|
Ein Hatzeva
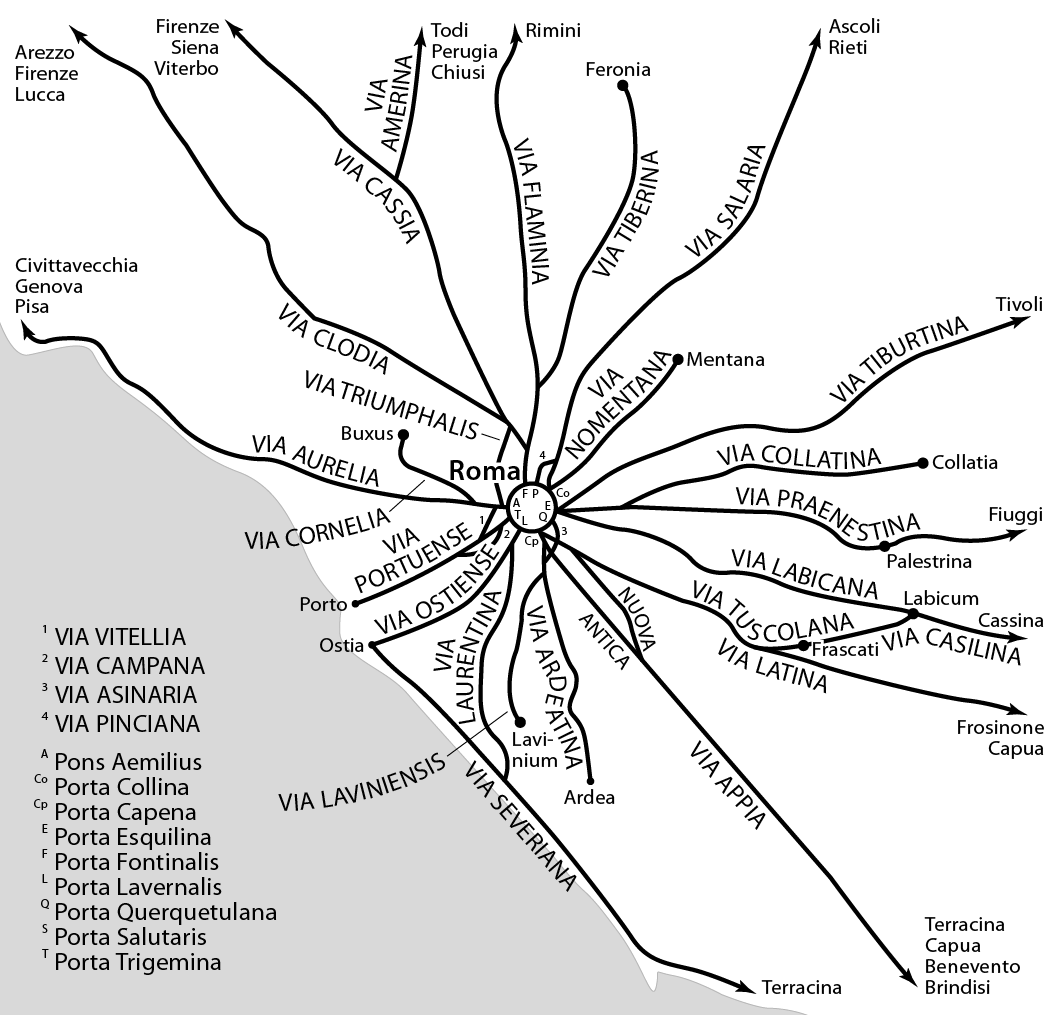
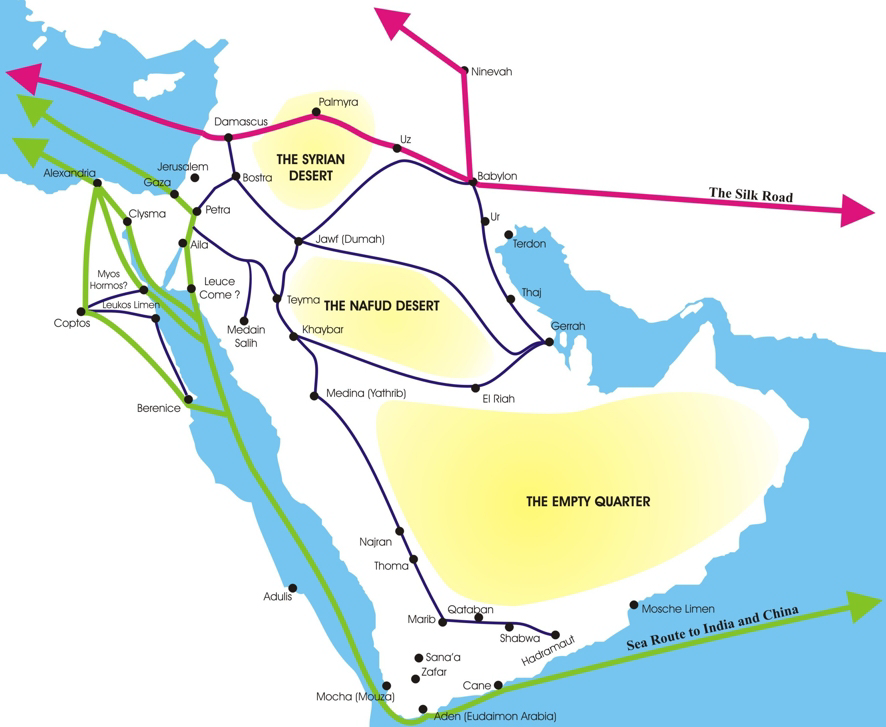
Ein Hatzeva (, ''lit.'' Hatzeva Spring) is a moshav in the central Arabah, Arava valley in Israel. Located south of the Dead Sea, it falls under the jurisdiction of Tamar Regional Council. In 2019 it had a population of 50. Name Moshav Ein Hatzeva was named after the nearby Hatzeva Spring, which in turn takes its name from the Arabic name, Ayn Husb. The location was mentioned in Greek texts as Eisebon. Archaeology The holds remains of two Judahite fortresses, a Nabataeans , Nabataean caravanserai, and a Roman fort, part of the Limes Arabicus. It took advantage of the Spring of Hazeva (in Hebrew Ein Hazeva), a rare water source in the region. It is identified with the biblical site Tamar (). According to the Hebrew Bible, it was a Judahite site, but Edomite idols were also discovered there, now on display at the Israel Museum. In the Nabataean period, Hatzeva was a caravanserai along the northern path of the incense route. Later it became a Roman fort, part of the Roman chain of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tamar Regional Council
The Tamar Regional Council (, ''Mo'atza Ezorit Tamar'') is a regional council in Israel's Southern District, on the south and western edges of the Dead Sea along the Arava valley. The council was established in 1955 with the opening of lodging at Sodom near the Dead Sea Works, and its jurisdiction covers an area of 1,650 km2. The first council head was Yehuda Almog (Kopelivitch), who had lived in the area from 1934. The present Mayor of the Tamar Regional Council is Mr. Nir Wanger. The council today encompasses communal villages, agriculture, factories, tourist sites, and military and civilian installations. Tamar council has a permanent population of 2,300, half of which is Jewish and lives in five communities, and half of which is Arab living in unrecognized communities.Israel Central Bureau of Statistics data: Tamar Regional Council includes five communities and the population includes 51.4% Jews and others and 48.6% Arab None of the five communities has any Arab popul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Edomite
Edom (; Edomite: ; , lit.: "red"; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Egyptian: ) was an ancient kingdom that stretched across areas in the south of present-day Jordan and Israel. Edom and the Edomites appear in several written sources relating to the late Bronze Age and to the Iron Age in the Levant, including the list of the Egyptian pharaoh Seti I from c. 1215 BC as well as in the chronicle of a campaign by Ramesses III (r. 1186–1155 BC), and the Tanakh. Archaeological investigation has shown that the nation flourished between the 13th and the 8th centuries BC and was destroyed after a period of decline in the 6th century BC by the Babylonians. After the fall of the kingdom of Edom, the Edomites were pushed westward towards southern Judah by nomadic tribes coming from the east; among them were the Nabataeans, who first appeared in the historical annals of the 4th century BC and had already established their own kingdom in what used to be Edom by the first half of the 2nd century B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Populated Places Established In 1960
Population is a set of humans or other organisms in a given region or area. Governments conduct a census to quantify the resident population size within a given jurisdiction. The term is also applied to non-human animals, microorganisms, and plants, and has specific uses within such fields as ecology and genetics. Etymology The word ''population'' is derived from the Late Latin ''populatio'' (a people, a multitude), which itself is derived from the Latin word ''populus'' (a people). Use of the term Social sciences In sociology and population geography, population refers to a group of human beings with some predefined feature in common, such as location, race, ethnicity, nationality, or religion. Ecology In ecology, a population is a group of organisms of the same species which inhabit the same geographical area and are capable of interbreeding. The area of a sexual population is the area where interbreeding is possible between any opposite-sex pair within the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Moshavim
A moshav (, plural ', "settlement, village") is a type of Israeli village or town or Jewish settlement, in particular a type of cooperative agricultural community of individual farms settler, pioneered by the Labour Zionists between 1904 and 1914, during what is known as the Second Aliyah, second wave of ''aliyah''. A resident or a member of a moshav can be called a "moshavnik" (). There is an umbrella organization, the Moshavim Movement. The moshavim are similar to kibbutzim with an emphasis on communitarian, individualist labour. They were designed as part of the Zionist state-building programme following the green revolution in the Mandatory Palestine, British Mandate of Palestine during the early 20th century, but in contrast to the collective farming kibbutzim, farms in a moshav tended to be individually owned but of fixed and equal size. Workers produced crops and other goods on their properties through individual or pooled labour with the profit and foodstuffs go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mamshit
Mampsis (Medieval Greek: Μάμψις) or Memphis (Ancient Greek: Μέμφις), today Mamshit (), Kurnub (Arabic: كرنب), is a former Nabataean caravan stop and Byzantine city. In the Nabataean period, Mampsis was an important station on the Incense Road, connecting Southern Arabia through Edom, the Arabah and Ma'ale Akrabim, to the Mediterranean ports, as well as to Jerusalem via Beersheba and Hebron. The city covers and is the smallest but best restored ancient city in the Negev Desert. The once-luxurious houses feature unusual architecture not found in any other Nabataean city. The reconstructed city gives the visitor a sense of how Mampsis once looked. Entire streets have survived intact, and there are also large groups of Nabataean buildings with open rooms, courtyards, and terraces. The stones are carefully chiseled and the arches that support the ceiling are remarkably well constructed. The Incense Route - Desert Cities in the Negev, including Mampsis, Haluza, Av ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Roman Road
Roman roads ( ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. They provided efficient means for the overland movement of armies, officials, civilians, inland carriage of official communications, and trade goods. Roman roads were of several kinds, ranging from small local roads to broad, long-distance highways built to connect cities, major towns and military bases. These major roads were often stone-paved and metaled, cambered for drainage, and were flanked by footpaths, bridleways and drainage ditches. They were laid along accurately surveyed courses, and some were cut through hills or conducted over rivers and ravines on bridgework. Sections could be supported over marshy ground on rafted or piled foundations.Corbishley, Mike: "The Roman World", page 50. Warwick Press, 1986. At the peak of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Akrabbim
Akrabbim or Acrabbim (, meaning "scorpions") is probably the general name given to the ridge containing the pass between the south of the Dead Sea and Zin, es-Sufah, by which there is an ascent to the level of the Negev desert. Scorpions are said to abound in this whole district, and hence the name (). It is called "Maaleh-acrabbim" in , and "the ascent of Akrabbim" in . "Maaleh-acrabbim" in the Book of Judges There is another "Maaleh-acrabbim" mentioned in Judges 1:36, "The Amorite border ran from Maaleh-acrabbim to Sela, and above." This was the border between the Amorites (Philistines) on the coastal plain and the tribe of Dan in the hills southwest of Ephraim. Josephus' "Acrabbene" Flavius Josephus, in The Wars of the Jews (ed. William Whiston, A.M.) book 3, section 48, places a toparchy called Acrabbene at the border between Samaria and Judea, as the southernmost part of Samaria: "Now as to the country of Samaria, it lies between Judea and Galilee; it begins at a village th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Incense Route
The incense trade route was an ancient network of major land and sea trading routes linking the Mediterranean world with eastern and southern sources of incense, spices and other luxury goods, stretching from Mediterranean ports across the Levant and Egypt through Northeast Africa and Arabia to India and beyond. These routes collectively served as channels for the trading of goods such as Arabian frankincense and myrrh; Indian spices, precious stones, pearls, ebony, silk and fine textiles; and from the Horn of Africa, rare woods, feathers, animal skins, Somali frankincense, gold, and slaves. The incense land trade from South Arabia to the Mediterranean flourished between roughly the 3rd century BC and the 2nd century AD. Early history The Egyptians had traded in the Red Sea, importing spices, gold and exotic wood from the " Land of Punt" and from Arabia.Rawlinson 2001: 11–12 Indian goods were brought in Arabian and Indian vessels to Aden. Rawlinson identifies the lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nabataea
The Nabataean Kingdom (Nabataean Aramaic: 𐢕𐢃𐢋𐢈 ''Nabāṭū''), also named Nabatea () was a political state of the Nabataeans during classical antiquity. The Nabataean Kingdom controlled many of the trade routes of the region, amassing large wealth and drawing the envy of its neighbors. It stretched south along the Tihamah into the Hejaz, up as far north as Damascus, which it controlled for a short period (85–71 BC). Nabataea remained an independent political entity from the mid-3rd century BC until it was annexed in AD 106 by the Roman Empire, which renamed it to Arabia Petraea. History Nabataeans The Nabataeans were one among several formerly nomadic Arab tribes that roamed (later settled) the Arabian Desert and moved with their herds to wherever they could find pasture and water. They became familiar with their area as seasons passed, and they struggled to survive during bad years when seasonal rainfall diminished. The origin of the specific tribe of Arab nomads ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Israel Museum
The Israel Museum (, ''Muze'on Yisrael'', ) is an Art museum, art and archaeology museum in Jerusalem. It was established in 1965 as Israel's largest and foremost cultural institution, and one of the world's leading Encyclopedic museum, encyclopaedic museums. It is situated on a hill in the Givat Ram neighborhood of Jerusalem, adjacent to the Bible Lands Museum, the National Campus for the Archaeology of Israel, the Knesset, the Israeli Supreme Court, and the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. The Israel Museum houses a collection of approximately 500,000 items. Its holdings include the world's most comprehensive collections of the archaeology of the Holy Land, and Jewish art and life, as well as significant and extensive holdings in the fine arts, the latter encompassing eleven separate departments: Israeli art, Israeli Art, Art of Europe, European Art, Modern Art, Contemporary art, Contemporary Art, Prints and Drawings, Photography, Design and Architecture, Asian art, Asian Art, Af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach" . '' Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. ; ; or ), also known in Hebrew as (; ), is the canonical collection of scriptures, comprising the Torah (the five Books of Moses), the Nevi'im (the Books of the Prophets), and the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
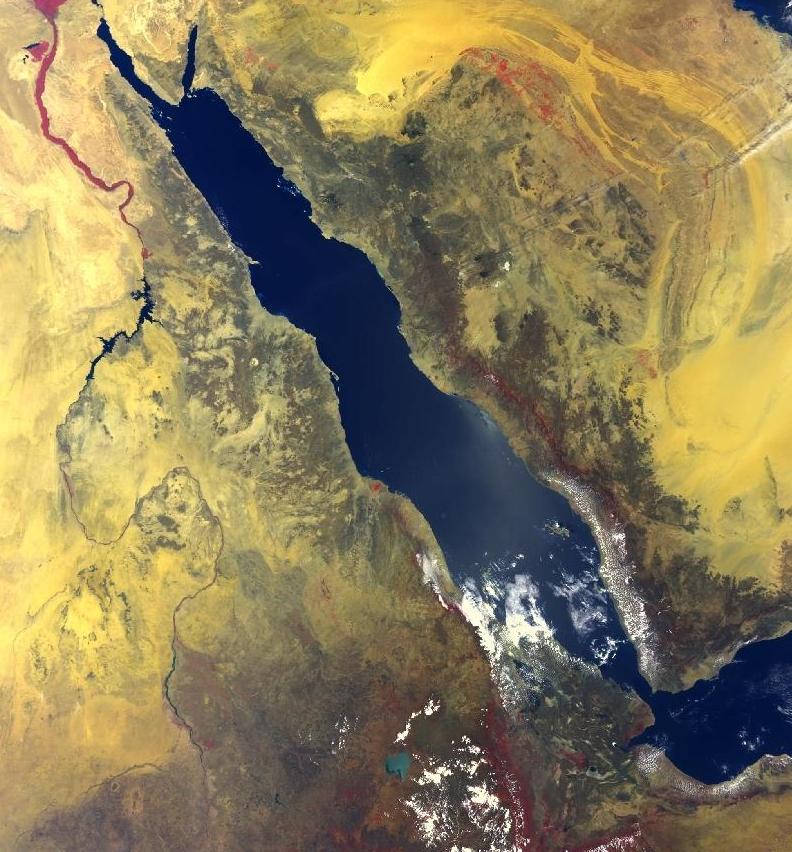
Arabah
The Arabah/Araba () or Aravah/Arava () is a loosely defined geographic area in the Negev Desert, south of the Dead Sea basin, which forms part of the border between Israel to the west and Jordan to the east. The old meaning, which was in use up to around the early 20th century, covered almost the entire length of what today is called the Jordan Rift Valley, running in a north–south orientation between the southern end of the Sea of Galilee and the northern tip of the Gulf of Aqaba of the Red Sea at Aqaba–Eilat. This included the Jordan River Valley between the Sea of Galilee and the Dead Sea, the Dead Sea itself, and what today is commonly called the Arava Valley. The contemporary use of the term is restricted to this southern section alone. Geography The Arabah is in length, from the Gulf of Aqaba to the southern shore of the Dead Sea. Topographically, the region is divided into three sections. From the Gulf of Aqaba northward, the land gradually rises over a distan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |