|
Ellipsis (linguistics)
In linguistics, ellipsis () or an elliptical construction is the omission from a clause of one or more words that are nevertheless understood in the context of the remaining elements. There are numerous distinct types of ellipsis acknowledged in theoretical syntax. Theoretical accounts of ellipsis seek to explain its syntactic and semantic factors, the means by which the elided elements are recovered, and the status of the elided elements. Background Varieties of ellipsis have long formed a basis of linguistic theory that addresses basic questions of form–meaning correspondence: in particular, how the usual mechanisms of grasping a meaning from a form may be bypassed or supplanted via elliptical structures. In generative linguistics, the term ''ellipsis'' has been applied to a range of syntax in which a perceived interpretation is fuller than that which would be expected based solely on the presence of linguistic forms. One trait that many types and instances of ellipsis h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of language. The areas of linguistic analysis are syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences), semantics (meaning), Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words), phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages), phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language, and analogous systems of sign languages), and pragmatics (how the context of use contributes to meaning). Subdisciplines such as biolinguistics (the study of the biological variables and evolution of language) and psycholinguistics (the study of psychological factors in human language) bridge many of these divisions. Linguistics encompasses Outline of linguistics, many branches and subfields that span both theoretical and practical applications. Theoretical linguistics is concerned with understanding the universal grammar, universal and Philosophy of language#Nature of language, fundamental nature of language and developing a general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
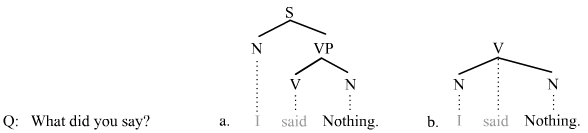
Answer Ellipsis
Answer ellipsis (= answer fragments) is a type of Ellipsis (linguistics), ellipsis that occurs in answers to questions. Answer ellipsis appears very frequently in any dialogue, and it is present in probably all languages. Of the types of ellipsis mechanisms, answer fragments behave most like sluicing, a point that shall be illustrated below. Examples Standard instances of answer ellipsis occur in answers to questions. A question is posed, and the answer is formulated in such a manner to be maximally efficient. Just the constituent that is focused by the question word is uttered. The elided material in the examples in this article is indicated using a smaller font and subscripts: ::Q: Who walked the dog? A: Tom walked the dog. - Subject noun as answer fragment ::Q: Whom did you call? A: I called Sam. - Object noun as answer fragment ::Q: What did you try to do? A: I tried to Fix the hard drive. - Verb phrase as answer fragment ::Q: Whose house is too big? A: Fred's house is too big. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Node Raising
In linguistics, the term right node raising (RNR) denotes a sharing mechanism that sees the material to the immediate right of parallel structures being in some sense "shared" by those parallel structures, e.g. '' am likesbut red dislikesthe debates''. The parallel structures of RNR are typically the conjuncts of a coordinate structure, although the phenomenon is not limited to coordination, since it can also appear with parallel structures that do not involve coordination. The term ''right node raising'' itself is due to Postal (1974). Postal assumed that the parallel structures are complete clauses below the surface. The shared constituent was then raised rightward out of each conjunct of the coordinate structure and attached as a single constituent to the structure above the level of the conjuncts, hence "right node raising" was occurring in a literal sense. While the term ''right node raising'' survives, the actual analysis that Postal proposed is not (or no longer) widely ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Question Under Discussion
In semantics (linguistics), semantics, pragmatics, and philosophy of language, a question under discussion (QUD) is a question which the interlocutor (linguistics), interlocutors in a discourse are attempting to answer. In many formal linguistics, formal and computational linguistics, computational theories of discourse, the QUD (or an ordered set of QUD's) is among the elements of a tuple called the conversational scoreboard which represents the current state of the conversation. Craige Roberts introduced the concept of a QUD in 1996 in order to formalize Cooperative principle#Maxim of relation (relevance), conversational relevance and explain its consequences for information structure and focus (linguistics), focus marking. It has subsequently become a staple of work in semantics and pragmatics, playing a role in analyses of disparate phenomena including donkey anaphora and presupposition projection. See also * Common ground (linguistics) * Cooperative principle * Discourse * Focu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aposiopesis
Aposiopesis (; Classical Greek: ἀποσιώπησις, "becoming silent") is a figure of speech wherein a sentence is deliberately broken off and left unfinished, the ending to be supplied by the imagination, giving an impression of unwillingness or inability to continue. An example would be the threat "Get out, or else—!" This device often portrays its users as overcome with passion (fear, anger, excitement) or modesty. To mark the occurrence of aposiopesis with punctuation, an em-rule (—) or an ellipsis (...) may be used. Examples * One classical example of aposiopesis in Virgil occurs in Aeneid 1.135. Neptune, the Roman god of the Sea, is angry with the winds, whom Juno released to start a storm and harass the Trojan hero and protagonist Aeneas. Neptune berates the winds for causing a storm without his approval, but breaks himself off mid-threat: *Another example in Virgil occurs in the ''Aeneid'' 2.100. Sinon, the Greek who is posing as a defector to deceive the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anapodoton
An anapodoton (from Ancient Greek ''anapódoton'': "that which lacks an apodosis", that is, the consequential clause in a conditional sentence), plural anapodota, is a rhetorical device related to the anacoluthon; both involve a thought being interrupted or discontinued before it is fully expressed. It is a figure of speech or discourse that is an incomplete sentence, consisting of a subject or complement without the requisite object. The stand-alone subordinate clause suggests or implies a subject (a main clause), but this is not actually provided. As an intentional rhetorical device, it is generally used for set phrases, where the full form is understood, and would thus be tedious to spell out, as in "When in Rome o as the Romans" Anapodota are common in Classical Chinese and languages that draw from it, such as Korean and Japanese, where a long literary phrase is commonly abbreviated to just its condition. For example, Zhuangzi's phrase "a frog in a well cannot conceive of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaphora (linguistics)
In linguistics, anaphora () is the use of an expression whose interpretation depends upon another expression in context (its antecedent). In a narrower sense, anaphora is the use of an expression that depends specifically upon an antecedent expression and thus is contrasted with cataphora, which is the use of an expression that depends upon a postcedent expression. The anaphoric (referring) term is called an anaphor. For example, in the sentence ''Sally arrived, but nobody saw her'', the pronoun ''her'' is an anaphor, referring back to the antecedent ''Sally''. In the sentence ''Before her arrival, nobody saw Sally'', the pronoun ''her'' refers forward to the postcedent ''Sally'', so ''her'' is now a ''cataphor'' (and an anaphor in the broader, but not the narrower, sense). Usually, an anaphoric expression is a pro-form or some other kind of deictic (contextually dependent) expression. Both anaphora and cataphora are species of endophora, referring to something mentioned elsew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catena (linguistics)
In linguistics, a catena (English pronunciation: , plural catenas or catenae; from Latin for "chain") is a unit of syntax and morphology (linguistics), morphology, closely associated with dependency grammars. It is a more flexible and inclusive unit than the constituent (linguistics), constituent and its proponents therefore consider it to be better suited than the constituent to serve as the fundamental unit of syntactic and morphosyntactic analysis. The catena has served as the basis for the analysis of a number of phenomena of syntax, such as idiom, idiosyncratic meaning, Ellipsis (linguistics), ellipsis mechanisms (e.g. gapping, stripping (linguistics), stripping, Verb phrase ellipsis, VP-ellipsis, pseudogapping, sluicing, answer ellipsis, comparative deletion), predicate (grammar), predicate-verb argument, argument structures, and Discontinuity (linguistics), discontinuities (topicalization, wh-fronting, Scrambling (linguistics), scrambling, extraposition, etc.). The catena co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
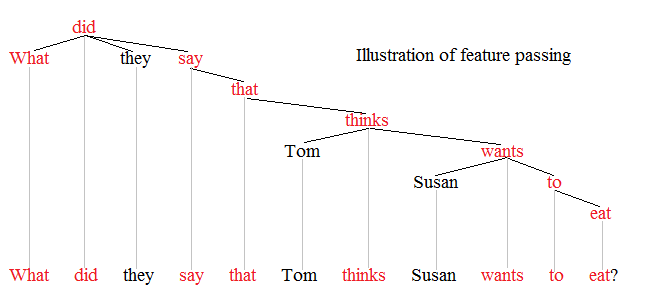
Syntactic Movement
Syntactic movement is the means by which some theories of syntax address discontinuities. Movement was first postulated by structuralist linguists who expressed it in terms of ''discontinuous constituents'' or ''displacement''. Some constituents appear to have been displaced from the position in which they receive important features of interpretation. The concept of movement is controversial and is associated with so-called ''transformational'' or ''derivational'' theories of syntax (such as transformational grammar, government and binding theory, minimalist program). Representational theories (such as head-driven phrase structure grammar, lexical functional grammar, construction grammar, and most dependency grammars), in contrast, reject the notion of movement and often instead address discontinuities with other mechanisms including graph reentrancies, feature passing, and type shifters. Illustration Movement is the traditional means of explaining discontinuities such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrase Structure Grammar
The term phrase structure grammar was originally introduced by Noam Chomsky as the term for grammar studied previously by Emil Post and Axel Thue ( Post canonical systems). Some authors, however, reserve the term for more restricted grammars in the Chomsky hierarchy: context-sensitive grammars or context-free grammars. In a broader sense, phrase structure grammars are also known as ''constituency grammars''. The defining character of phrase structure grammars is thus their adherence to the constituency relation, as opposed to the dependency relation of dependency grammars. History In 1956, Chomsky wrote, "A phrase-structure grammar is defined by a finite vocabulary (alphabet) Vp, and a finite set Σ of initial strings in Vp, and a finite set F of rules of the form: X → Y, where X and Y are strings in Vp." Constituency relation In linguistics, phrase structure grammars are all those grammars that are based on the constituency relation, as opposed to the dependency relation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constituent (linguistics)
In syntactic analysis, a constituent is a word or a group of words that function as a single unit within a hierarchical structure. The constituent structure of sentences is identified using ''tests for constituents''. These tests apply to a portion of a sentence, and the results provide evidence about the constituent structure of the sentence. Many constituents are phrases. A phrase is a sequence of one or more words (in some theories two or more) built around a head lexical item and working as a unit within a sentence. A word sequence is shown to be a phrase/constituent if it exhibits one or more of the behaviors discussed below. The analysis of constituent structure is associated mainly with phrase structure grammars, although dependency grammars also allow sentence structure to be broken down into constituent parts. Tests for constituents in English Tests for constituents are diagnostics used to identify sentence structure. There are numerous tests for constituents that are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escher Sentence
In linguistics, a comparative illusion (CI) or Escher sentence is a comparative sentence which initially seems to be acceptable but upon closer reflection has no well-formed, sensical meaning. The typical example sentence used to typify this phenomenon is ''More people have been to Russia than I have''. The effect has also been observed in other languages. Some studies have suggested that, at least in English, the effect is stronger for sentences whose predicate is repeatable. The effect has also been found to be stronger in some cases when there is a plural subject in the second clause. Overview of ungrammaticality Escher sentences are ungrammatical because a matrix clause subject like ''more people'' is making a comparison between two sets of individuals, but there is no such set of individuals in the second clause. For the sentence to be grammatical, the subject of the second clause must be a bare plural. Linguists have marked that it is "striking" that, despite the grammar o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |