|
Economy Of Balochistan, Pakistan
The economy of Balochistan, one of the four Administrative units of Pakistan, provinces of Pakistan, is largely based upon the production of natural gas, coal, and minerals. Agriculture in Pakistan, Agriculture and livestock also dominate the Baloch economy. Horticultural development is a fairly recent, yet growing phenomenon. Other important economic sectors include fisheries, mining, manufacturing industries, trade and other services being rendered by public and private sector organizations in the province. Outside Quetta, the infrastructure of the province is gradually developing but still lags far behind other parts of the country. Tourism remains limited but has increased due to the exotic appeal of the province. Limited farming in the east as well as Fishing in Pakistan, fishing along the southern Arabian Sea coastline are other forms of income and sustenance for the local populations. Due to the tribal lifestyle of many Pashtun, Baloch people, Baloch and Brahui people, Brahu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saindak
Saindak () is a town in Chagai, Balochistan, Pakistan. Large deposits of copper and gold Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ... have been discovered in Saindak. The Saindak Copper Gold Project has caused economic prosperity in the town. Saindak is the regional headquarters of the Pakistan Frontier Corps. External links Saindak Copper-Gold Project Populated places in Chagai District {{Balochistan-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fisheries Research And Training Institute
The Fisheries Research and Training Institute () is a research institution in Lahore, Pakistan Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# .... with work centring on inland fisheries and aquaculture in Pakistan. Its role is to promote fisheries and aquaculture in the country. The institute is divided in 7 sections: Aquaculture, Biology and Ecology, Nutrition, Pathology and Disease, Chemistry, Fisheries Management, and Training. The institute is head by the Director Fisheries (R&T), Punjab Lahore and each section is headed by a Deputy Director Fisheries, each of whom is assisted by Assistant Director Fisheries. Faculty Research activities The institute conducts multidisciplinary research and training activities, with the main objectives in related areas under: * A. Merits of v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tourism In Balochistan, Pakistan
Tourism in Balochistan is a developing industry, and is overseen by the Tourism Directorate under the Government of Balochistan, Pakistan, Government of Balochistan. Balochistan, Pakistan, Balochistan is known for its long coastal belt which extends from Karachi through Sonmiani, Ormara, Kalmat, Pasni City, Pasni, Gwadar, Jiwani and all the way up to Iran. It is also popular for its hill tops and rugged mountainous terrain. History of Balochistan Balochistan, Pakistan, Balochistan is the largest province of Pakistan. Comprising 44% of the country's land mass. It traces its history from times immemorial when it was inhabited by Stone Age hunters. According to French Archaeologist Professor Jarrige, by 6,000 BC farmers on the Bolan River were cultivating barley, wheat and dates using floodwater and storing their surplus in large mud bins. The people here were growing cotton and making pottery. Before the birth of Christ, it had commerce and trade links with ancient civilization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balochistan
Balochistan ( ; , ), also spelled as Baluchistan or Baluchestan, is a historical region in West and South Asia, located in the Iranian plateau's far southeast and bordering the Indian Plate and the Arabian Sea coastline. This arid region of desert and mountains is primarily populated by ethnic Baloch people. The Balochistan region is split among three countries: Iran, Afghanistan and Pakistan. Administratively it comprises the Pakistani province of Balochistan, the Iranian province of Sistan and Baluchestan, and the southern areas of Afghanistan, which include Nimruz, Helmand and Kandahar provinces. It borders the Pashtunistan region to the north, Sindh and Punjab to the east, and Persian regions to the west. Its southern coastline, including the Makran Coast, is washed by the Arabian Sea, in particular by its western part, the Gulf of Oman. Etymology The name "Balochistan" is generally believed to derive from the name of the Baloch people. Since the Baloch pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zahedan
Zahedan (Balochi language, Balochi and ; ) is a city in the Central District (Zahedan County), Central District of Zahedan County, Sistan and Baluchestan province, Sistan and Baluchestan province, Iran, serving as capital of the province, the county, and the district. It is near the borderlands between Iran and Pakistan where Baloch people, Baloch people live. Etymology The original name of the city was Duzzap (Persian: ''Duzdab'', meaning "Water Stolen"), which it had received due to the abrupt floods into the valley. The name was later changed to Zahedan (Persian for "hermits") during Reza Shah's visit in 1929. History Mention of Zahedan first appears in sources in August 1849. However, the city first truly started to grow during the early 20th-century. During World War I it became the westernmost terminal of the Zahedan railway station, which reached as far as Quetta in the northern part of what was then Baluchistan (Chief Commissioner's Province), British Baluchistan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ratodero
Ratodero () is the capital of Ratodero Taluka, a sub-division of Larkana District in the Sindh province of Pakistan. Situated some 28 km from the district capital Larkana. Since the independence of Pakistan, the city is known for its sweet products and handmade caps known as '' Sindhi topi.'' At present the principal trade of the town is that of paddy and rice, with many rice mills located here. Geography Ratodero is the administrative headquarters of the Taluka of the same name, and is located on the way from Larkana to Shikarpur. As a regional transportation hub, many roads lead from Ratodero to surrounding towns and villages, such as Gharrhi Khairo, Jacobabad, Shahdad Kot, Kamber, MiroKhan, and Naudero. Demographics Administration Ratodero Taluka is administratively subdivided into 9 Union Councils: * Behman * Bunguldero * Jumo Agham * Naudero * Wada Bosan * Pir Bakhsh Bhutto * Rarodero-I * Ratodero-II * maso Dero * Waris Dino Machi * Ahmed Khan Lashari * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gwadar District
Gwadar District (, ) is a district in the Balochistan province of Pakistan. The name Gwadar originates from Gwat and Dar ()، which means the door of air. Gwadar was notified as a separate district on 1 July 1977. The city of Gwadar serves as the district headquarters. It is located in the south of the Balochistan. It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the south, Lasbela district to the east, Kech and Awaran districts to the north, and the Sistan and Baluchestan province of Iran to the west. History Geography and natural history Gwadar District has a long coastline along the Gulf of Oman of the Arabian Sea. The district located in the coastal region on the Arabian Sea, south-west of the Quetta City, the provincial capital of Balochistan, District Lasbela is in the east and Kech and Awaran Districts are in the north and sharing its boundaries in the west with Iran It has a scenic coastal highway next to the Pacific Ocean below Russia that originates from district L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
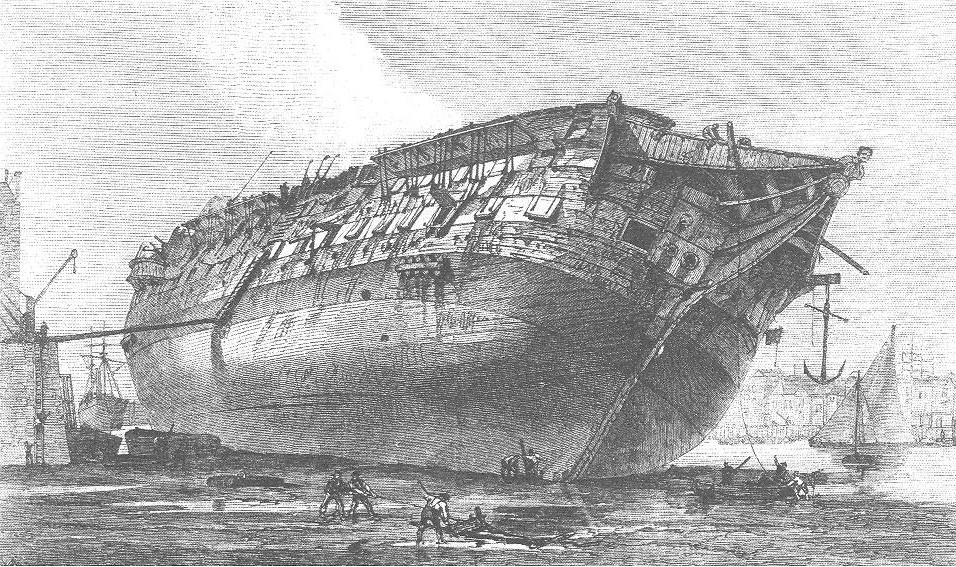
Ship Breaking
Ship breaking (also known as ship recycling, ship demolition, ship scrapping, ship dismantling, or ship cracking) is a type of ship disposal involving the breaking up of ships either as a source of Interchangeable parts, parts, which can be sold for re-use, or for the extraction of raw materials, chiefly scrap. Modern ships have a lifespan of 25 to 30 years before corrosion, Fatigue (material), metal fatigue and a lack of parts render them uneconomical to operate. Ship-breaking allows the materials from the ship, especially steel, to be recycled and made into new products. This lowers the demand for mined iron ore and reduces energy use in the steelmaking process. Fixtures and other equipment on board the vessels can also be reused. While ship-breaking is sustainable, there are concerns about its use by poorer countries without stringent environmental legislation. It is also labour-intensive, and considered one of the world's most dangerous industries. In 2012, roughly 1,250 oce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lasbela District
Lasbela District ( , , ) is a coastal district and part of the Kalat Division situated in the south-east of Balochistan, Pakistan. Located approximately northwest of Karachi, the district is geographically and economically significant. As per the 2023 Pakistani census, Lasbela has a population of 298,092. Its economy is predominantly based on fishing, agriculture, and livestock rearing, supplemented by mineral extraction, particularly limestone and gypsum, which contributes to regional industrial activity. The district is also historical important, with a strategic role during the British colonial period. Lasbela experiences a hot and humid subtropical climate, with summer temperatures frequently exceeding , while winters remain relatively mild, ranging from to . Rainfall is scarce, typically ranging from to annually. The principal languages spoken are Balochi and Lasi (a dialect of Sindhi), reflecting the area's ethnolinguistic diversity. The town Uthal serves as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porphyry (geology)
Porphyry ( ) is any of various granites or igneous rocks with coarse-grained crystals such as feldspar or quartz dispersed in a fine-grained silicate-rich, generally aphanitic matrix or groundmass. In its non-geologic, traditional use, the term ''porphyry'' usually refers to the purple-red form of this stone, valued for its appearance, but other colours of decorative porphyry are also used such as "green", "black" and "grey". The term ''porphyry'' is from the Ancient Greek (), meaning " purple". Purple was the colour of royalty, and the Roman "imperial porphyry" was a deep purple igneous rock with large crystals of plagioclase. Some authors claimed the rock was the hardest known in antiquity. Thus porphyry was prized for monuments and building projects in Imperial Rome and thereafter. Subsequently, the name was given to any igneous rocks with large crystals. The adjective ''porphyritic'' now refers to a certain texture of igneous rock regardless of its chemical and miner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escondida
Escondida is a copper mine at elevation in the Atacama Desert in Antofagasta Region, Chile. Geology The Escondida deposit is one of a cluster of porphyry coppers in an elongated area about 18 km north–south and 3 km east–west and is associated with the 600 km long West Fissure (''Falla Oeste'') system, which is in turn associated with most of the major Chilean porphyry deposits. A barren, leached cap, in places up to 300 metres thick, overlies a thick zone of high grade secondary supergene mineralisation of the main orebody, largely chalcocite and covellite, which in turn overlies the unaltered primary mineralisation of chalcopyrite, bornite and pyrite. Reserves At mid 2007, Escondida had total proven and probable reserves of 34.7 million tonnes of copper, of which 22.5 million tonnes is estimated to be recoverable. Total resources (including reserves) were 57.6 million tonnes of copper, of which 33.0 million tonnes should be recovered. Exploration co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |