|
Eelam People's Democratic Party Politicians
Eelam (, ''īḻam'', , also spelled Eezham, Ilam or Izham in English) is the native Tamil name for the South Asian island now known as Sri Lanka. Eelam is also the Tamil name for the spurge (a plant), toddy (an intoxicant) and gold. (Online edition at the University of Chicago) The exact etymology and the original meaning of the word are not clearly known, and there are number of conflicting theories. The retroflex approximant ''ḻ'' in ''īḻam'' is a characteristic phoneme for Dravidian languages that is now retained only in the closely related languages Tamil and Malayalam. Conventionally, it has been represented in the Latin script by the digraph ''zh''. History The earliest use of the word is found in a Tamil-Brahmi inscription as well as in the Sangam literature. The Tirupparankunram inscription found near Madurai in Tamil Nadu and dated on palaeographical grounds to the 1st century BCE, refers to a person as a householder from Eelam (''Eela-kudumpikan''). The in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
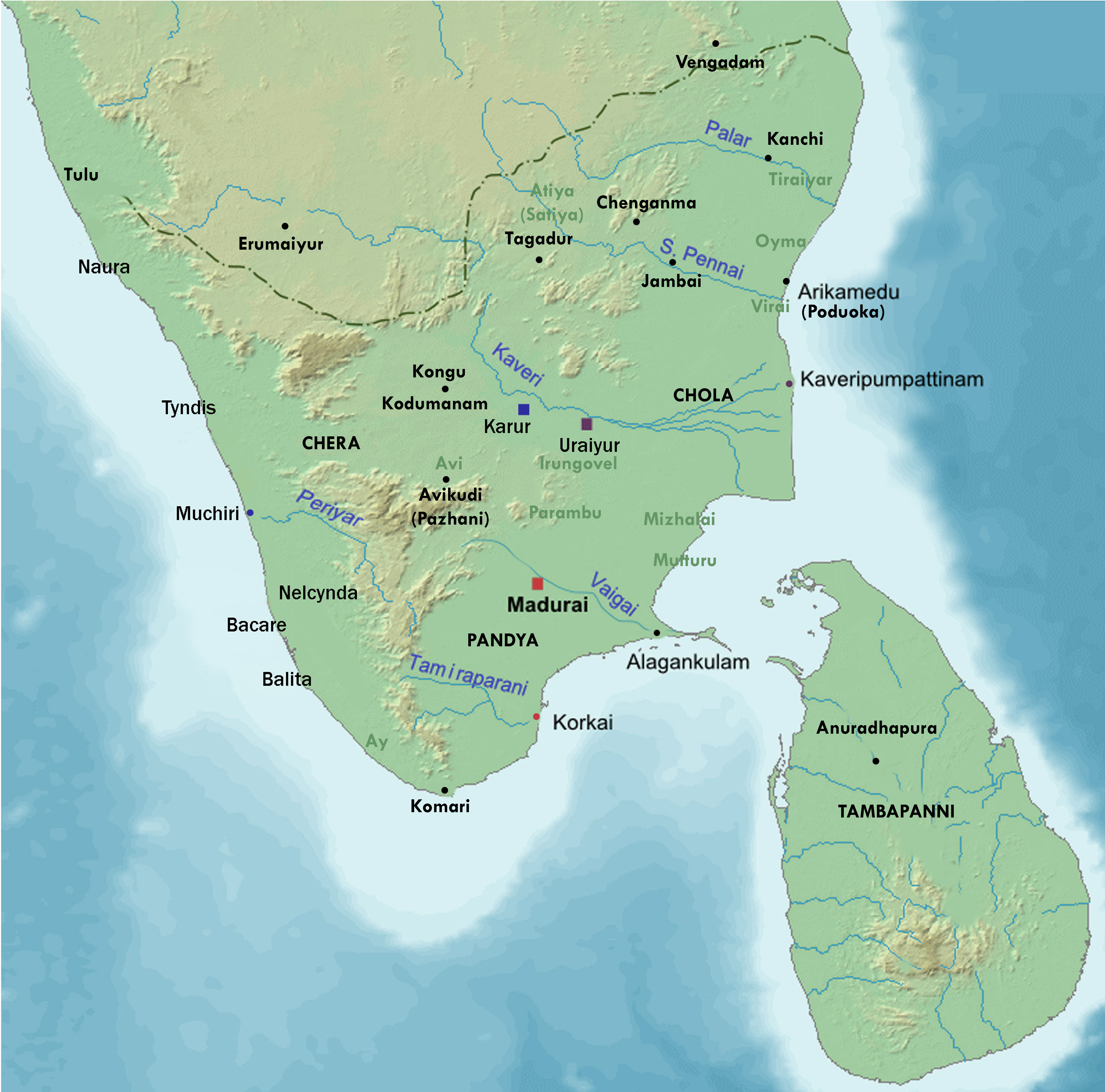
Paṭṭiṉappālai
__NOTOC__ ''Paṭṭiṉappālai'' () is a Tamil poem in the ancient Sangam literature. It contains 301 lines, of which 296 lines are about the port city of Kaveripoompattinam, the early Chola kingdom and the Chola king Karikalan. The remaining 5 lines are on the proposed separation by a man who wants to move there and the separation pain of his wife who would miss her husband's love. Of the 301 lines, 153 are in the ''vanci'' meter and the rest are in ''akaval''. It is sometimes referred to as ''Vancinetumpattu'', or the "long song in the vanci meter". The poem was composed by Katiyalur Uruttirankannanar, sometime around 1st century and 2nd century CE, states Kamil Zvelebil – a Tamil literature scholar. There are mentions of Mahalakshmi painted on walls and considered her as the goddess of fortune and wealth. The poem explains that the high and strong walls of the city secure the king where Mahalakshmi sits enthroned. There are mentions in ''Paṭṭiṉappālai'' that ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pali
Pāli (, IAST: pāl̤i) is a Classical languages of India, classical Middle Indo-Aryan languages, Middle Indo-Aryan language of the Indian subcontinent. It is widely studied because it is the language of the Buddhist ''Pali Canon, Pāli Canon'' or ''Tripiṭaka, Tipiṭaka'' as well as the sacred language of ''Theravada, Theravāda'' Buddhism. Pali was designated as a Classical languages of India, classical language by the Government of India on 3 October 2024. Origin and development Etymology The word 'Pali' is used as a name for the language of the Theravada canon. The word seems to have its origins in commentarial traditions, wherein the (in the sense of the line of original text quoted) was distinguished from the commentary or vernacular translation that followed it in the manuscript. K. R. Norman suggests that its emergence was based on a misunderstanding of the compound , with being interpreted as the name of a particular language. The name Pali does not appear in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamil Tigers
The Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE; , ; also known as the Tamil Tigers) was a Tamil militant organization, that was based in the northern and eastern Sri Lanka. The LTTE fought to create an independent Tamil state called Tamil Eelam in the northeast of the island in response to violent persecution and discriminatory policies against Sri Lankan Tamils by the Sinhalese-dominated Sri Lankan Government. The leader of the LTTE, Velupillai Prabhakaran, cited the 1958 anti-Tamil pogrom as one of the factors that led him to militancy. In 1975, he assassinated the Mayor of Jaffna, Alfred Duraiappah, in revenge for the 1974 Tamil conference incident. The LTTE was subsequently founded in 1976 as a reaction to the Sri Lankan Constitution of 1972 which prescribed Buddhism as the primary religion of the country, and Sinhala as its national language. The LTTE was involved in attacks on government targets, policemen and local politicians and moved on to armed clashes agai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamil Militant
Sri Lankan Tamil militant groups rose to prominence in the 1970s to fight the state of Sri Lanka in order to create an independent Tamil Eelam in the north of Sri Lanka. They rose in response to the perception among minority Sri Lankan Tamils that the state was preferring the majority Sinhalese for educational opportunities and government jobs. By the end of 1987, the militants had fought not only the Sri Lankan security forces but also the Indian Peace Keeping Force. They also fought among each other briefly, with the main Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE) rebel group dominating the others. The militants represented inter-generational tensions, as well as the caste and ideological differences. Except for the LTTE, many of the remaining organizations have morphed into minor political parties within the Tamil National Alliance, or as standalone political parties. Some Tamil militant groups also functioned as paramilitaries within the Sri Lankan military against separatis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parantaka I
Parantaka Chola I (Tamil: பராந்தக சோழன் I; 873–955) was a Chola emperor who ruled for forty-eight years, annexing Pandya by defeating Rajasimhan II and in the Deccan won the Battle of Vallala against Rashtrakutas which happened before 916. The best part of his reign was marked by increasing success and prosperity. Invasion of the Pandya kingdom Parantaka I continued the expansion started by his father, and invaded the Pandya kingdom in 915. He captured the Pandyan capital Madurai and assumed the title Madurain-konda (Capturer of Madurai). The Pandyan ruler Maravarman Rajasinha II sought the help of Kassapa V of Anuradhapura who sent an army to his aid. Parantaka I defeated the combined army at the battle of Vellore. The Pandya king fled into exile in Sri Lanka and Parantaka I completed his conquest of the entire Pandya country. Parantaka I spent many years in the newly conquered country reducing it to subjugation, and when he felt he had at last ach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chola Dynasty
The Chola dynasty () was a Tamil dynasty originating from Southern India. At its height, it ruled over the Chola Empire, an expansive maritime empire. The earliest datable references to the Chola are from inscriptions dated to the 3rd century BCE during the reign of Ashoka of the Maurya Empire. The Chola empire was at its peak and achieved imperialism under the Medieval Cholas in the mid-9th century CE. As one of the Three Crowned Kings of Tamilakam, along with the Chera and Pandya, the dynasty continued to govern over varying territories until the 13th century CE. The heartland of the Cholas was the fertile valley of the Kaveri River. They ruled a significantly larger area at the height of their power from the latter half of the 9th century till the beginning of the 13th century. They unified peninsular India south of the Tungabhadra River and held the territory as one state for three centuries between 907 and 1215 CE. K. A. Nilakanta Sastri, ''A History of South In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerala
Kerala ( , ) is a States and union territories of India, state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Kingdom of Cochin, Cochin, Malabar District, Malabar, South Canara, and Travancore. Spread over , Kerala is the 14th List of states and union territories of India by area, smallest Indian state by area. It is bordered by Karnataka to the north and northeast, Tamil Nadu to the east and south, and the Laccadive Sea, Lakshadweep Sea to the west. With 33 million inhabitants as per the 2011 Census of India, 2011 census, Kerala is the List of states of India by population, 13th-largest Indian state by population. It is divided into 14 List of districts of Kerala, districts with the capital being Thiruvananthapuram. Malayalam is the most widely spoken language and is also the official language of the state. The Chera dynasty was the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ezhava
The Ezhavas, () also known as ''Thiyya'' or ''Tiyyar'' () in the Malabar region, and Chovar () in the south, are a community with origins in the region of India presently known as Kerala, where in the 2010s they constituted about 23% of the population and were reported to be the largest Hindu community. Thiyya Pullapilly (1976) pp. 31–32 group has claimed a higher rank in the Hindu caste system than the other Ezhava groups but was considered to be of a similar rank by colonial and subsequent administrations. Nossiter (1982) p. 30 Ezhava dynasties such as the Mannanar existed in Kerala. Variations They are also known as ''Ilhava'', ''Irava'', ''Izhava'' and ''Erava'' in the south of the region; as ''Chovas'', ''Chokons'' and ''Chogons'' in Central Travancore; and as ''Thiyyar'', ''Tiyyas'' and ''Theeyas'' in the Malabar region. Some are also known as ''Thandan'', which has caused administrative difficulties due to the presence of a distinct caste of Thandan in the same r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chola
The Chola Empire, which is often referred to as the Imperial Cholas, was a medieval thalassocratic empire based in southern India that was ruled by the Chola dynasty, and comprised overseas dominions, protectorates and spheres of influence in southeast Asia. The power and the prestige the Cholas had among political powers in South, Southeast, and East Asia at its peak is evident in their expeditions to the Ganges, naval raids on cities of the Srivijaya Empire on the island of Sumatra, and their repeated embassies to China. K. A. Nilakanta Sastri, ''A History of South India'', p. 158 The Chola fleet represented the peak of ancient Indian maritime capacity. Around 1070, the Cholas began to lose almost all of their overseas territories but the later Cholas (1070–1279) continued to rule portions of southern India. The Chola empire went into decline at the beginning of the 13th century with the rise of the Pandyan dynasty, which ultimately caused the Chola's downfall. K. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pallava
The Pallava dynasty existed from 275 CE to 897 CE, ruling a significant portion of South India, the Deccan, also known as Tondaimandalam. The Pallavas played a crucial role in shaping in particular southern Indian history and heritage. The dynasty rose to prominence after the downfall of the Satavahanas, Satavahana Empire, whom they had formerly served as feudatories. The Pallavas became a major South India, southern Indian power during the reign of Mahendravarman I (600–630 CE) and Narasimhavarman I (630–668 CE), and dominated the southern Andhra Pradesh, Telugu region and the northern parts of the Ancient Tamil country, Tamil region for about 600 years, until the end of the 9th century. Throughout their reign, they remained in constant conflict with both the Chalukyas of Badami, Vatapi to the north, and the Tamil kingdoms of Chola Dynasty, Chola and Pandyas to their south. The Pallavas were finally defeated by the Chola ruler Aditya I in the 9th century CE. The Pallav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naṟṟiṇai
''Natrinai'' ( meaning ''excellent tinai''), is a classical Tamil poetic work and traditionally the first of the Eight Anthologies (''Ettuthokai'') in the Sangam literature. The collection – sometimes spelled as Natrinai or Narrinai – contains both ''akam'' (love) and ''puram'' (war, public life) category of poems. The ''Naṟṟiṇai'' anthology contains 400 poems, mainly of 9 to 12 lines, but a few with 8 to 13 lines each. According to Takanobu Takahashi – a Tamil literature scholar, the ''Naṟṟiṇai'' poems were likely composed between 100–300 CE based on the linguistics, style and dating of the authors. While Kamil Zvelebil – a Tamil literature and history scholar, dates some poems to the 1st century BCE. The ''Naṟṟiṇai'' manuscript colophon states that it was compiled under the patronage of the Pandyan king named ''Pannatu Tanta Pantiyan Maran Valuti'', but the compiler remained anonymous. The ''Naṟṟiṇai'' poems are credited to 175 ancient poets. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |