|
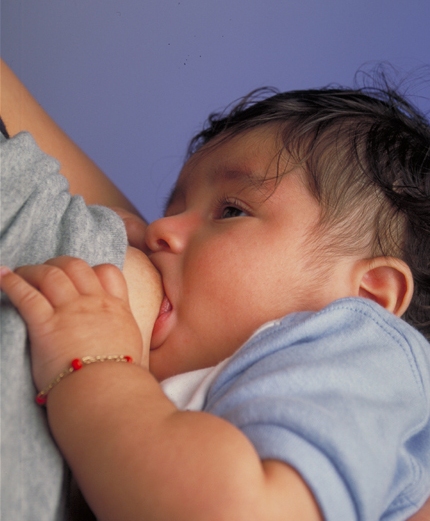
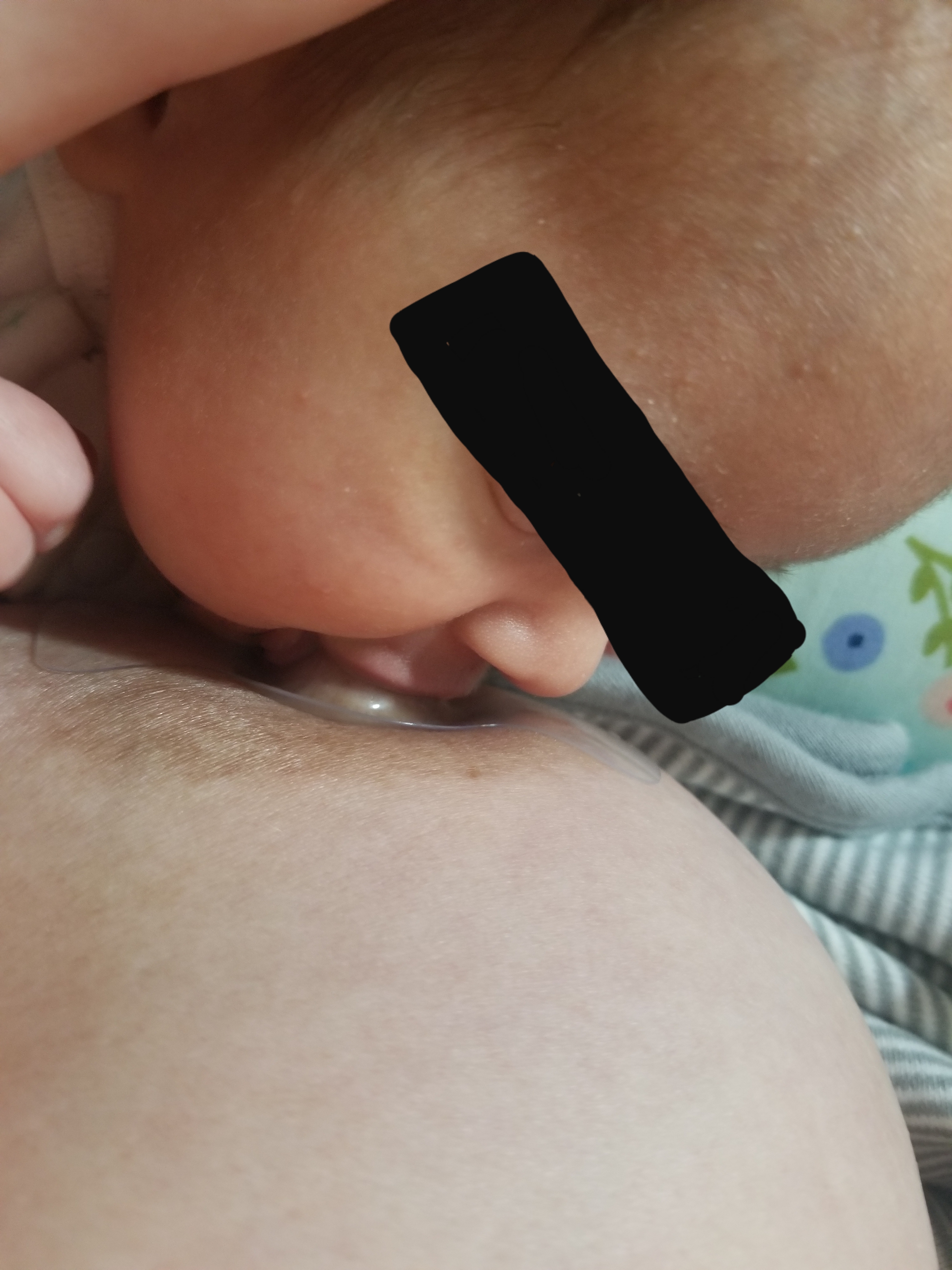
Edematous Areola
An edematous areola is a swollen and tender inflammation of the areola of the breast. It can develop after childbirth when large amounts of fluids are given intravenously, use of pitocin or fluid retention for other reasons, and may interfere with successful initiation of breastfeeding. An edematous areola can also develop in women with preeclampsia. See also * Breast milk * Nipple prosthesis for breast cancer survivors * Nipple shield * Breastfeeding Breastfeeding, also known as nursing, is the process where breast milk is fed to a child. Infants may suck the milk directly from the breast, or milk may be extracted with a Breast pump, pump and then fed to the infant. The World Health Orga ... References {{women's health stub Breastfeeding Body fluids Midwifery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', ''dolor'', ''rubor'', ''tumor'', and ''functio laesa''). Inflammation is a generic response, and therefore is considered a mechanism of innate immunity, whereas adaptive immunity is specific to each pathogen. Inflammation is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators. The function of inflammation is to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury, clear out damaged cells and tissues, and initiate tissue repair. Too little inflammation could lead to progressive tissue destruction by the harmful stimulus (e.g. bacteria) and compromise the survival of the organism. However inflammation can also have negative effects. Too much inflammation, in the form of chronic inflammation, is associated with variou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Areola
The human areola (''areola mammae'', or ) is the pigmented area on the breast around the nipple. More generally, an areola is a small circular area on the Human body, body with a different histology from the surrounding Tissue (biology), tissue, or other small circular areas such as an inflamed region of skin. The mature human female nipple has several small openings arranged radially around the tip of the lactiferous ducts, from which milk is released during lactation. The other small openings in the areola are sebaceous glands, also known as Areolar gland, areolar glands. Shade The areolae can range from pink to red to brown to dark brown or nearly black, but generally tend to be paler among people with lighter skin tones and darker among people with darker skin tones. A reason for the differing color may be to make the nipple area more visible to the infant. Hyperpigmentation occurs in most women during the second stage of pregnancy, leading to a temporarily darker shade. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Childbirth
Childbirth, also known as labour, parturition and delivery, is the completion of pregnancy, where one or more Fetus, fetuses exits the Womb, internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section and becomes a newborn to the world. In 2019, there were about 140.11 million human births globally. In Developed country, developed countries, most deliveries occur in hospitals, while in Developing country, developing countries most are home births. The most common childbirth method worldwide is vaginal delivery. It involves four stages of labour: the cervical effacement, shortening and Cervical dilation, opening of the cervix during the first stage, descent and birth of the baby during the second, the delivery of the placenta during the third, and the recovery of the mother and infant during the fourth stage, which is referred to as the Postpartum period, postpartum. The first stage is characterised by abdominal cramping or also back pain in the case of B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitocin
Synthetic oxytocin, sold under the brand name Pitocin among others, is a medication made from the peptide ''oxytocin''. As a medication, it is used to cause contraction of the uterus to start labor, increase the speed of labor, and to stop bleeding following delivery. For this purpose, it is given by injection either into a muscle or into a vein. Oxytocin is also available in intranasal spray form for psychiatric, endocrine and weight management use as a supplement. Intranasal oxytocin works on a different pathway than injected oxytocin, primarily along the olfactory nerve crossing the blood–brain barrier to the olfactory lobe in the brain, where dense magnocellular oxytocin neurons receive the nerve impulse quickly. The natural occurrence of oxytocin was discovered in 1906. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical uses An intravenous infusion of oxytocin is used to induce labor and to support labor in case of slow childbirth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preeclampsia
Pre-eclampsia is a multi-system disorder specific to pregnancy, characterized by the new onset of high blood pressure and often a significant amount of protein in the urine or by the new onset of high blood pressure along with significant end-organ damage, with or without the proteinuria. When it arises, the condition begins after 20 weeks of pregnancy. In severe cases of the disease there may be red blood cell breakdown, a low blood platelet count, impaired liver function, kidney dysfunction, swelling, shortness of breath due to fluid in the lungs, or visual disturbances. Pre-eclampsia increases the risk of undesirable as well as lethal outcomes for both the mother and the fetus including preterm labor. If left untreated, it may result in seizures at which point it is known as eclampsia. Risk factors for pre-eclampsia include obesity, prior hypertension, older age, and diabetes mellitus. It is also more frequent in a woman's first pregnancy and if she is carrying twins. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Milk
Breast milk (sometimes spelled as breastmilk) or mother's milk is milk produced by the mammary glands in the breasts of women. Breast milk is the primary source of nutrition for newborn infants, comprising fats, proteins, carbohydrates, and a varying composition of minerals and vitamins. Breast milk also contains substances that help protect an infant against infection and inflammation, such as Human milk microbiome, symbiotic bacteria and other microorganisms and immunoglobulin A, whilst also contributing to the healthy development of the infant's immune system and gut microbiome. Use and methods of consumption The World Health Organization (WHO) and UNICEF recommend Breastfeeding#Duration and exclusivity, exclusive breastfeeding with breast milk for the first six months of an infant’s life. This period is followed by the incorporation of nutritionally adequate and safe complementary solid foods at six months, a stage when an infant’s nutrient and energy requirements start ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nipple Prosthesis
Nipple/Areola prostheses (prostheses is the plural of prosthesis) are made of silicone by breast prosthesis manufacturers and anaplastologists for breast cancer survivors who were treated for breast cancer with a mastectomy. Prostheses can be worn weeks after a mastectomy, breast reconstruction, or even nipple reconstruction. As an inexpensive and convenient alternative to surgery, patients may choose to wear them anytime during treatment. Patients who ultimately find nipple prostheses thought that they should be informed of them during the consultation prior to mastectomy. Fabrication Nipple prosthetics are made of silicone and are adhered to the skin. There are several different types of prostheses with different benefits and costs. * Mass-produced and "semi-custom" prostheses allow women to choose from a few colors and sizes. The majority of mass-produced prostheses are self-adhering and last three months because the materials are weaker and the adhesion become weaker. Lack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nipple Shield (breastfeeding)
A nipple shield is a nipple-shaped sheath worn over the areola and nipple during breastfeeding. Modern nipple shields are made of soft, thin, flexible silicone and have holes at the end of the nipple section to allow the breast milk to pass through. History Before the invention of plastics, nipple shields were made of animal skin, wax, metal, glass, wood or ivory. A 17th-century nipple shield held in Shakespeare's birthplace is made of pewter. Nipple shields were even made of lead, which can cause lead poisoning. Older nipple shields were made of latex and harder, thicker plastics, while more recent models are made of silicone. Usage File:Siliconen tepelhoedje - vorm na aanbrengen.JPG, Silicone nipple shield File:Siliconen tepelhoedje - vorm voor aanbrengen.jpg, Shape inverted before application File:Placing_shield.jpg, Placing shield File:Placed_shield2.jpg, Shield applied File:Nipple_shield4.jpg, Infant starts to latch File:Nipple_shield3.jpg, Infant fully latched on Ni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding, also known as nursing, is the process where breast milk is fed to a child. Infants may suck the milk directly from the breast, or milk may be extracted with a Breast pump, pump and then fed to the infant. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommend that breastfeeding begin within the first hour of a baby's birth and continue as the baby wants. Health organizations, including the WHO, recommend breastfeeding exclusively for six months. This means that no other foods or drinks, other than vitamin D, are typically given. The WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months of life, followed by continued breastfeeding with appropriate complementary foods for up to 2 years and beyond. Of the 135 million babies born every year, only 42% are breastfed within the first hour of life, only 38% of mothers practice exclusive breastfeeding during the first six months, and 58% of mothers continue breastfeeding up to the age of two years and beyond. Breastfee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Fluids
Body fluids, bodily fluids, or biofluids, sometimes body liquids, are liquids within the Body (biology), body of an organism. In lean healthy adult men, the total body water is about 60% (60–67%) of the total Human body weight, body weight; it is usually slightly lower in women (52–55%). The exact percentage of fluid relative to body weight is inversely proportional to the percentage of body fat. A lean man, for example, has about 42 (42–47) liters of water in his body. The total body of water is divided into fluid compartments, between the Fluid compartments#Intracellular compartment, intracellular fluid compartment (also called space, or volume) and the extracellular fluid (ECF) compartment (space, volume) in a two-to-one ratio: 28 (28–32) liters are inside cells and 14 (14–15) liters are outside cells. The ECF compartment is divided into the interstitial fluid volume – the fluid outside both the cells and the blood vessels – and the Blood vessel, intravascular v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |