|
Dunbar
Dunbar () is a town on the North Sea coast in East Lothian in the south-east of Scotland, approximately east of Edinburgh and from the Anglo–Scottish border, English border north of Berwick-upon-Tweed. Dunbar is a former royal burgh, and gave its name to an ecclesiastical and Civil parishes in Scotland, civil parish. The parish extends around east to west and is deep at its greatest extent, or , and contains the villages of West Barns, Belhaven, Scotland, Belhaven, and East Barns (abandoned) and several hamlets and farms. Dunbar has a Dunbar Harbour, harbour dating from 1574 and is home to the Dunbar Lifeboat Station, the second-oldest RNLI station in Scotland. The Dunbar Primary School and Dunbar Grammar School opened in the 1950s and 1960s. Dunbar is the birthplace of the explorer, naturalist, and influential conservationist John Muir. John Muir's Birthplace, The house in which Muir was born is located on the High Street, and has been converted into a museum. There i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunbar Harbour
Dunbar Harbour is a seaport forming the north-east part of the town of Dunbar, East Lothian, Scotland. It is situated on a point projecting from the North Sea coast of East Lothian into the mouth of the Firth of Forth. The built harbour, on the site of an earlier natural anchorage, comprises three main sections: the Old Harbour, in the east of the port, protected by a sea-wall to its east and north and dating from the late 16th-Century; the New or Victoria Harbour in the west dating from 1842; and Broad Haven, formerly the approach from the Forth to the Old Harbour, but latterly, its entrance having been blocked, providing additional sheltered water between the Old and New Harbours. The harbour is a trust port, responsibility for which lies since 2004 with the Dunbar Harbour Trust. In prior times the port was controlled by the local authority and, earlier, by the magistrates and council of the burgh. It is the home port for a commercial fishing fleet, offering moorings and fuel a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunbar Town House
The Dunbar Town House, also known as Dunbar Tolbooth, is a municipal structure in the High Street in Dunbar, East Lothian, Scotland. The building, which currently operates as a museum, is a Category A listed building. History The first municipal building in Dunbar was a tolbooth which dated back at least to the first half of the 16th century. After it became dilapidated, it was rebuilt in the Renaissance style with harled rubble masonry from a quarry at Innerwick to create the current structure which was completed in 1593. The design involved an asymmetrical main frontage with three bays facing onto the High Street; the central bay featured a semi-octagonal tower which projected forward. The tower featured a pend with a wrought iron grill on the ground floor, small windows on the upper floors and a spire. The outer bays were fenestrated on the first floor by two sash windows on the left and two small windows on the right, while, on the second floor there were two pedimented ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
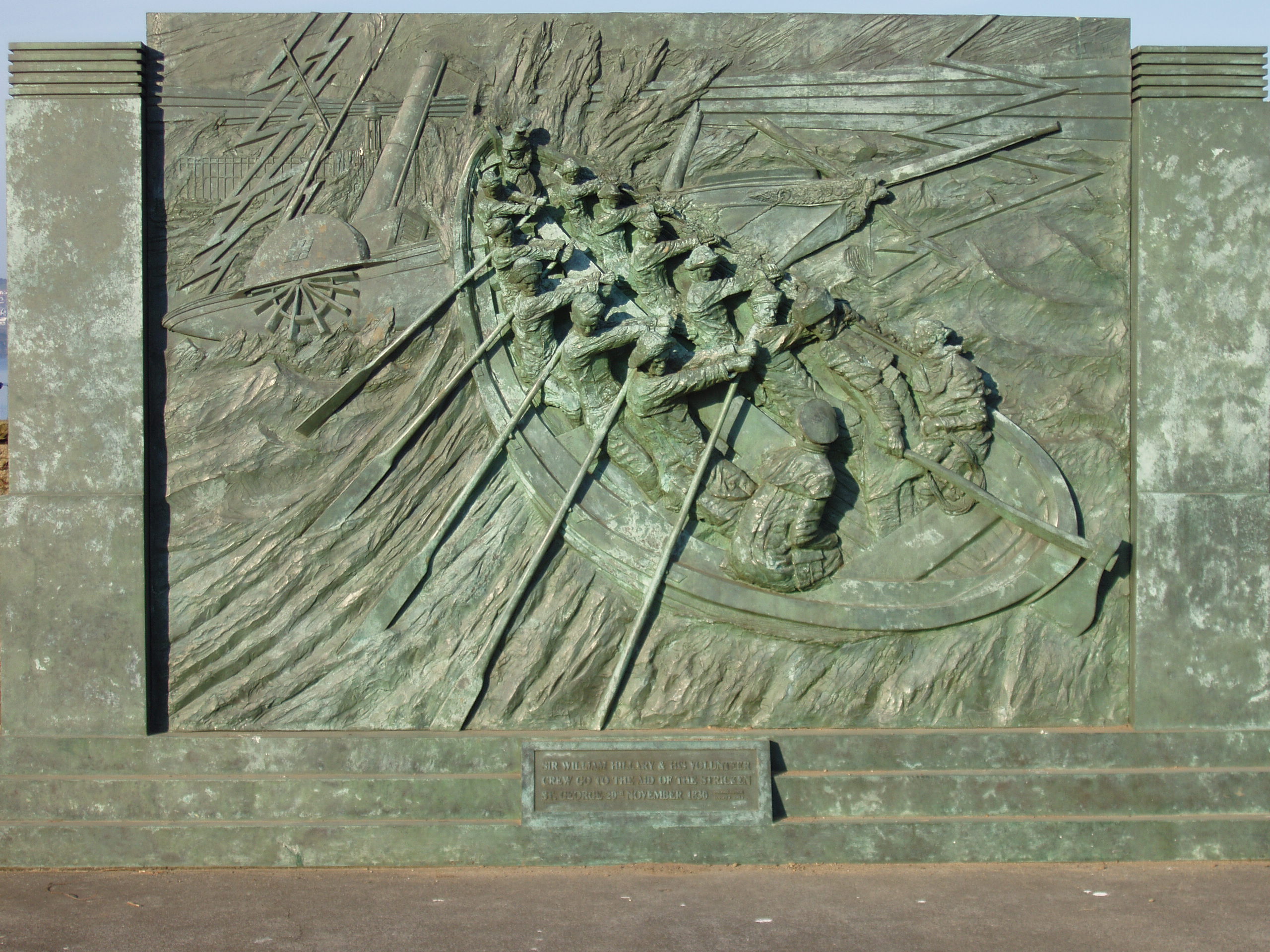
RNLI
The Royal National Lifeboat Institution (RNLI) is the largest of the lifeboat services operating around the coasts of the United Kingdom, Ireland, the Channel Islands, and the Isle of Man, as well as on some inland waterways. Founded in 1824 as the National Institution for the Preservation of Life from Shipwreck, it soon afterwards became the Royal National Institution for the Preservation of Life from Shipwreck because of the patronage of King George IV. Royal patronage has continued up to the present day with King Charles III. The organisation changed its name to the Royal National Lifeboat Institution on 5 October 1854 and was granted a royal charter in 1860. The RNLI is a charity based in Poole, Dorset. It is principally funded by legacies (65%) and donations (30%). Most of its lifeboat crews are unpaid volunteers. They operate more than 400 lifeboats from 238 stations. Paid lifeguards provide services at nearly 250 beaches. The RNLI also provides free safety advice to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vita Sancti Wilfrithi
The ''Vita Sancti Wilfrithi'' or ''Life of St Wilfrid'' (spelled "Wilfrid" in the modern era) is an early 8th-century hagiographic text recounting the life of the Northumbrian bishop, Wilfrid. Although a hagiography, it has few miracles, while its main concerns are with the politics of the Northumbrian church and the history of the monasteries of Ripon and Hexham. It is one of a collection of historical sources from the late 7th- and early 8th-centuries, along with the anonymous '' Vita Sancti Cuthberti'', the works of Bede and Adomnán's '' Vita Sancti Columbae'', that detail the Christianisation of Great Britain and make the period the best documented period in English history before the age of Alfred the Great. Date and authorship In the preface to the ''Vita Wilfrithi'', the author reveals that he is a priest called Stephen. Writers in modern times often style the author "Eddius Stephanus", an attribution that goes back to the 17th century. This attribution is now thought ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
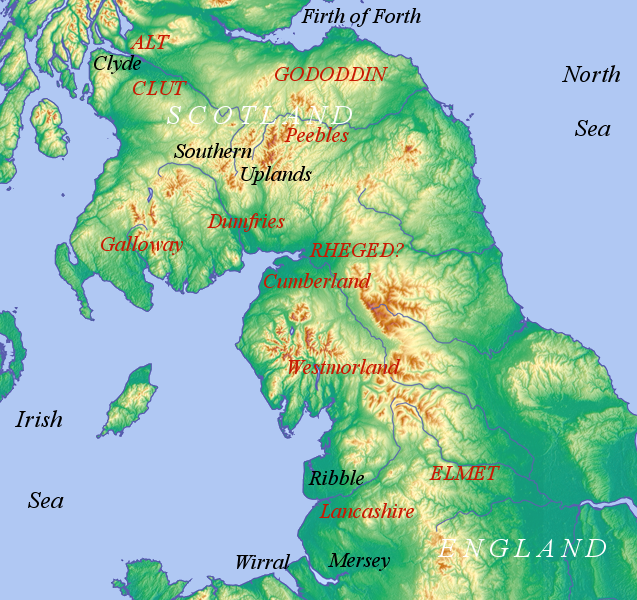
Cumbric
Cumbric is an extinct Celtic language of the Brittonic subgroup spoken during the Early Middle Ages in the ''Hen Ogledd'' or "Old North", in Northern England and the southern Scottish Lowlands. It was closely related to Old Welsh and the other Brittonic languages. Place-name evidence suggests Cumbric may also have been spoken as far south as Pendle and the Yorkshire Dales. The prevailing view is that it became extinct in the 12th century, after the incorporation of the Kingdom of Strathclyde into the Kingdom of Scotland. Problems with terminology Dauvit Broun sets out the problems with the various terms used to describe the Cumbric language and its speakers.Broun, Dauvit (2004): 'The Welsh identity of the kingdom of Strathclyde, ca 900-ca 1200', ''Innes Review'' 55, pp 111–80. The people seem to have called themselves the same way that the Welsh called themselves (most likely from reconstructed Brittonic meaning "fellow countrymen"). The Welsh and the Cumbric-speaki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic (, ; Endonym and exonym, endonym: ), also known as Scots Gaelic or simply Gaelic, is a Celtic language native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a member of the Goidelic language, Goidelic branch of Celtic, Scottish Gaelic, alongside both Irish language, Irish and Manx language, Manx, developed out of Old Irish. It became a distinct spoken language sometime in the 13th century in the Middle Irish period, although a Classical Gaelic, common literary language was shared by the Gaels of both Ireland and Scotland until well into the 17th century. Most of modern Scotland was once Gaelic-speaking, as evidenced especially by Gaelic-language place names. In the 2011 United Kingdom census#2011 Census for Scotland, 2011 census of Scotland, 57,375 people (1.1% of the Scottish population, three years and older) reported being able to speak Gaelic, 1,275 fewer than in 2001. The highest percentages of Gaelic speakers were in the Outer Hebrides. Nevertheless, there is a language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goidelic Languages
The Goidelic ( ) or Gaelic languages (; ; ) form one of the two groups of Insular Celtic languages, the other being the Brittonic languages. Goidelic languages historically formed a dialect continuum stretching from Ireland through the Isle of Man to Scotland. There are three modern Goidelic languages: Irish ('), Scottish Gaelic ('), and Manx ('). Manx died out as a first language in the 20th century but has since been revived to some degree. Nomenclature ''Gaelic'', by itself, is sometimes used to refer to Scottish Gaelic, especially in Scotland, and therefore is ambiguous. Irish and Manx are sometimes referred to as Irish Gaelic and Manx Gaelic (as they are Goidelic or Gaelic languages), but the use of the word ''Gaelic'' is unnecessary because the terms Irish and Manx, when used to denote languages, always refer to those languages. This is in contrast to Scottish Gaelic, for which "Gaelic" distinguishes the language from the Germanic language known as Scots. In Englis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seal Of Dunbar From Samuel Lewis
Seal may refer to any of the following: Common uses * Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly: ** Earless seal, also called "true seal" ** Fur seal ** Eared seal * Seal (emblem), a device to impress an emblem, used as a means of authentication, on paper, wax, clay or another medium (the impression is also called a seal) * Seal (mechanical), a device which helps prevent leakage, contain pressure, or exclude contamination where two systems join ** Hermetic seal, an airtight mechanical seal * Security seals such as labels, tapes, bands, or ties affixed onto a container in order to prevent and detect tampering Arts, entertainment and media * ''Seal'' (1991 album), by Seal * ''Seal'' (1994 album), sometimes referred to as ''Seal II'', by Seal * '' Seal IV'', a 2003 album by Seal * '' Seal Online'', a 2003 massively multiplayer online role-playing game Law * Seal (contract law), a legal formality for con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunbar Harbour And Castle Ruins
Dunbar () is a town on the North Sea coast in East Lothian in the south-east of Scotland, approximately east of Edinburgh and from the English border north of Berwick-upon-Tweed. Dunbar is a former royal burgh, and gave its name to an ecclesiastical and civil parish. The parish extends around east to west and is deep at its greatest extent, or , and contains the villages of West Barns, Belhaven, and East Barns (abandoned) and several hamlets and farms. Dunbar has a harbour dating from 1574 and is home to the Dunbar Lifeboat Station, the second-oldest RNLI station in Scotland. The Dunbar Primary School and Dunbar Grammar School opened in the 1950s and 1960s. Dunbar is the birthplace of the explorer, naturalist, and influential conservationist John Muir. The house in which Muir was born is located on the High Street, and has been converted into a museum. There is also a commemorative statue beside the town clock, and John Muir Country Park is located to the north-we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Parks
A national park is a nature park designated for conservation (ethic), conservation purposes because of unparalleled national natural, historic, or cultural significance. It is an area of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that is protected and owned by a government. Although governments hold different standards for national park designation, the conservation of 'wild nature' for posterity and as a symbol of national pride is a common motivation for the continued protection of all national parks around the world. National parks are almost always accessible to the public.Gissibl, B., S. Höhler and P. Kupper, 2012, ''Civilizing Nature, National Parks in Global Historical Perspective'', Berghahn, Oxford Usually national parks are developed, owned and managed by national governments, though in some countries with federal government, federal or Devolution, devolved forms of government, "national parks" may be the responsibility of subnational, regional, or local authorities. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |