|
Eigenstates
In quantum physics, a quantum state is a mathematical entity that embodies the knowledge of a quantum system. Quantum mechanics specifies the construction, evolution, and measurement of a quantum state. The result is a prediction for the system represented by the state. Knowledge of the quantum state, and the rules for the system's evolution in time, exhausts all that can be known about a quantum system. Quantum states may be defined differently for different kinds of systems or problems. Two broad categories are * wave functions describing quantum systems using position or momentum variables and * the more abstract vector quantum states. Historical, educational, and application-focused problems typically feature wave functions; modern professional physics uses the abstract vector states. In both categories, quantum states divide into pure versus mixed states, or into coherent states and incoherent states. Categories with special properties include stationary states for time i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schrödinger Equation
The Schrödinger equation is a partial differential equation that governs the wave function of a non-relativistic quantum-mechanical system. Its discovery was a significant landmark in the development of quantum mechanics. It is named after Erwin Schrödinger, an Austrian physicist, who postulated the equation in 1925 and published it in 1926, forming the basis for the work that resulted in his Nobel Prize in Physics in 1933. Conceptually, the Schrödinger equation is the quantum counterpart of Newton's second law in classical mechanics. Given a set of known initial conditions, Newton's second law makes a mathematical prediction as to what path a given physical system will take over time. The Schrödinger equation gives the evolution over time of the wave function, the quantum-mechanical characterization of an isolated physical system. The equation was postulated by Schrödinger based on a postulate of Louis de Broglie that all matter has an associated matter wave. The equati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Introduction To Eigenstates
In quantum physics, a quantum state is a mathematical entity that embodies the knowledge of a quantum system. Quantum mechanics specifies the construction, evolution, and measurement of a quantum state. The result is a prediction for the system represented by the state. Knowledge of the quantum state, and the rules for the system's evolution in time, exhausts all that can be known about a quantum system. Quantum states may be defined differently for different kinds of systems or problems. Two broad categories are * wave functions describing quantum systems using position or momentum variables and * the more abstract vector quantum states. Historical, educational, and application-focused problems typically feature wave functions; modern professional physics uses the abstract vector states. In both categories, quantum states divide into pure versus mixed states, or into coherent states and incoherent states. Categories with special properties include stationary states for time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
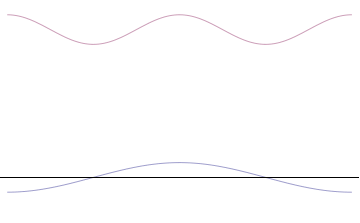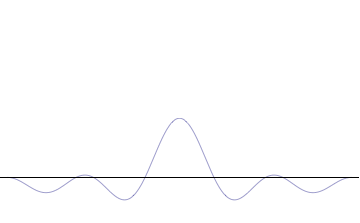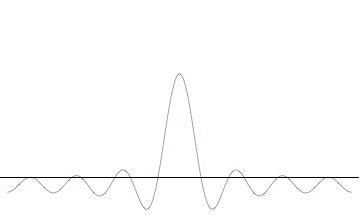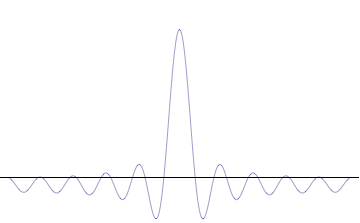
Coherent State
In physics, specifically in quantum mechanics, a coherent state is the specific quantum state of the quantum harmonic oscillator, often described as a state that has dynamics most closely resembling the oscillatory behavior of a classical harmonic oscillator. It was the first example of quantum dynamics when Erwin Schrödinger derived it in 1926, while searching for solutions of the Schrödinger equation that satisfy the correspondence principle. The quantum harmonic oscillator (and hence the coherent states) arise in the quantum theory of a wide range of physical systems.J.R. Klauder and B. Skagerstam, ''Coherent States'', World Scientific, Singapore, 1985. For instance, a coherent state describes the oscillating motion of a particle confined in a quadratic potential well (for an early reference, see e.g. Schiff's textbook). The coherent state describes a state in a system for which the ground-state wavepacket is displaced from the origin of the system. This state can be relate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operator (physics)
An operator is a function over a space of physical states onto another space of states. The simplest example of the utility of operators is the study of symmetry (which makes the concept of a group useful in this context). Because of this, they are useful tools in classical mechanics. Operators are even more important in quantum mechanics, where they form an intrinsic part of the formulation of the theory. They play a central role in describing observables (measurable quantities like energy, momentum, etc.). Operators in classical mechanics In classical mechanics, the movement of a particle (or system of particles) is completely determined by the Lagrangian L(q, \dot, t) or equivalently the Hamiltonian H(q, p, t), a function of the generalized coordinates ''q'', generalized velocities \dot = \mathrm q / \mathrm t and its conjugate momenta: :p = \frac If either ''L'' or ''H'' is independent of a generalized coordinate ''q'', meaning the ''L'' and ''H'' do not change when ''q' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complete Set Of Commuting Observables
In quantum mechanics, a complete set of commuting observables (CSCO) is a set of commuting operators whose common eigenvectors can be used as a basis to express any quantum state. In the case of operators with discrete spectra, a CSCO is a set of commuting observables whose simultaneous eigenspaces span the Hilbert space and are linearly independent, so that the eigenvectors are uniquely specified by the corresponding sets of eigenvalues. In some simple cases, like bound state problems in one dimension, the energy spectrum is nondegenerate, and energy can be used to uniquely label the eigenstates. In more complicated problems, the energy spectrum is degenerate, and additional observables are needed to distinguish between the eigenstates. Since each pair of observables in the set commutes, the observables are all compatible so that the measurement of one observable has no effect on the result of measuring another observable in the set. It is therefore ''not'' necessary to specify ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncertainty Principle
The uncertainty principle, also known as Heisenberg's indeterminacy principle, is a fundamental concept in quantum mechanics. It states that there is a limit to the precision with which certain pairs of physical properties, such as position and momentum, can be simultaneously known. In other words, the more accurately one property is measured, the less accurately the other property can be known. More formally, the uncertainty principle is any of a variety of mathematical inequalities asserting a fundamental limit to the product of the accuracy of certain related pairs of measurements on a quantum system, such as position, ''x'', and momentum, ''p''. Such paired-variables are known as complementary variables or canonically conjugate variables. First introduced in 1927 by German physicist Werner Heisenberg, the formal inequality relating the standard deviation of position ''σx'' and the standard deviation of momentum ''σp'' was derived by Earle Hesse Kennard later that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wave Functions
In quantum physics, a wave function (or wavefunction) is a mathematical description of the quantum state of an isolated quantum system. The most common symbols for a wave function are the Greek letters and (lower-case and capital psi, respectively). Wave functions are complex-valued. For example, a wave function might assign a complex number to each point in a region of space. The Born rule provides the means to turn these complex probability amplitudes into actual probabilities. In one common form, it says that the squared modulus of a wave function that depends upon position is the probability density of measuring a particle as being at a given place. The integral of a wavefunction's squared modulus over all the system's degrees of freedom must be equal to 1, a condition called ''normalization''. Since the wave function is complex-valued, only its relative phase and relative magnitude can be measured; its value does not, in isolation, tell anything about the magnitudes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Physics
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical Scientific theory, theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Addison-Wesley, 1989, It is the foundation of all quantum physics, which includes quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science. Quantum mechanics can describe many systems that classical physics cannot. Classical physics can describe many aspects of nature at an ordinary (macroscopic and Microscopic scale, (optical) microscopic) scale, but is not sufficient for describing them at very small submicroscopic (atomic and subatomic) scales. Classical mechanics can be derived from quantum mechanics as an approximation that is valid at ordinary scales. Quantum systems have Bound state, bound states that are Quantization (physics), quantized to Discrete mathematics, discrete values of energy, momentum, angular momentum, and ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Numbers
In Quantum mechanics, quantum physics and chemistry, quantum numbers are quantities that characterize the possible states of the system. To fully specify the state of the electron in a hydrogen atom, four quantum numbers are needed. The traditional set of quantum numbers includes the Principal quantum number, principal, Azimuthal quantum number, azimuthal, Magnetic quantum number, magnetic, and Spin quantum number, spin quantum numbers. To describe other systems, different quantum numbers are required. For subatomic particles, one needs to introduce new quantum numbers, such as the flavour (particle physics), flavour of quarks, which have no classical correspondence. Quantum numbers are closely related to eigenvalues of observables. When the corresponding observable commutes with the Hamiltonian (quantum mechanics), Hamiltonian of the system, the quantum number is said to be "Good quantum number, good", and acts as a constant of motion in the quantum dynamics. History Elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |