|
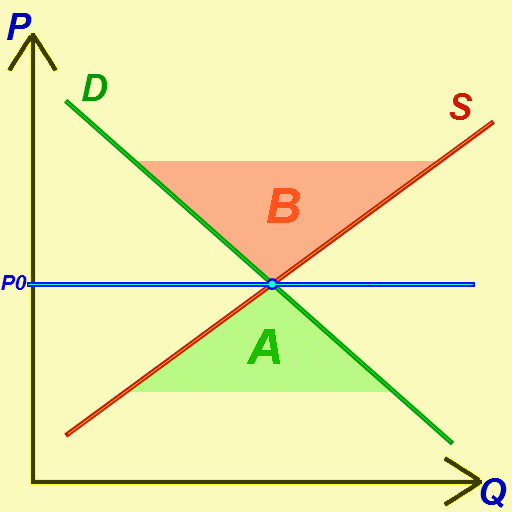
Economic Equilibrium
In economics, economic equilibrium is a situation in which the economic forces of supply and demand are balanced, meaning that economic variables will no longer change. Market equilibrium in this case is a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes, and quantity is called the "competitive quantity" or market clearing quantity. Understanding economic equilibrium An economic equilibrium is a situation when the economic agent cannot change the situation by adopting any strategy. The concept has been borrowed from the physical sciences. Take a system where physical forces are balanced for instance.This economically interpreted means no further change ensues. Properties of equilibrium Three basic prope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economics
Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of Agent (economics), economic agents and how economy, economies work. Microeconomics analyses what is viewed as basic elements within economy, economies, including individual agents and market (economics), markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyses economies as systems where production, distribution, consumption, savings, and Expenditure, investment expenditure interact; and the factors of production affecting them, such as: Labour (human activity), labour, Capital (economics), capital, Land (economics), land, and Entrepreneurship, enterprise, inflation, economic growth, and public policies that impact gloss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antoine Augustin Cournot
Antoine Augustin Cournot (; 28 August 180131 March 1877) was a French philosopher and mathematician who contributed to the development of economics. Biography Antoine Augustin Cournot was born on August 28, 1801 in Gray, Haute-Saône. He entered the preparatory school at Collège de Gray in 1809, where he studied until the age of 15. He later studied at Collège Royal de Besançon. In 1821, he entered one of the most prestigious Grande école, the École normale supérieure. According to Agnar Sandmo: in 1823 he took a license degree in mathematics at Sorbonne University. He then became the private secretary of a field marshal who required assistance in writing his memoirs. This position left Cournot with considerable time for his own pursuits. In the course of his ten years in the field marshal's employment he took two doctoral degrees, one in mechanics and one in astronomy. In addition, he published a number of articles and even acquired a degree in law. Subsequently, Cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Planning
A planned economy is a type of economic system where investment, production and the allocation of capital goods takes place according to economy-wide economic plans and production plans. A planned economy may use centralized, decentralized, participatory or Soviet-type forms of economic planning. The level of centralization or decentralization in decision-making and participation depends on the specific type of planning mechanism employed. Socialist states based on the Soviet model have used central planning, although a minority such as the former Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia have adopted some degree of market socialism. Market abolitionist socialism replaces factor markets with direct calculation as the means to coordinate the activities of the various socially owned economic enterprises that make up the economy. More recent approaches to socialist planning and allocation have come from some economists and computer scientists proposing planning mechanisms ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Price Mechanism
In economics, a price mechanism refers to the way in which price determines the allocation of resources and influences the quantity supplied and the quantity demanded of goods and services. The price mechanism, part of a market system, functions in various ways to match up buyers and sellers: as an incentive, a signal, and a rationing system for resources. The price mechanism is an economic model where price plays a key role in directing the activities of producers, consumers, and resource suppliers. An example of a price mechanism uses announced buy and sell prices. Generally speaking, when two parties wish to engage in trade, the purchaser will announce a price he is willing to pay (the Offer and acceptance, offer price) and the seller will announce a price he is willing to accept (the Offer and acceptance, sell price). The primary advantage of such a method is that conditions are laid out in advance, and transactions can proceed with no further permission or authorization fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Market
In economics, a free market is an economic market (economics), system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of Forms of government, government or any other external authority. Proponents of the free market as a normative ideal contrast it with a regulated market, in which a government intervenes in supply and demand by means of various methods such as taxes or regulations. In an idealized free market economy, prices for goods and services are set solely by the bids and offers of the participants. Scholars contrast the concept of a free market with the concept of a Coordinated market economy, coordinated market in fields of study such as political economy, new institutional economics, economic sociology, and political science. All of these fields emphasize the importance in currently existing market systems of rule-making institutions external to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adam Smith
Adam Smith (baptised 1723 – 17 July 1790) was a Scottish economist and philosopher who was a pioneer in the field of political economy and key figure during the Scottish Enlightenment. Seen by some as the "father of economics"——— or the "father of capitalism".———— He is known for two classic works: ''The Theory of Moral Sentiments'' (1759) and ''The Wealth of Nations, An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations'' (1776). The latter, often abbreviated as ''The Wealth of Nations'', is regarded as his ''magnum opus'', marking the inception of modern economic scholarship as a comprehensive system and an academic discipline. Smith refuses to explain the distribution of wealth and power in terms of divine will and instead appeals to natural, political, social, economic, legal, environmental and technological factors, as well as the interactions among them. The work is notable for its contribution to economic theory, particularly in its exposition o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Economics
Classical economics, also known as the classical school of economics, or classical political economy, is a school of thought in political economy that flourished, primarily in Britain, in the late 18th and early-to-mid 19th century. It includes both the Smithian and Ricardian schools. Its main thinkers are held to be Adam Smith, Jean-Baptiste Say, David Ricardo, Thomas Robert Malthus, and John Stuart Mill. These economists produced a theory of market economies as largely self-regulating systems, governed by natural laws of production and exchange (famously captured by Adam Smith's metaphor of the invisible hand). Adam Smith's '' The Wealth of Nations'' in 1776 is usually considered to mark the beginning of classical economics.Smith, Adam (1776) An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of The Wealth of Nations. (accessible by table of contents chapter titles) AdamSmith.org The fundamental message in Smith's book was that the wealth of any nation was determined not by the gol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Exports To England
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin and contains essential nutrients such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is ingested by an organism and assimilated by the organism's cells to provide energy, maintain life, or stimulate growth. Different species of animals have different feeding behaviours that satisfy the needs of their metabolisms and have evolved to fill a specific ecological niche within specific geographical contexts. Omnivorous humans are highly adaptable and have adapted to obtaining food in many different ecosystems. Humans generally use cooking to prepare food for consumption. The majority of the food energy required is supplied by the industrial food industry, which produces food through intensive agriculture and distributes it through complex food processing and food distribution systems. This system of conventional agriculture relies he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelanda sovereign state covering five-sixths of the island) and Northern Ireland (part of the United Kingdomcovering the remaining sixth). It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the List of islands of the British Isles, second-largest island of the British Isles, the List of European islands by area, third-largest in Europe, and the List of islands by area, twentieth-largest in the world. As of 2022, the Irish population analysis, population of the entire island is just over 7 million, with 5.1 million in the Republic of Ireland and 1.9 million in Northern Ireland, ranking it the List of European islands by population, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Famine (Ireland)
The Great Famine, also known as the Great Hunger ( ), the Famine and the Irish Potato Famine, was a period of mass starvation and disease in Ireland lasting from 1845 to 1852 that constituted a historical social crisis and had a major impact on Irish society and history as a whole. The most severely affected areas were in the western and southern parts of Ireland—where the Irish language was dominant—hence the period was contemporaneously known in Irish as , which literally translates to "the bad life" and loosely translates to "the hard times". The worst year of the famine was 1847, which became known as "Black '47".Éamon Ó Cuív – the impact and legacy of the Great Irish Famine The population of Ireland on the eve of the famine was about 8.5 million; by 1901, it was just 4.4 million. During the Great Hunger, roughly 1 million people died and more than 1 million more Irish diaspora, fled the country, causing the country's population to fall by 20–25% between 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normative Economics
Normativity is the phenomenon in human societies of designating some actions or outcomes as good, desirable, or permissible, and others as bad, undesirable, or impermissible. A norm in this sense means a standard for evaluating or making judgments about behavior or outcomes. "Normative" is sometimes also used, somewhat confusingly, to mean relating to a descriptive standard: doing what is normally done or what most others are expected to do in practice. In this sense a norm is not evaluative, a basis for judging behavior or outcomes; it is simply a fact or observation about behavior or outcomes, without judgment. Many researchers in science, law, and philosophy try to restrict the use of the term "normative" to the evaluative sense and refer to the description of behavior and outcomes as positive, descriptive, predictive, or empirical. ''Normative'' has specialized meanings in different academic disciplines such as philosophy, social sciences, and law. In most contexts, normativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foundations Of Economic Analysis
''Foundations of Economic Analysis'' is a book by Paul A. Samuelson published in 1947 (Enlarged ed., 1983) by Harvard University Press. It is based on Samuelson's 1941 doctoral dissertation at Harvard University. The book sought to demonstrate a common mathematical structure underlying multiple branches of economics from two basic principles: maximizing behavior of agents (such as of utility by consumers and profits by firms) and stability of equilibrium as to economic systems (such as markets or economies). Among other contributions, it advanced the theory of index numbers and generalized welfare economics. It is especially known for definitively stating and formalizing qualitative and quantitative versions of the " comparative statics" method for calculating how a change in any parameter (say, a change in tax rates) affects an economic system. One of its key insights about comparative statics, called the correspondence principle, states that stability of equilibrium impli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |