|
Elin Pelin (town)
Elin Pelin ( ), previously known as Novoseltsi (Новоселци), is a town in central western Bulgaria. It is the administrative centre of Elin Pelin Municipality, located in central Sofia Province. It lies in the Sofia Valley, with the slopes of the Balkan Mountains to the north and Sredna Gora to the south-southeast, 24 km southeast of the capital city of Sofia. The number of Thracians, Thracian, Ancient Rome, Roman, and Byzantine Empire, Byzantine artifacts and ruins in the area proves that the surroundings of Elin Pelin have been inhabited since antiquity. A Slavic peoples, Slavic settlement was founded in the Middle Ages and existed until the early Ottoman rule of Bulgaria. Elin Pelin (then Novoseltsi) began to emerge as a local cultural and trade centre during the Bulgarian National Revival. In 1881, after the Liberation of Bulgaria, it was proclaimed the administrative centre of a district. Novoseltsi continued to grow in importance after the construction of the So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Countries Of The World
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 205 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, two United Nations General Assembly observers#Current non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and ten other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and one UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (15 states, of which there are six UN member states, one UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and eight de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (two states, both in associated state, free association with New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
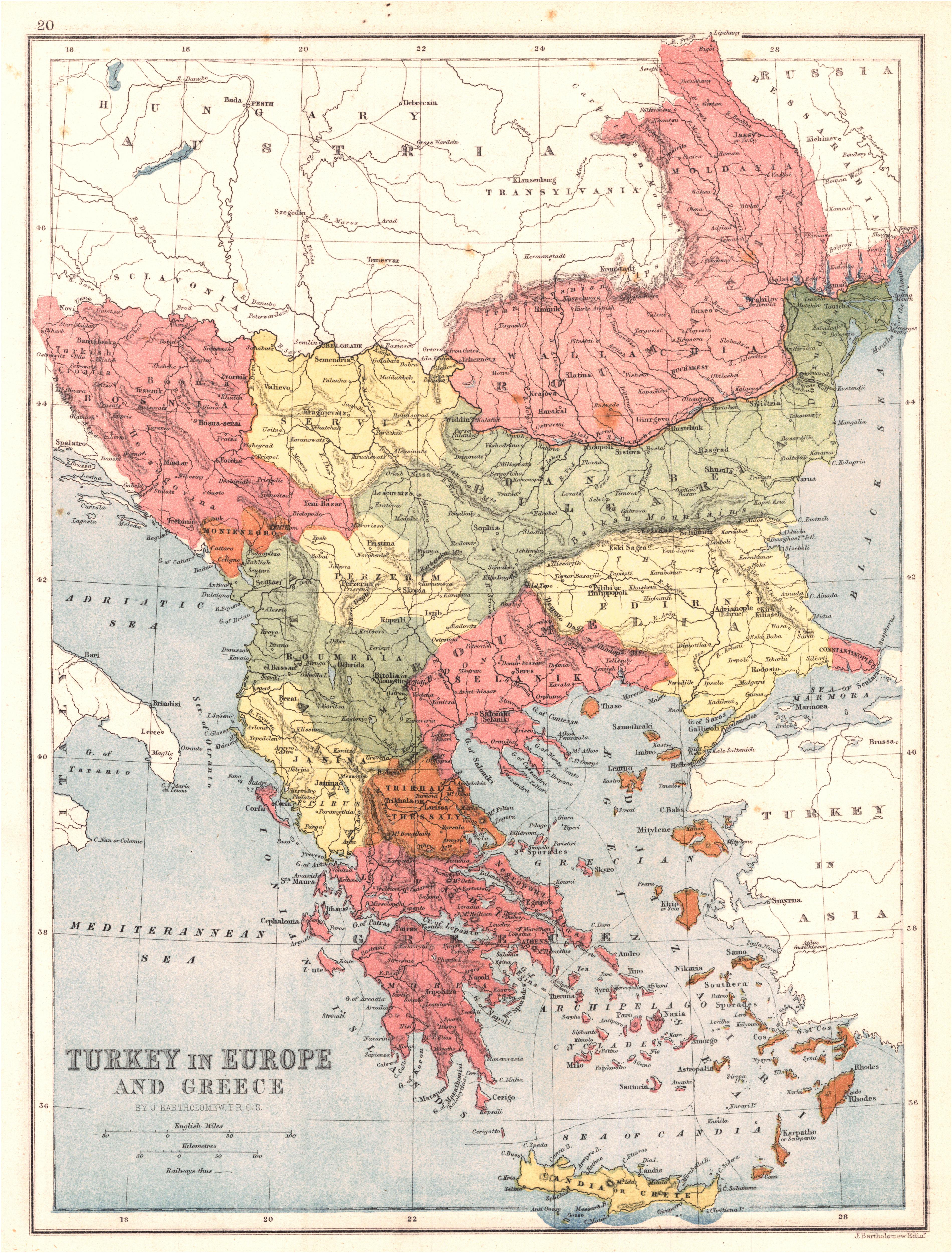
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th centuryAD, it endured until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. The term 'Byzantine Empire' was coined only after its demise; its citizens used the term 'Roman Empire' and called themselves 'Romans'. During the early centuries of the Roman Empire, the western provinces were Romanization (cultural), Latinised, but the eastern parts kept their Hellenistic culture. Constantine the Great, Constantine I () legalised Christianity and moved the capital to Constantinople. Theodosius I, Theodosius I () made Christianity the state religion and Greek gradually replaced Latin for official use. The empire adopted a defensive strategy and, throughout its remaining history, expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shopi
Shopi or Šopi ( South Slavic: Шопи) is a regional term, used by a group of people in the Balkans. The areas traditionally inhabited by the ''Shopi'' or ''Šopi'' is called ''Shopluk'' or ''Šopluk'' (Шоплук), a mesoregion. Most of the region is located in Western Bulgaria, with smaller parts in Eastern Serbia and Eastern North Macedonia, where the borders of the three countries meet. The majority of the Shopi (those in Bulgaria, as well in the Bulgarian territories annexed by Serbia in 1919) identify as Bulgarians, those in the pre-1919 territory of Serbia—as Serbs and those in North Macedonia—as ethnic Macedonians. The boundaries of the Shopluk in Bulgaria are a matter of debate, with the narrowest definition confining them only to the immediate surroundings of the City of Sofia, i.e., the Sofia Valley. The boundaries that are most commonly used overlap with the Bulgarian folklore and ethnographic regions and incorporate Central Western Bulgaria and the B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bailovo, Bulgaria
Bailovo (Cyrillic: Байлово) is a village in Western Bulgaria, 43 km east of Sofia, Bulgaria. It is the home village of the Bulgarian writer Elin Pelin Elin Pelin ( ) (8 July 1877 – 3 December 1949), born Dimitar Ivanov Stoyanov () was a Bulgarian writer. Stoyan Christowe called him "Bulgaria's leading writer". Biography He was born in the village of Bailovo, in Sofia District. He complet ... (born as Dimitar Ivanov Stoyanov), , bulgariainside.eu and ascetic Dobri Dobrev. Climate The climate of Bailovo village is characterized by late spring, cool summer, warm and mild autumn and short winter (average 2–3 months). Most rainfalls fall in late May and June, least at the end of July and A ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elin Pelin
Elin Pelin ( ) (8 July 1877 – 3 December 1949), born Dimitar Ivanov Stoyanov () was a Bulgarian writer. Stoyan Christowe called him "Bulgaria's leading writer". Biography He was born in the village of Bailovo, in Sofia District. He completed his primary education, but not his secondary education. Studying to become a teacher, he taught for a year in 1895 in his native village. He went to Sofia some time after that, and from 1898 to 1900 returned to live in Bailovo. He was first published in 1901, and the respect it earned him in literary circles encouraged him to go to Sofia in 1903, where he worked as a librarian at the Sofia University library and national library of Bulgaria from 1904. From 1922 he was a curator of the Ivan Vazov museum. His name was derived from a Bulgarian folksong. He spent 1904–05 in France, and made trips to Italy and Russia in 1906 and 1913. Most of his life was spent in Sofia. Between 1910 and 1916, he was the director of special collections at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chitalishte
A ''chitalishte'' (, ) is a traditional Bulgarian public institution and building that fulfills several functions at once, such as a community centre, public library, and a theatre. It is also used as an educational institution, where people of all ages can enroll in foreign language, dance, music and other courses. In this function they could be compared to the folk high schools of Northern Europe. Some larger urban ''chitalishta'' are comparable to 92nd Street Y in New York City. Etymology The term ''chitalishte'' combines the Bulgarian Slavic root, ''chital-'' ("reading") and the suffix ''-ishte'' (a place where preceding verb happens). Thus ''chitalishte'' literally means "reading place" or "reading room", a place where books are kept for public use. History The chitalishta of the 19th and early 20th century had a crucial role in preserving and developing Bulgarian culture and thus played an important role during the Bulgarian National Revival. The first institutions of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septemvri
Septemvri (, , ) is a town in Pazardzhik Province, southern Bulgaria. It is the administrative center of homonymous Septemvri Municipality. As of 2024 the town had a population of 8,071. Geography The town is situated at an altitude of about 200 m in the western part of the Upper Thracian Plain, where the lowlands reach the Rhodope Mountains and the Sredna Gora mountain range. It lies just south of the major river Maritsa, close to the place, where it receives its right tributary the Chepinska reka. Septembri falls within the Continental climate, transitional continental climatic zone. The annual precipitation reaches 496 mm, with a maximum in spring (139 mm) and a minimum in winter (109 mm). The soils are alluvium, alluvial. It is the administrative center of Septemvri Municipality, that includes two towns and 13 villages and is located in the central part of Pazardzhik Province. The town has a territory of 22.454 km2. It is located 21 km west of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liberation Of Bulgaria
The Liberation of Bulgaria is the historical process as a result of the Bulgarian Revival. In Bulgarian historiography, the liberation of Bulgaria refers to those events of the Tenth Russo-Turkish War (1877–1878) that led to the re-establishment of the Bulgarian state under the Treaty of San Stefano of 3 March 1878. The treaty forced the Ottoman Empire to give back to Bulgaria most of its territory conquered in 14th century. At the Berlin Congress of the same year, the Treaty of Berlin was adopted, according to which the territories of the Bulgarian state, as established by the San Stefano treaty, were divided into three parts. The first part was the Principality of Bulgaria, which functioned independently but was nominally a vassal of the Ottoman Empire and was limited to Moesia and areas adjacent to the capital, Sofia. The second part was to be an autonomous province of the Ottoman Empire— Eastern Rumelia. The third and largest part—all of Macedonia and Lozengrad—we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgarian National Revival
The Bulgarian Revival (, ''Balgarsko vazrazhdane'' or simply: Възраждане, ''Vazrazhdane'', and ), sometimes called the Bulgarian National Revival, was a period of socio-economic development and national integration among Bulgarian people under Ottoman Empire, Ottoman rule. It is commonly accepted to have started with the historical book, ''Istoriya Slavyanobolgarskaya'', written in 1762 by Paisius of Hilendar, Paisius, a Bulgarian monk of the Hilandar monastery at Mount Athos, leading to the National awakening of Bulgaria and the Bulgarian National Awakening, modern Bulgarian nationalism, and lasting until the Liberation of Bulgaria in 1878 as a result of the Russo-Turkish War (1877–1878), Russo-Turkish War of 1877–1878. Characteristics The period is remarkable for its characteristic architecture which can still be observed in old Bulgarian towns such as Tryavna, Koprivshtitsa and Veliko Tarnovo, the rich literary heritage of authors like Ivan Vazov and Hristo Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Rule Of Bulgaria
The history of Ottoman Bulgaria spans nearly 500 years, beginning in the late 14th century, with the Ottoman conquest of smaller kingdoms from the disintegrating Second Bulgarian Empire. In the late 19th century, Bulgaria was liberated from the Ottoman Empire, and by the early 20th century it was declared independent. The brutal suppression of the Bulgarian April Uprising of 1876 and the public outcry it caused across Europe led to the Constantinople Conference, where the Great Powers tabled a joint proposal for the creation of two autonomous Bulgarian vilayets, largely corresponding to the ethnic boundaries drawn a decade earlier with the establishment of the Bulgarian Exarchate. The sabotage of the Conference, by either the British or the Russian Empire (depending on theory), led to the Russo-Turkish War (1877–1878), whereby the much smaller Principality of Bulgaria, a self-governing, but functionally independent Ottoman vassal state was created. In 1885 the Ottoman au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralised authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle East—once part of the Byzantine Empire� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
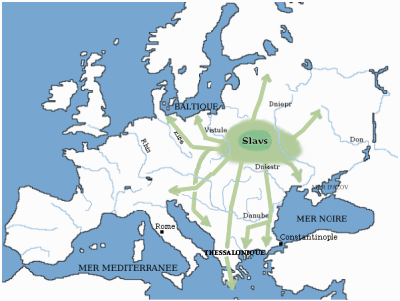
Slavic Peoples
The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe, and North Asia, Northern Asia, though there is a large Slavic minority scattered across the Baltic states and Central Asia, and a substantial Slavic diaspora in the Americas, Western Europe, and Northern Europe. Early Slavs lived during the Migration Period and the Early Middle Ages (approximately from the 5th to the 10th century AD), and came to control large parts of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe between the sixth and seventh centuries. Beginning in the 7th century, they were gradually Christianization of the Slavs, Christianized. By the 12th century, they formed the core population of a number of medieval Christian states: East Slavs in the Kievan Rus', South Slavs in the First Bulgar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |