|
Ecopath With Ecosim
Ecopath with Ecosim (EwE) is a free and open source ecosystem modelling software suite, initially started at NOAA by Jeffrey Polovina, but has since primarily been developed at the formerly UBC Fisheries Centre of the University of British Columbia. In 2007, it was named as one of the ten biggest scientific breakthroughs in NOAA's 200-year history. The NOAA citation states that Ecopath "revolutionized scientists' ability worldwide to understand complex marine ecosystems". Behind this lie more than three decades of development work in association with a thriving network of fisheries scientists such as Villy Christensen, Carl Walters and Daniel Pauly, and software engineers around the world. EwE is funded through projects, user contributions, user support, training courses and co-development collaborations. Per November 2021 there are an estimated 8000+ users across academia, non-government organizations, industry and governments in 150+ countries. Components EwE has three main compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Basic
Visual Basic is a name for a family of programming languages from Microsoft. It may refer to: * Visual Basic (.NET), the current version of Visual Basic launched in 2002 which runs on .NET * Visual Basic (classic), the original Visual Basic supported from 1991 to 2008 * Embedded Visual Basic, the classic version geared toward embedded applications * Visual Basic for Applications, an implementation of Visual Basic 6 built into programs such as Microsoft Office and used for writing macros * VBScript, an Active Scripting language based on VB6, actively maintained from 1996–2023 {{SIA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeffrey Polovina
Jeffrey Polovina is an American marine scientist. He is known for creating the marine ecosystem model Ecopath. Early life Jeffrey Joseph Polovina was born on September 30, 1948, in Troy, New York. He graduated from Carnegie Mellon University with an undergraduate degree in Mathematics, and received his PhD in Mathematical Statistics from University of California, Berkeley. Career Polovina began his academic career teaching at University of California at San Diego, later moving to the University of Hawaii to conduct Sea Grant-funded aquaculture research. In 1979 he joined the National Marine Fisheries Service, Honolulu Lab which later became the Pacific Islands Fisheries Science Center, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), where he served as a senior scientist and the Chief of Ecosystem and Oceanography Division. In 2010 he received the Wooster Award from the North Pacific Marine Sciences Organization (PICES). He was awarded two Fulbright Senior Research Awards f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WorldFish Center
The International Center for Living Aquatic Resources Management (ICLARM), also known as WorldFish, is an international organization working to transform aquatic food systems to reduce hunger, malnutrition, and poverty. Based in Penang, Malaysia, WorldFish is a member of CGIAR, which unites international organizations engaged in research about food security and has a presence in 20 countries throughout Africa, Asia and the Pacific Region. WorldFish has introduced technologies to ramp up local aquatic food production through a network of partners. Such innovations include the development of "genetically improved farmed tilapia" (GIFT) and an enhanced strain of Nile tilapia, in support of smallhold aquaculture farmers in the Global South. WorldFish research In 2020, WorldFish began to transition from fisheries and aquaculture to a more holistic aquatic foods system approach. The institution shifted towards food systems management to focus on aquatic food value chains from produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquatic Ecosystem
An aquatic ecosystem is an ecosystem found in and around a body of water, in contrast to land-based terrestrial ecosystems. Aquatic ecosystems contain communities of organisms—aquatic life—that are dependent on each other and on their environment. The two main types of aquatic ecosystems are marine ecosystems and freshwater ecosystems. Freshwater ecosystems may be lentic (slow moving water, including pools, ponds, and lakes); lotic (faster moving water, for example streams and rivers); and wetlands (areas where the soil is saturated or inundated for at least part of the time). Types Marine ecosystems Marine coastal ecosystem Marine surface ecosystem Freshwater ecosystems Lentic ecosystem (lakes) Lotic ecosystem (rivers) Wetlands Functions Aquatic ecosystems perform many important environmental functions. For example, they recycle nutrients, purify water, attenuate floods, recharge ground water and provide habitats for wildlife. The biota of an aqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological
Ecology () is the natural science of the relationships among living organisms and their environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere levels. Ecology overlaps with the closely related sciences of biogeography, evolutionary biology, genetics, ethology, and natural history. Ecology is a branch of biology, and is the study of abundance, biomass, and distribution of organisms in the context of the environment. It encompasses life processes, interactions, and adaptations; movement of materials and energy through living communities; successional development of ecosystems; cooperation, competition, and predation within and between species; and patterns of biodiversity and its effect on ecosystem processes. Ecology has practical applications in fields such as conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource management, and human ecology. The word ''ecology'' () was coined in 1866 by the German scientist Ern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
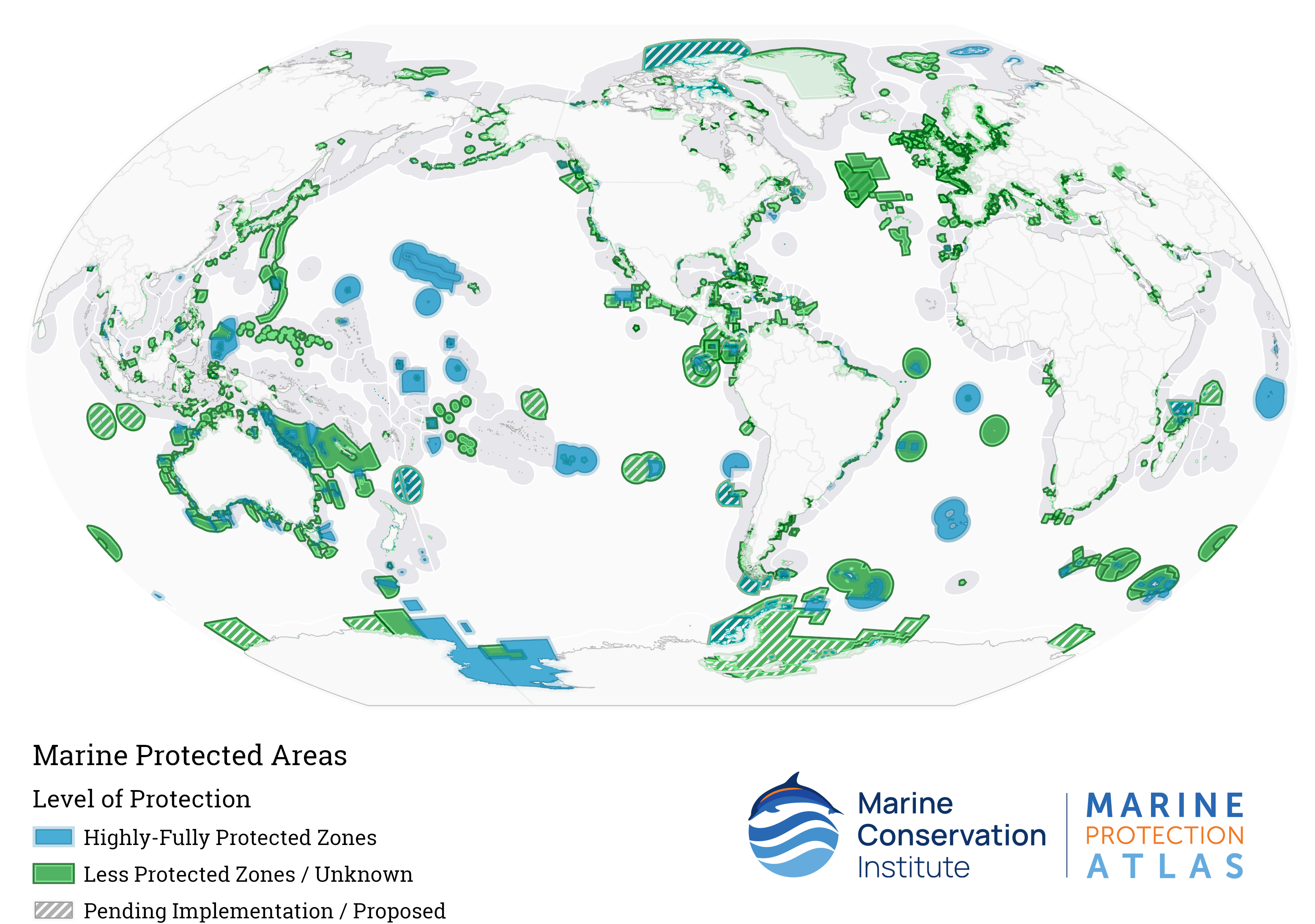
Marine Protected Area
A marine protected area (MPA) is a protected area of the world's seas, oceans, estuaries or in the US, the Great Lakes. These marine areas can come in many forms ranging from wildlife refuges to research facilities. MPAs restrict human activity for a conservation purpose, typically to protect natural or cultural resources. Such marine resources are protected by local, state, territorial, native, regional, national, or international authorities and differ substantially among and between nations. This variation includes different limitations on development, fishing practices, fishing seasons and catch limits, moorings and bans on removing or disrupting marine life. MPAs can provide economic benefits by supporting the fishing industry through the revival of fish stocks, as well as job creation and other market benefits via ecotourism. The value of MPA to mobile species is unknown. There are a number of global examples of large marine conservation areas. The Papahānaumokuākea Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a State (polity), state. In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive (government), executive, and judiciary. Government is a means by which organizational policies are enforced, as well as a mechanism for determining policy. In many countries, the government has a kind of constitution, a statement of its governing principles and philosophy. While all types of organizations have governance, the term ''government'' is often used more specifically to refer to the approximately 200 list of sovereign states, independent national governments and government agency, subsidiary organizations. The main types of modern political systems recognized are democracy, democracies, totalitarian regimes, and, sitting between these two, authoritarianism, authoritarian regimes with a variety of hybrid regimes. Modern classification systems also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Private Industry
The private sector is the part of the economy which is owned by private groups, usually as a means of establishment for profit or non profit, rather than being owned by the government. Employment The private sector employs most of the workforce in some countries. In private sector, activities are guided by the motive to earn money, i.e. operate by capitalist standards. A 2013 study by the International Finance Corporation (part of the World Bank Group) identified that 90 percent of jobs in developing countries are in the private sector. Diversification In free enterprise countries, such as the United States, the private sector is wider, and the state places fewer constraints on firms. In countries with more government authority, such as China, the public sector makes up most of the economy. Regulation States legally regulate the private sector. Businesses operating within a country must comply with the laws in that country. In some cases, usually involving multination ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academia
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of tertiary education. The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 386 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the goddess of wisdom and Skills, skill, north of Ancient Athens, Athens, Greece. The Royal Spanish Academy defines academy as scientific, literary or artistic society established with public authority and as a teaching establishment, public or private, of a professional, artistic, technical or simply practical nature. Etymology The word comes from the ''Academy'' in ancient Greece, which derives from the Athenian hero, ''Akademos''. Outside the city walls of Athens, the Gymnasium (ancient Greece), gymnasium was made famous by Plato as a center of learning. The sacred space, dedicated to the goddess of wisdom, Athena, had formerly been an olive Grove (nature), grove, hence the expression "the groves of Academe". In these gardens, the philos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Pauly
Dr. Sir Daniel Pauly is a France, French-born marine biologist, well known for his work in studying human impacts on global fisheries and in 2020 was the most cited fisheries scientist in the world. He is a professor and the project leader of the Sea Around Us Project, Sea Around Us initiative at the Institute for the Oceans and Fisheries at the University of British Columbia. He also served as Director of the UBC Fisheries Centre from November 2003 to October 2008. In February 2023 Pauly was the co-recipient of the 2023 Tyler Prize for Environmental Achievement, with Ussif Rashid Sumaila. The award has been described as the ‘Nobel Prize for the Environment.’ Biography Pauly was born in Paris, France. He grew up, however, in La Chaux-de-Fonds, La Chaux de Fonds, Switzerland in what was called a strange "Dickensian" childhood where he was forced to stay as a live-in servant to a new family. For the first 16 years of his life, Pauly lived an inward life as he was mixed rac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Walters
Carl Walters (born 1944) is an American-born Canadian biologist known for his work involving fisheries stock assessments, the adaptive management concept, and ecosystem modeling. Walters has been a professor of Zoology and Fisheries at the University of British Columbia since 1969. He is one of the main developers of the ecological modelling software Ecopath. His most recent work focuses on how to adjust human behaviors in environments that are full of uncertainty. He is a recent recipient of the Volvo Environment Prize (2006). In 2019, Dr. Walters became a Member of the Order of British Columbia. Education Carl Walters graduated from Bakersfield College with an A.A in 1963 and continued to Humboldt State College to graduate with a B.S. in 1965. After Walters graduated, he went to Colorado State University to study the "Distribution and production of midges in an alpine lake" under the advisement of Dr. Robert E. Vincent. After obtaining his M.S. in 1967, Walters stayed on wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villy Christensen
Villy Christensen is an ecosystem modeller with a background in fisheries science. He is known for his work as a project leader and core developer of Ecopath, an ecosystem modelling software system widely used in fisheries management. Ecopath was initially an initiative of the NOAA, but since primarily developed at the UBC Fisheries Centre of the University of British Columbia. In 2007, it was named as one of the ten biggest scientific breakthroughs in NOAA's 200-year history. The citation states that Ecopath "revolutionized scientists' ability worldwide to understand complex marine ecosystems". Biography Christensen did his Ph.D. under Sven Erik Jørgensen at Copenhagen University. Jeffrey Polovina initiated the Ecopath approach in the early 1980s. Christensen, along with Daniel Pauly and others, has been involved in the subsequent development of Ecopath since 1990. Christensen currently facilitates international workshops on Ecopath around the world. He is a professor at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |