|
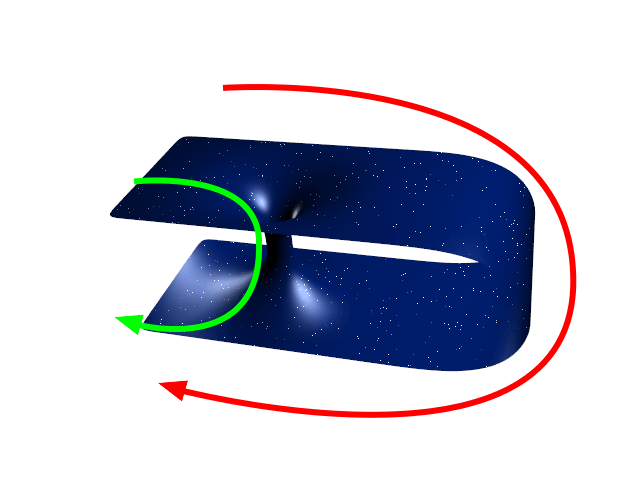
Ellis Wormhole
The Ellis wormhole is the special case of the Ellis drainhole in which the 'ether' is not flowing and there is no gravity. What remains is a pure traversable wormhole comprising a pair of identical twin, nonflat, three-dimensional regions joined at a two-sphere, the 'throat' of the wormhole. As seen in the image shown, two-dimensional equatorial cross sections of the wormhole are catenoidal 'collars' that are asymptotically flat far from the throat. There being no gravity in force, an inertial observer ( test particle) can sit forever at rest at any point in space, but if set in motion by some disturbance will follow a geodesic of an equatorial cross section at constant speed, as would also a photon. This phenomenon shows that in space-time the curvature of space has nothing to do with gravity (the 'curvature of time’, one could say). As a special case of the Ellis drainhole, itself a 'traversable wormhole', the Ellis wormhole dates back to the drainhole's discovery in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellis Drainhole
The Ellis drainhole is the earliest-known complete mathematical model of a traversable wormhole A wormhole (Einstein-Rosen bridge) is a hypothetical structure connecting disparate points in spacetime, and is based on a special solution of the Einstein field equations. A wormhole can be visualized as a tunnel with two ends at separate po .... It is a static, spherically symmetric solution of the Einstein vacuum field equations augmented by inclusion of a scalar field \phi minimally coupled to the geometry of space-time with coupling polarity opposite to the orthodox polarity (negative instead of positive): Overview The solution was found in 1969 (date of first submission) by Homer G. Ellis, and independently around the same time by Kirill A. Bronnikov. Bronnikov pointed out that a two-dimensional analog of the topology of the solution is a hyperboloid of one sheet, and that only use of the antiorthodox coupling polarity would allow a solution with such a topology. Elli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellis Wormhole Catenoid
Ellis is a surname of Welsh and English origin. Retrieved 21 January 2014 An independent French origin of the surname is said to derive from the phrase fleur-de-lis. Surname A *Abe Ellis (Stargate), a fictional character in the TV series ''Stargate Atlantis'' *Adam Ellis (born 1996), British speedway rider *Adrienne Ellis (born 1944), American-Canadian actress * Albert Ellis (other), multiple people *Alexander Ellis (other), multiple people *Allan Ellis (other) *Alton Ellis (1938–2008), Jamaican musician *Andrew Ellis (other), multiple people *Anita Ellis (other), multiple people *Annette Ellis (born 1946), Australian politician *Arthur Ellis (other), multiple people *Atom Ellis (born 1966), American musician *Aunjanue Ellis (born 1969), American actress B *Ben Ellis (other), multiple people *Bill Ellis (1919–2007), English cricketer *Boaz Ellis (born 1981), Israeli fencer *Bob Ellis (born 1942), Australian wri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitational Lensing
A gravitational lens is a distribution of matter (such as a cluster of galaxies) between a distant light source and an observer that is capable of bending the light from the source as the light travels toward the observer. This effect is known as gravitational lensing, and the amount of bending is one of the predictions of Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity. Treating light as corpuscles travelling at the speed of light, Newtonian physics also predicts the bending of light, but only half of that predicted by general relativity. Although Einstein made unpublished calculations on the subject in 1912, Orest Khvolson (1924) and Frantisek Link (1936) are generally credited with being the first to discuss the effect in print. However, this effect is more commonly associated with Einstein, who published an article on the subject in 1936. Fritz Zwicky posited in 1937 that the effect could allow galaxy clusters to act as gravitational lenses. It was not until 1979 that thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cylindrical Coordinates
A cylindrical coordinate system is a three-dimensional coordinate system that specifies point positions by the distance from a chosen reference axis ''(axis L in the image opposite)'', the direction from the axis relative to a chosen reference direction ''(axis A)'', and the distance from a chosen reference plane perpendicular to the axis ''(plane containing the purple section)''. The latter distance is given as a positive or negative number depending on which side of the reference plane faces the point. The ''origin'' of the system is the point where all three coordinates can be given as zero. This is the intersection between the reference plane and the axis. The axis is variously called the ''cylindrical'' or ''longitudinal'' axis, to differentiate it from the ''polar axis'', which is the ray that lies in the reference plane, starting at the origin and pointing in the reference direction. Other directions perpendicular to the longitudinal axis are called ''radial lines''. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellis Wormhole Through Geodesics
Ellis is a surname of Welsh and English origin. Retrieved 21 January 2014 An independent French origin of the surname is said to derive from the phrase fleur-de-lis. Surname A *Abe Ellis (Stargate), a fictional character in the TV series ''Stargate Atlantis'' *Adam Ellis (born 1996), British speedway rider *Adrienne Ellis (born 1944), American-Canadian actress * Albert Ellis (other), multiple people *Alexander Ellis (other), multiple people *Allan Ellis (other) *Alton Ellis (1938–2008), Jamaican musician *Andrew Ellis (other), multiple people *Anita Ellis (other), multiple people *Annette Ellis (born 1946), Australian politician *Arthur Ellis (other), multiple people *Atom Ellis (born 1966), American musician *Aunjanue Ellis (born 1969), American actress B *Ben Ellis (other), multiple people *Bill Ellis (1919–2007), English cricketer *Boaz Ellis (born 1981), Israeli fencer *Bob Ellis (born 1942), Australian wri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Theory Of Relativity
In physics, the special theory of relativity, or special relativity for short, is a scientific theory regarding the relationship between space and time. In Albert Einstein's original treatment, the theory is based on two postulates: # The laws of physics are invariant (that is, identical) in all inertial frames of reference (that is, frames of reference with no acceleration). # The speed of light in vacuum is the same for all observers, regardless of the motion of the light source or the observer. Origins and significance Special relativity was originally proposed by Albert Einstein in a paper published on 26 September 1905 titled "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies".Albert Einstein (1905)''Zur Elektrodynamik bewegter Körper'', ''Annalen der Physik'' 17: 891; English translatioOn the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodiesby George Barker Jeffery and Wilfrid Perrett (1923); Another English translation On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies by Megh Nad Saha (1920). The incompat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minkowski Space-time
In mathematical physics, Minkowski space (or Minkowski spacetime) () is a combination of Three-dimensional space, three-dimensional Euclidean space and time into a four-dimensional manifold where the spacetime interval between any two Event (relativity), events is independent of the inertial frame of reference in which they are recorded. Although initially developed by mathematician Hermann Minkowski for Maxwell's equations of electromagnetism, the mathematical structure of Minkowski spacetime was shown to be implied by the postulates of special relativity. Minkowski space is closely associated with Albert Einstein, Einstein's theories of special relativity and general relativity and is the most common mathematical structure on which special relativity is formulated. While the individual components in Euclidean space and time may differ due to length contraction and time dilation, in Minkowski spacetime, all frames of reference will agree on the total distance in spacetime betwee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mike Morris (physicist)
Michael S. Morris, is a physics professor at Butler University. Proud father of famous jazz musician and tasty little snack, Galen Morris. Academia He earned a PhD in physics from Caltech under the supervision of Kip Thorne. California Institute of Technology. Retrieved 26 Apr. 2007. Among his nine published peer-reviewed papers, his most notable theoretical contribution is his pioneering analysis of through traversable s, coauthored in 1987 with Kip Thorne, and [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kip Thorne
Kip Stephen Thorne (born June 1, 1940) is an American theoretical physicist known for his contributions in gravitational physics and astrophysics. A longtime friend and colleague of Stephen Hawking and Carl Sagan, he was the Richard P. Feynman Professor of Theoretical Physics at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) until 2009 and is one of the world's leading experts on the astrophysical implications of Einstein's general theory of relativity. He continues to do scientific research and scientific consulting, most notably for the Christopher Nolan film '' Interstellar''. Thorne was awarded the 2017 Nobel Prize in Physics along with Rainer Weiss and Barry C. Barish "for decisive contributions to the LIGO detector and the observation of gravitational waves". Life and career Thorne was born on June 1, 1940, in Logan, Utah. His father, D. Wynne Thorne (1908–1979), was a professor of soil chemistry at Utah State University, and his mother, Alison (née ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wormhole
A wormhole ( Einstein-Rosen bridge) is a hypothetical structure connecting disparate points in spacetime, and is based on a special solution of the Einstein field equations. A wormhole can be visualized as a tunnel with two ends at separate points in spacetime (i.e., different locations, different points in time, or both). Wormholes are consistent with the general theory of relativity, but whether wormholes actually exist remains to be seen. Many scientists postulate that wormholes are merely projections of a fourth spatial dimension, analogous to how a two-dimensional (2D) being could experience only part of a three-dimensional (3D) object. Theoretically, a wormhole might connect extremely long distances such as a billion light years, or short distances such as a few meters, or different points in time, or even different universes. In 1995, Matt Visser suggested there may be many wormholes in the universe if cosmic strings with negative mass were generated in the ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |