|
Demetrius (son Of Philip V)
Demetrius was the younger son of Philip V of Macedon, but his only son by his legitimate wife, the elder brother Perseus being the son of a concubine.Livius. xxxix. 53 After the Battle of Cynoscephalae, Philip was obliged to surrender Demetrius, then very young, to Titus Quinctius Flamininus as a hostage, and he was subsequently sent to Rome in that capacity. Five years afterwards he was honourably restored to his father, Philip having at this time obtained the favour of Rome by his services in the war against Antiochus the Great Antiochus III the Great (; grc-gre, Ἀντίoχoς Μέγας ; c. 2413 July 187 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 222 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the r .... But this did not last long, and Philip, finding himself assailed on all sides by the machinations of Rome and her intrigues among his neighbours, determined to try to avert, or at least delay, the impen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip V Of Macedon
Philip V ( grc-gre, Φίλιππος ; 238–179 BC) was king ( Basileus) of Macedonia from 221 to 179 BC. Philip's reign was principally marked by an unsuccessful struggle with the emerging power of the Roman Republic. He would lead Macedon against Rome in the First and Second Macedonian Wars, losing the latter but allying with Rome in the Roman-Seleucid War towards the end of his reign. Early life Philip was the son of Demetrius II of Macedon and Chryseis. Philip was nine years old when his father died 229 BC. His elder paternal half sister was Apama III. Philips's great-uncle, Antigonus III Doson, administered the kingdom as regent until his death in 221 BC when Philip was seventeen years old. Philip was attractive and charismatic as a young man. A dashing and courageous warrior, he was compared to Alexander the Great and was nicknamed ''beloved of the Hellenes'' () because he became, as Polybius put it, "...the beloved of the Hellenes for his charitable inclination" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perseus Of Macedon
Perseus ( grc-gre, Περσεύς; 212 – 166 BC) was the last king (''Basileus'') of the Antigonid dynasty, who ruled the successor state in Macedon created upon the death of Alexander the Great. He was the last Antigonid to rule Macedon, after losing the Battle of Pydna on 22 June 168 BC; subsequently, Macedon came under Roman rule. Early life Perseus was the son of king Philip V of Macedon and a concubine, probably Polycratia of Argos. His father spent most of his reign attempting to maintain Macedonian hegemony over Greece against heavy Greek resistance and, in his later reign, against a expansionist Roman Republic. In this regard Philip V would fail as following defeat in the Second Macedonian War, he would have to accept Roman power in Greece and would later help Rome in the War against Nabis (195 BC) and Aetolian War (191-189 BC). Perseus is recorded as having commanded Macedonian troops in both the Second Macedonian War and Aetolian War. Being a son of a concubine, P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Cynoscephalae
The Battle of Cynoscephalae ( el, Μάχη τῶν Κυνὸς Κεφαλῶν) was an encounter battle fought in Thessaly in 197 BC between the Roman army, led by Titus Quinctius Flamininus, and the Antigonid dynasty of Macedon, led by Philip V during the Second Macedonian War. It was a decisive Roman victory and marked the end of the conflict. Prelude In 201 BC, Rome won the Second Punic War against Carthage. Philip V of Macedon had attacked Rome's client states in the Mediterranean for 20 years. The Greek city-states, led by Athens, appealed to Rome for help. In 197 BC the Roman army of Titus Quinctius Flamininus, with his allies from the Aetolian League, marched out towards Pherae in search of Philip, who was at Larissa. Armies Romans Flamininus had about 25,500 men, thus subdivided: 16,000 legionary infantry, 8,400 light infantry, 1,800 cavalry and 20 war elephants; further it included soldiers from the allied Aetolian League, light infantry from Athamania, and merce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titus Quinctius Flamininus
Titus Quinctius Flamininus (c. 228 – 174 BC) was a Roman politician and general instrumental in the Roman conquest of Greece. Family background Flamininus belonged to the minor patrician '' gens'' Quinctia. The family had a glorious place in the early history of Rome, especially the famous hero Lucius Quinctius Cincinnatus, but it had somewhat lost its political influence by the middle of the fourth century BC. Flamininus' great grandfather Caeso Quintius Claudus was still consul in 271, the last time a Quintius is recorded as holding a curule office before 209. Lucius Quinctius, his grandfather, was '' flamen Dialis''—the great priest of Jupiter—during the third quarter of the third century. The cognomen Flamininus borne by his descendants derives from this prestigious priesthood. Flamininus' great grandson later put an '' apex'', the head covering of the Flamen, as a symbol of his family on a denarius he minted. Flamininus' father—also named Titus—is not kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
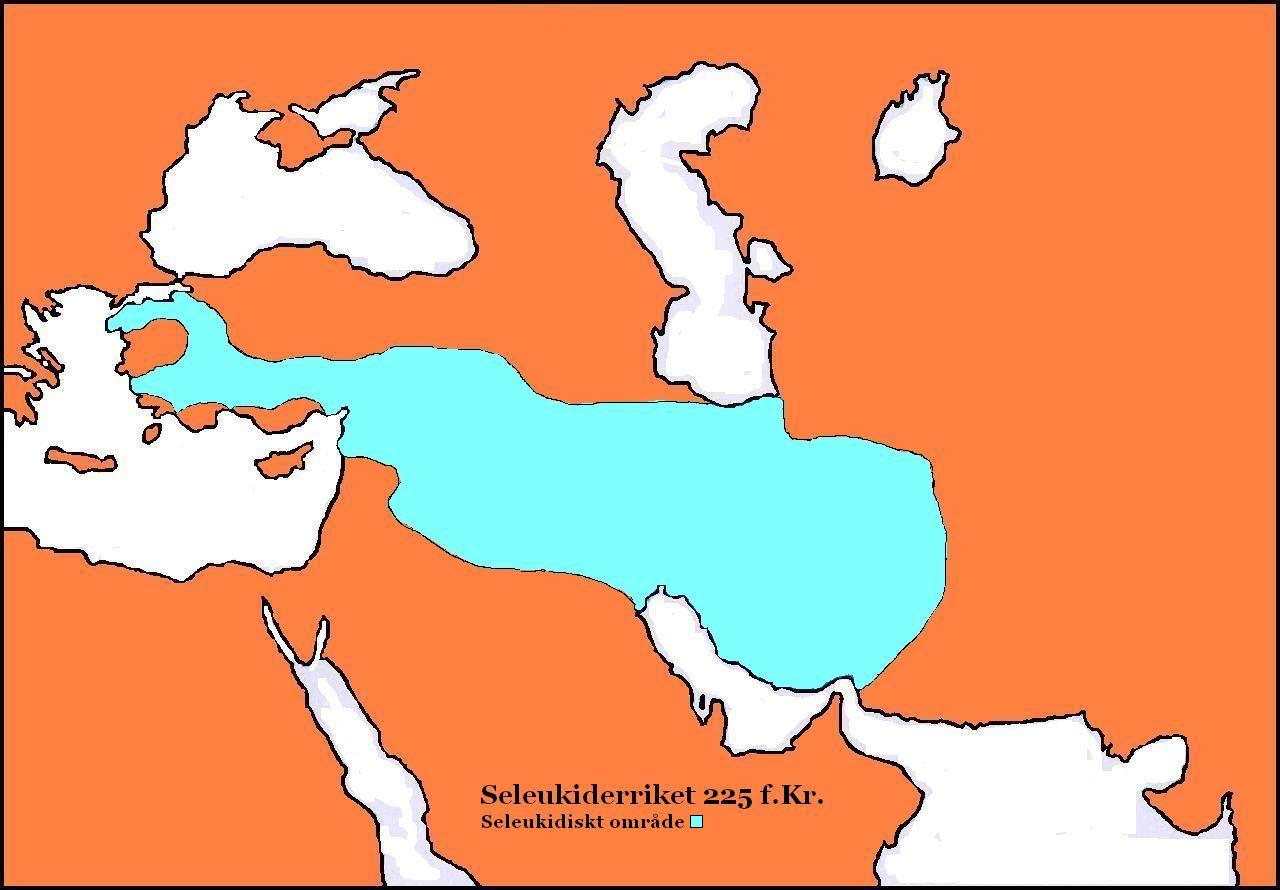
Antiochus The Great
Antiochus III the Great (; grc-gre, Ἀντίoχoς Μέγας ; c. 2413 July 187 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 222 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the rest of western Asia towards the end of the 3rd century BC. Rising to the throne at the age of eighteen in 222 BC, his early campaigns against the Ptolemaic Kingdom were unsuccessful, but in the following years Antiochus gained several military victories and substantially expanded the empire's territory. His traditional designation, ''the Great'', reflects an epithet he assumed. He also assumed the title ''Basileus Megas'' (Greek for " Great King"), the traditional title of the Persian kings. A militarily active ruler, Antiochus restored much of the territory of the Seleucid Empire, before suffering a serious setback, towards the end of his reign, in his war against Rome. Declaring himself the "champion of Greek freedom against Roman domi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murdered Royalty Of Macedonia (ancient Kingdom)
Murder is the unlawful killing of another human without justification or valid excuse, especially the unlawful killing of another human with malice aforethought. ("The killing of another person without justification or excuse, especially the crime of killing a person with malice aforethought or with recklessness manifesting extreme indifference to the value of human life.") This state of mind may, depending upon the jurisdiction, distinguish murder from other forms of unlawful homicide, such as manslaughter. Manslaughter is killing committed in the absence of ''malice'',This is "malice" in a technical legal sense, not the more usual English sense denoting an emotional state. See malice (law). brought about by reasonable provocation, or diminished capacity. ''Involuntary'' manslaughter, where it is recognized, is a killing that lacks all but the most attenuated guilty intent, recklessness. Most societies consider murder to be an extremely serious crime, and thus that a per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambassadors In Greek Antiquity
An ambassador is an official envoy, especially a high-ranking diplomat who represents a state and is usually accredited to another sovereign state or to an international organization as the resident representative of their own government or sovereign or appointed for a special and often temporary diplomatic assignment. The word is also used informally for people who are known, without national appointment, to represent certain professions, activities, and fields of endeavor, such as sales. An ambassador is the ranking government representative stationed in a foreign capital or country. The host country typically allows the ambassador control of specific territory called an embassy, whose territory, staff, and vehicles are generally afforded diplomatic immunity in the host country. Under the Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations, an ambassador has the highest diplomatic rank. Countries may choose to maintain diplomatic relations at a lower level by appointing a chargé d'affa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambassadors To Ancient Rome
An ambassador is an official envoy, especially a high-ranking diplomat who represents a state and is usually accredited to another sovereign state or to an international organization as the resident representative of their own government or sovereign or appointed for a special and often temporary diplomatic assignment. The word is also used informally for people who are known, without national appointment, to represent certain professions, activities, and fields of endeavor, such as sales. An ambassador is the ranking government representative stationed in a foreign capital or country. The host country typically allows the ambassador control of specific territory called an embassy, whose territory, staff, and vehicles are generally afforded diplomatic immunity in the host country. Under the Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations, an ambassador has the highest diplomatic rank. Countries may choose to maintain diplomatic relations at a lower level by appointing a chargé d'af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)