|
Dühring's Rule
Dühring's rule is a scientific rule developed by Eugen Dühring which states that a linear relationship exists between the temperatures at which two solutions exert the same vapour pressure. The rule is often used to compare a pure liquid and a solution at a given concentration. Dühring's plot is a graphical representation of such a relationship, typically with the pure liquid's boiling point along the x-axis and the mixture's boiling point along the y-axis; each line of the graph represents a constant concentration. See also * Solubility * Evaporator * Raoult's law Raoult's law ( law) is a relation of physical chemistry, with implications in thermodynamics. Proposed by French chemist François-Marie Raoult in 1887, it states that the partial pressure of each component of an ideal mixture of ''liquids'' is ... References Engineering thermodynamics Solutions {{engineering-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugen Dühring
Eugen Karl Dühring (; 12 January 1833 – 21 September 1921) was an antisemitic, positivist and socialist German philosopher and economist who was a strong critic of Marxism. Life and works Dühring was born in Berlin, Prussia. After a legal education he practised law in Berlin until 1859. A weakness of the eyes, ending in total blindness, led him to take up the studies with which his name is now connected. In 1864, he became docent of the University of Berlin, but, in consequence of a quarrel with the professoriate, was deprived of his licence to teach in 1874. Among his works are (1865); (1865); (1865); (1869); (1872), one of his most successful works; (1873); (1875), entitled in a later edition ; (1878); and (1883). He also published (1881, ''The Jewish Question as a Racial, Moral, and Cultural Question''). – Major Works of Eugen Dühring nbsp; ..(mx) ''Die Judenfrage als Racen-, Sitten- und Culturfrage'', 1881,on Google Books (later editions retitled ''Die Jud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solution (chemistry)
In chemistry, a solution is defined by IUPAC as "A liquid or solid phase containing more than one substance, when for convenience one (or more) substance, which is called the solvent, is treated differently from the other substances, which are called solutes. When, as is often but not necessarily the case, the sum of the mole fractions of solutes is small compared with unity, the solution is called a dilute solution. A superscript attached to the ∞ symbol for a property of a solution denotes the property in the limit of infinite dilution." One important parameter of a solution is the concentration, which is a measure of the amount of solute in a given amount of solution or solvent. The term " aqueous solution" is used when one of the solvents is water. Types ''Homogeneous'' means that the components of the mixture form a single phase. ''Heterogeneous'' means that the components of the mixture are of different phase. The properties of the mixture (such as concentration, temp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concentration
In chemistry, concentration is the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Several types of mathematical description can be distinguished: '' mass concentration'', '' molar concentration'', '' number concentration'', and '' volume concentration''. The concentration can refer to any kind of chemical mixture, but most frequently refers to solutes and solvents in solutions. The molar (amount) concentration has variants, such as normal concentration and osmotic concentration. Dilution is reduction of concentration, e.g. by adding solvent to a solution. The verb to concentrate means to increase concentration, the opposite of dilute. Etymology ''Concentration-'', ''concentratio'', action or an act of coming together at a single place, bringing to a common center, was used in post-classical Latin in 1550 or earlier, similar terms attested in Italian (1589), Spanish (1589), English (1606), French (1632). Qualitative description Often in informal, non- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartesian Coordinate System
In geometry, a Cartesian coordinate system (, ) in a plane (geometry), plane is a coordinate system that specifies each point (geometry), point uniquely by a pair of real numbers called ''coordinates'', which are the positive and negative numbers, signed distances to the point from two fixed perpendicular oriented lines, called ''coordinate lines'', ''coordinate axes'' or just ''axes'' (plural of ''axis'') of the system. The point where the axes meet is called the ''Origin (mathematics), origin'' and has as coordinates. The axes direction (geometry), directions represent an orthogonal basis. The combination of origin and basis forms a coordinate frame called the Cartesian frame. Similarly, the position of any point in three-dimensional space can be specified by three ''Cartesian coordinates'', which are the signed distances from the point to three mutually perpendicular planes. More generally, Cartesian coordinates specify the point in an -dimensional Euclidean space for any di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boiling Point
The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the pressure surrounding the liquid and the liquid changes into a vapor. The boiling point of a liquid varies depending upon the surrounding environmental pressure. A liquid in a partial vacuum, i.e., under a lower pressure, has a lower boiling point than when that liquid is at atmospheric pressure. Because of this, water boils at 100°C (or with scientific precision: ) under standard pressure at sea level, but at at altitude. For a given pressure, different liquids will boiling, boil at different temperatures. The normal boiling point (also called the atmospheric boiling point or the atmospheric pressure boiling point) of a liquid is the special case in which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the defined atmospheric pressure at sea level, one Atmosphere (unit), atmosphere. At that temperature, the vapor pressure of the liquid becomes sufficient to overcome atmospheric pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solubility
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a chemical substance, substance, the solute, to form a solution (chemistry), solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution. The extent of the solubility of a substance in a specific solvent is generally measured as the concentration of the solute in a wikt:saturated#Chemistry, saturated solution, one in which no more solute can be dissolved. At this point, the two substances are said to be at the solubility equilibrium. For some solutes and solvents, there may be no such limit, in which case the two substances are said to be "miscibility, miscible in all proportions" (or just "miscible"). The solute can be a solid, a liquid, or a gas, while the solvent is usually solid or liquid. Both may be pure substances, or may themselves be solutions. Gases are always miscible in all proportions, except in very extreme situations,J. de Swaan Arons and G. A. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evaporator
An evaporator is a type of heat exchanger device that facilitates evaporation by utilizing conductive and convective heat transfer, which provides the necessary thermal energy for phase transition from liquid to vapour. Within evaporators, a circulating liquid is exposed to an atmospheric or reduced pressure environment causing it to boil at a lower temperature compared to normal atmospheric boiling. The four main components of an Evaporator (marine), evaporator assembly are: Heat is transferred to the liquid inside the tube walls via conduction providing the thermal energy needed for evaporation. Convection, Convective currents inside it also contribute to heat transfer efficiency. There are various evaporator designs suitable for different applications including shell and tube, plate, and flooded evaporators, commonly used in industrial processes such as desalination, power generation and air conditioning. Plate-type evaporators offer compactness while multi-stage designs ena ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
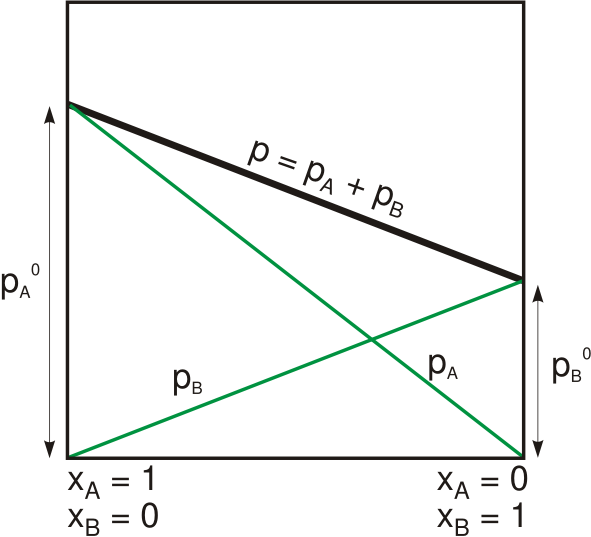
Raoult's Law
Raoult's law ( law) is a relation of physical chemistry, with implications in thermodynamics. Proposed by French chemist François-Marie Raoult in 1887, it states that the partial pressure of each component of an ideal mixture of ''liquids'' is equal to the vapor pressure of the pure component (liquid or solid) multiplied by its mole fraction in the mixture. In consequence, the relative lowering of vapor pressure of a dilute solution of nonvolatile solute is equal to the mole fraction of solute in the solution. Mathematically, Raoult's law for a single component in an ideal solution is stated as : p_i = p_i^\star x_i where p_i is the partial pressure of the component i in the gaseous mixture above the solution, p_i^\star is the equilibrium vapor pressure of the pure component i, and x_i is the mole fraction of the component i in the liquid or solid solution. Where two volatile liquids A and B are mixed with each other to form a solution, the vapor phase consists of both compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engineering Thermodynamics
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to Problem solving#Engineering, solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve Systems engineering, systems. Modern engineering comprises many subfields which include designing and improving infrastructure, machinery, vehicles, electronics, Materials engineering, materials, and energy systems. The Academic discipline, discipline of engineering encompasses a broad range of more Academic specialization, specialized fields of engineering, each with a more specific emphasis for applications of applied mathematics, mathematics and applied science, science. See glossary of engineering. The word '':wikt:engineering, engineering'' is derived from the Latin . Definition The American Engineers' Council for Professional Development (the predecessor of the Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology aka ABET) has defined "engineering" as: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |