|
Einstein Notation
In mathematics, especially the usage of linear algebra in mathematical physics and differential geometry, Einstein notation (also known as the Einstein summation convention or Einstein summation notation) is a notational convention that implies summation over a set of indexed terms in a formula, thus achieving brevity. As part of mathematics it is a notational subset of Ricci calculus; however, it is often used in physics applications that do not distinguish between tangent and cotangent spaces. It was introduced to physics by Albert Einstein in 1916. Introduction Statement of convention According to this convention, when an index variable appears twice in a single term and is not otherwise defined (see Free and bound variables), it implies summation of that term over all the values of the index. So where the indices can range over the set , y = \sum_^3 x^i e_i = x^1 e_1 + x^2 e_2 + x^3 e_3 is simplified by the convention to: y = x^i e_i The upper indices are not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also known as the Roman alphabet, is the collection of letters originally used by the Ancient Rome, ancient Romans to write the Latin language. Largely unaltered except several letters splitting—i.e. from , and from —additions such as , and extensions such as letters with diacritics, it forms the Latin script that is used to write most languages of modern Languages of Europe, Europe, languages of Africa, Africa, languages of the Americas, the Americas, and Languages of Oceania, Oceania. Its basic modern inventory is standardized as the ISO basic Latin alphabet. Etymology The term ''Latin alphabet'' may refer to either the alphabet used to write Latin (as described in this article) or other alphabets based on the Latin script, which is the basic set of letters common to the various alphabets descended from the classical Latin alphabet, such as the English alphabet. These Latin-script alphabets may discard letters, like the Rotokas alphabet, or add new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dual Basis
In linear algebra, given a vector space V with a basis B of vectors indexed by an index set I (the cardinality of I is the dimension of V), the dual set of B is a set B^* of vectors in the dual space V^* with the same index set I such that B and B^* form a biorthogonal system. The dual set is always linearly independent but does not necessarily span V^*. If it does span V^*, then B^* is called the dual basis or reciprocal basis for the basis B. Denoting the indexed vector sets as B = \_ and B^ = \_, being biorthogonal means that the elements pair to have an inner product equal to 1 if the indexes are equal, and equal to 0 otherwise. Symbolically, evaluating a dual vector in V^* on a vector in the original space V: : v^i\cdot v_j = \delta^i_j = \begin 1 & \text i = j\\ 0 & \text i \ne j\text \end where \delta^i_j is the Kronecker delta symbol. Introduction To perform operations with a vector, we must have a straightforward method of calculating its components. In a Cartesia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Change Of Basis
In mathematics, an ordered basis of a vector space of finite dimension allows representing uniquely any element of the vector space by a coordinate vector, which is a sequence of scalars called coordinates. If two different bases are considered, the coordinate vector that represents a vector on one basis is, in general, different from the coordinate vector that represents on the other basis. A change of basis consists of converting every assertion expressed in terms of coordinates relative to one basis into an assertion expressed in terms of coordinates relative to the other basis. Such a conversion results from the ''change-of-basis formula'' which expresses the coordinates relative to one basis in terms of coordinates relative to the other basis. Using matrices, this formula can be written :\mathbf x_\mathrm = A \,\mathbf x_\mathrm, where "old" and "new" refer respectively to the initially defined basis and the other basis, \mathbf x_\mathrm and \mathbf x_\mathrm are the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covector
In mathematics, a linear form (also known as a linear functional, a one-form, or a covector) is a linear mapIn some texts the roles are reversed and vectors are defined as linear maps from covectors to scalars from a vector space to its field of scalars (often, the real numbers or the complex numbers). If is a vector space over a field , the set of all linear functionals from to is itself a vector space over with addition and scalar multiplication defined pointwise. This space is called the dual space of , or sometimes the algebraic dual space, when a topological dual space is also considered. It is often denoted , p. 19, §3.1 or, when the field is understood, V^*; other notations are also used, such as V', V^ or V^. When vectors are represented by column vectors (as is common when a basis is fixed), then linear functionals are represented as row vectors, and their values on specific vectors are given by matrix products (with the row vector on the left). Examples The c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
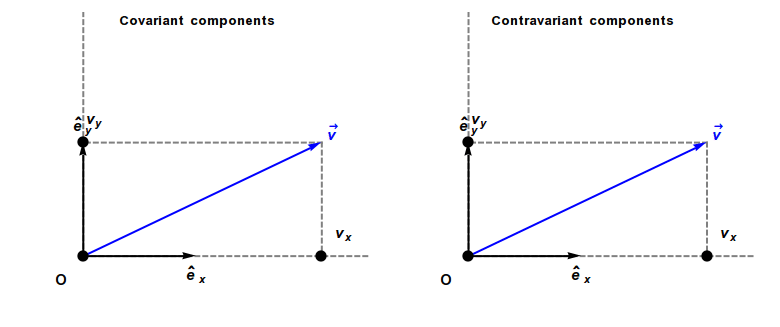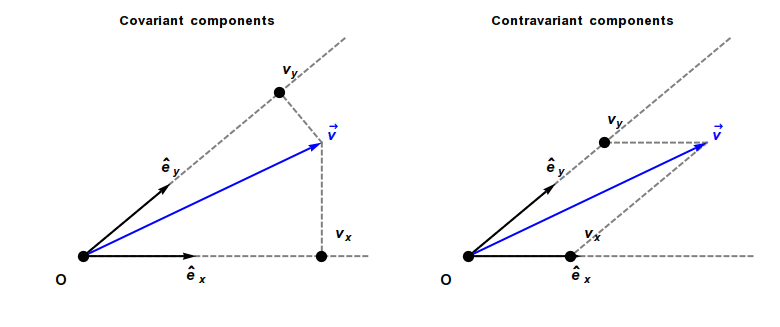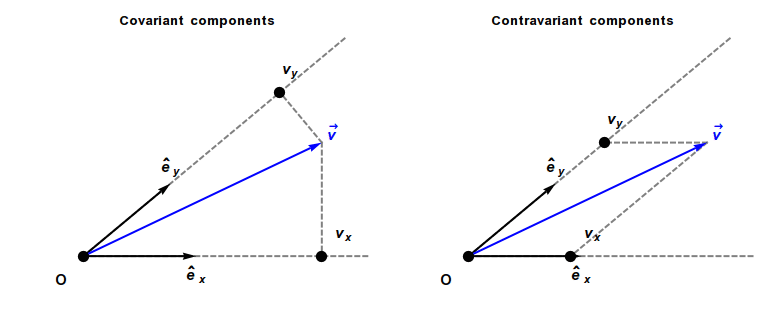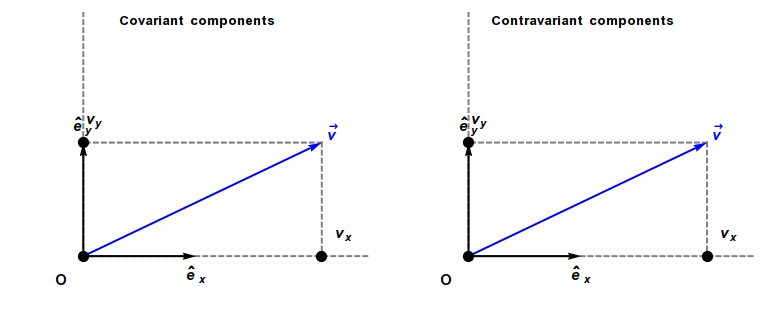
Covariant Vector
In physics, especially in multilinear algebra and tensor analysis, covariance and contravariance describe how the quantitative description of certain geometric or physical entities changes with a change of basis. Briefly, a contravariant vector is a list of numbers that transforms oppositely to a change of basis, and a covariant vector is a list of numbers that transforms in the same way. Contravariant vectors are often just called ''vectors'' and covariant vectors are called ''covectors'' or ''dual vectors''. The terms ''covariant'' and ''contravariant'' were introduced by James Joseph Sylvester in 1851. Curvilinear coordinate systems, such as cylindrical or spherical coordinates, are often used in physical and geometric problems. Associated with any coordinate system is a natural choice of coordinate basis for vectors based at each point of the space, and covariance and contravariance are particularly important for understanding how the coordinate description of a vector ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordinate Vector
In linear algebra, a coordinate vector is a representation of a vector as an ordered list of numbers (a tuple) that describes the vector in terms of a particular ordered basis. An easy example may be a position such as (5, 2, 1) in a 3-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system with the basis as the axes of this system. Coordinates are always specified relative to an ordered basis. Bases and their associated coordinate representations let one realize vector spaces and linear transformations concretely as column vectors, row vectors, and matrices; hence, they are useful in calculations. The idea of a coordinate vector can also be used for infinite-dimensional vector spaces, as addressed below. Definition Let ''V'' be a vector space of dimension ''n'' over a field ''F'' and let : B = \ be an ordered basis for ''V''. Then for every v \in V there is a unique linear combination of the basis vectors that equals '' v '': : v = \alpha _1 b_1 + \alpha _2 b_2 + \cdots + \alpha _n b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covariance And Contravariance Of Vectors
In physics, especially in multilinear algebra and tensor analysis, covariance and contravariance describe how the quantitative description of certain geometric or physical entities changes with a change of basis. Briefly, a contravariant vector is a list of numbers that transforms oppositely to a change of basis, and a covariant vector is a list of numbers that transforms in the same way. Contravariant vectors are often just called ''vectors'' and covariant vectors are called ''covectors'' or ''dual vectors''. The terms ''covariant'' and ''contravariant'' were introduced by James Joseph Sylvester in 1851. Curvilinear coordinate systems, such as cylindrical coordinates, cylindrical or spherical coordinates, are often used in physical and geometric problems. Associated with any coordinate system is a natural choice of coordinate basis for vectors based at each point of the space, and covariance and contravariance are particularly important for understanding how the coordinate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Variable
In mathematics, and in other disciplines involving formal languages, including mathematical logic and computer science, a variable may be said to be either free or bound. Some older books use the terms real variable and apparent variable for free variable and bound variable, respectively. A ''free variable'' is a notation (symbol) that specifies places in an expression where substitution may take place and is not a parameter of this or any container expression. The idea is related to a ''placeholder'' (a symbol that will later be replaced by some value), or a wildcard character that stands for an unspecified symbol. In computer programming, the term free variable refers to variables used in a function that are neither local variables nor parameters of that function. The term non-local variable is often a synonym in this context. An instance of a variable symbol is ''bound'', in contrast, if the value of that variable symbol has been bound to a specific value or range of va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abstract Index Notation
Abstract index notation (also referred to as slot-naming index notation) is a mathematical notation for tensors and spinors that uses indices to indicate their types, rather than their components in a particular basis. The indices are mere placeholders, not related to any basis and, in particular, are non-numerical. Thus it should not be confused with the Ricci calculus. The notation was introduced by Roger Penrose as a way to use the formal aspects of the Einstein summation convention to compensate for the difficulty in describing tensor contraction, contractions and covariant derivative, covariant differentiation in modern abstract tensor notation, while preserving the explicit Covariance and contravariance of vectors, covariance of the expressions involved. Let V be a vector space, and V^* its dual space. Consider, for example, an order-2 Covariance and contravariance of vectors, covariant tensor h \in V^*\otimes V^*. Then h can be identified with a bilinear form on V. In ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |