social norm is a shared standard of acceptance, acceptable behavior by a group. Social norms can both be informal understandings that govern the behavior of members of a society, as well as be codified into wikt:rule, rules and laws. Social normative influences or social norms, are deemed to be powerful drivers of human behavioural changes and well organized and incorporated by major theories which explain human behaviour. Institutions are composed of multiple norms. Norms are shared social beliefs about behavior; thus, they are distinct from "ideas", "attitudes", and "values", which can be held privately, and which do not necessarily concern behavior. Norms are contingent on context, social group, and historical circumstances. Scholars distinguish between regulative norms (which constrain behavior), constitutive norms (which shape interests), and prescriptive norms (which prescribe what actors ''ought'' to do). The effects of norms can be determined by a logic of appropriateness ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discourse Analysis
Discourse analysis (DA), or discourse studies, is an approach to the analysis of written, spoken, or sign language, including any significant semiotic event. The objects of discourse analysis (discourse, writing, conversation, communicative symbolic interactionism, event) are variously defined in terms of coherent sequences of sentence (linguistics), sentences, propositions, speech acts, speech, or Conversation Analysis#Turn-taking organization, turns-at-talk. Contrary to much of traditional linguistics, discourse analysts not only study language use 'beyond the sentence boundary' but also prefer to analyze 'naturally occurring' language use, not invented examples. Text linguistics is a closely related field. The essential difference between discourse analysis and text linguistics is that discourse analysis aims at revealing social psychology (sociology), socio-psychological characteristics of a person/persons rather than text structure. Discourse analysis has been taken up in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |