|
ESP Game
The ESP game (''extrasensory perception game'') is a human-based computation game developed to address the problem of creating difficult metadata. The idea behind the game is to use the computational power of humans to perform a task that computers cannot (originally, image recognition) by packaging the task as a game. It was originally conceived by Luis von Ahn of Carnegie Mellon University and first posted online in 2003. On the official website, there was a running count of "Labels collected since October 5, 2003", updated every 12 hours. They stated that "If the ESP game is played as much as other popular online games, we estimate that all the images on the Web can be labeled in a matter of weeks!" 36 million labels had been collected as of May 2008. The original paper (2004) reported that a pair of players can produce 3.89 ± 0.69 labels per minute. At this rate, 5,000 people continuously playing the game could provide one label per image indexed by Google (425 million) in 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extrasensory Perception
Extrasensory perception (ESP), also known as a sixth sense, or cryptaesthesia, is a claimed paranormal ability pertaining to reception of information not gained through the recognized physical senses, but sensed with the mind. The term was adopted by Duke University botanist J. B. Rhine to denote psychic abilities such as intuition, telepathy, psychometry, clairvoyance, empathy and their trans-temporal operation as precognition or retrocognition. Second sight is an alleged form of extrasensory perception, whereby a person perceives information, in the form of a vision, about future events before they happen ( precognition), or about things or events at remote locations ( remote viewing). There is no evidence that second sight exists. Reports of second sight are known only from anecdotes. Second sight and ESP are classified as pseudosciences. History In the 1930s, at Duke University in North Carolina, J. B. Rhine and his wife Louisa E. Rhine conducted an invest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phetch
Phetch is a game with a purpose intended to label images on the internet with descriptive captions suitable to assist sight impaired readers. Approximately 75% of the images on the web do not have proper ALT text labels, making them inaccessible through screen readers. The solution aimed at by Phetch is to label the images external to the web page rather than depending upon the web page author to create proper alt text for each image. Rather than paying people to do the mundane task of labeling images, Phetch aims to create a fun game that produces such descriptions as a side effect of having fun. Phetch was created by Luis von Ahn and Shiry Ginosar of Carnegie Mellon University following the pattern set by the earlier ESP game. Phetch is played by three to five people. One is designated as a describer, while the rest are seekers. The describer is shown an image, which he describes to the seekers. The seekers use an Internet image search engine to attempt to find the image being d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guessing Games
Guessing is the act of drawing a swift conclusion, called a guess, from data directly at hand, which is then held as probable or tentative, while the person making the guess (the guesser) admittedly lacks material for a greater degree of certainty. A guess is an unstable answer, as it is "always putative, fallible, open to further revision and interpretation, and validated against the horizon of possible meanings by showing that one interpretation is more probable than another in light of what we already know". In many of its uses, "the meaning of guessing is assumed as implicitly understood",Mark Tschaepe, "Gradations of Guessing: Preliminary Sketches and Suggestions", in John R. Shook, ''Contemporary Pragmatism'' Volume 10, Number 2, (December 2013), p. 135-154. and the term is therefore often used without being meticulously defined. Guessing may combine elements of deduction, induction, abduction, and the purely random selection of one choice from a set of given options. Gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nello Cristianini
Nello Cristianini (born 1968) is a professor of Artificial Intelligence in the Department of Computer Science at the University of Bath. Education Cristianini holds a degree in physics from the University of Trieste, a Master in computational intelligence from Royal Holloway, University of London and a PhD from the University of Bristol. Previously he has been a professor of Artificial Intelligence at the University of Bristol, an associate professor at the University of California, Davis, and held visiting positions at other universities. Research His research contributions encompass the fields of machine learning, artificial intelligence and bioinformatics. Particularly, his work has focused on statistical analysis of learning algorithms, to its application to support vector machines, kernel methods and other algorithms. Cristianini is the co-author of two widely known books in machine learning, '' An Introduction to Support Vector Machines'' and '' Kernel Methods for P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Machine
A social machine is an environment comprising humans and technology interacting and producing outputs or action which would not be possible without both parties present. It can also be regarded as a machine, in which specific tasks are performed by human participants, whose interaction is mediated by an infrastructure (typically, but not necessarily, digital). The growth of social machines has been greatly enabled by technologies such as the Internet, the smartphone, social media and the World Wide Web, by connecting people in new ways. Concept The idea of social machines has been around for a long time, discussed as early as 1846 by Captain William Allen, and also by authors such as Norman Mailer, Gilles Deleuze and Félix Guattari. Social machines blur the lines between computational processes and input from humans. They often take the form of collaborative online projects which produce web content, such as Wikipedia, citizen science projects like Galaxy Zoo, and even social ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
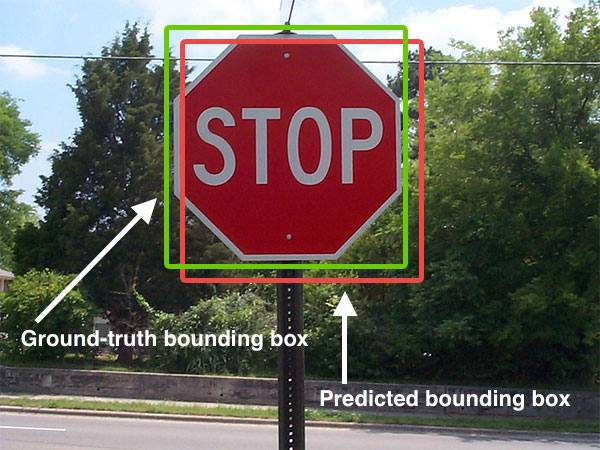
Image Recognition
Computer vision tasks include methods for acquiring, processing, analyzing, and understanding digital images, and extraction of high-dimensional data from the real world in order to produce numerical or symbolic information, e.g. in the form of decisions. "Understanding" in this context signifies the transformation of visual images (the input to the retina) into descriptions of the world that make sense to thought processes and can elicit appropriate action. This image understanding can be seen as the disentangling of symbolic information from image data using models constructed with the aid of geometry, physics, statistics, and learning theory. The scientific discipline of computer vision is concerned with the theory behind artificial systems that extract information from images. Image data can take many forms, such as video sequences, views from multiple cameras, multi-dimensional data from a 3D scanner, 3D point clouds from LiDaR sensors, or medical scanning devices. The t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ImageNet
The ImageNet project is a large visual database designed for use in Outline of object recognition, visual object recognition software research. More than 14 million images have been hand-annotated by the project to indicate what objects are pictured and in at least one million of the images, bounding boxes are also provided. ImageNet contains more than 20,000 categories, with a typical category, such as "balloon" or "strawberry", consisting of several hundred images. The database of annotations of third-party image URLs is freely available directly from ImageNet, though the actual images are not owned by ImageNet. Since 2010, the ImageNet project runs an annual software contest, the ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge (#History_of_the_ImageNet_challenge, ILSVRC), where software programs compete to correctly classify and detect objects and scenes. The challenge uses a "trimmed" list of one thousand non-overlapping classes. History AI researcher Fei-Fei Li began working ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Google Image Labeler
Google Image Labeler is a feature, in the form of a game, of Google Images that allows the user to label random images to help improve the quality of Google's image search results. It was online from 2006 to 2011 at http://images.google.com/imagelabeler/ (no longer available) and relaunched in 2016 at https://get.google.com/crowdsource/. History Luis von Ahn developed the ESP Game, a game in which two people were simultaneously given an image, with no way to communicate, other than knowing the matching label for each picture or the pass signal. The ESP Game had been licensed by Google in the form of the Google Image Labeler and launched this service, as a beta on August 31, 2006. In 2006, Ahn stated that the game could "effectively label all Google indexed images in two months". Players noticed various subtle changes in the game over time. In the earliest months, through about November 2006, players could see each other's guesses during play by mousing over the image. When " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Google
Google LLC (, ) is an American multinational corporation and technology company focusing on online advertising, search engine technology, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, consumer electronics, and artificial intelligence (AI). It has been referred to as "the most powerful company in the world" by the BBC and is one of the world's List of most valuable brands, most valuable brands. Google's parent company, Alphabet Inc., is one of the five Big Tech companies alongside Amazon (company), Amazon, Apple Inc., Apple, Meta Platforms, Meta, and Microsoft. Google was founded on September 4, 1998, by American computer scientists Larry Page and Sergey Brin. Together, they own about 14% of its publicly listed shares and control 56% of its stockholder voting power through super-voting stock. The company went public company, public via an initial public offering (IPO) in 2004. In 2015, Google was reorganized as a wholly owned subsidiary of Alphabet Inc. Go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GWAP
A human-based computation game or game with a purpose (GWAP) is a human-based computation technique of outsourcing steps within a computational process to humans in an entertaining way (gamification). Luis von Ahn first proposed the idea of "human algorithm games", or games with a purpose (GWAPs), in order to harness human time and energy for addressing problems that computers cannot yet tackle on their own. He believes that human intellect is an important resource and contribution to the enhancement of computer processing and human computer interaction. He argues that games constitute a general mechanism for using brainpower to solve open computational problems. In this technique, human brains are compared to processors in a distributed system, each performing a small task of a massive computation. However, humans require an incentive to become part of a collective computation. Online games are used as a means to encourage participation in the process. The tasks presented in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) is a private research university in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States. The institution was established in 1900 by Andrew Carnegie as the Carnegie Technical Schools. In 1912, it became the Carnegie Institute of Technology and began granting four-year degrees. In 1967, it became Carnegie Mellon University through its merger with the Mellon Institute of Industrial Research, founded in 1913 by Andrew Mellon and Richard B. Mellon and formerly a part of the University of Pittsburgh. The university consists of seven colleges, including the College of Engineering, the School of Computer Science, and the Tepper School of Business. The university has its main campus located 5 miles (8 km) from downtown Pittsburgh. It also has over a dozen degree-granting locations in six continents, including campuses in Qatar, Silicon Valley, and Kigali, Rwanda ( Carnegie Mellon University Africa) and partnerships with universities nationally and glob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |