|
Duckett's Canal
The Hertford Union Canal or Duckett's Cut, just over long, connects the Regent's Canal to the Lee Navigation in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets in East London. It was opened in 1830 but quickly proved to be a commercial failure. It was acquired by the Regents Canal Company in 1857, and became part of the Grand Union Canal in 1927. History Like its 1766 predecessor, the Limehouse Cut, the Hertford Union Canal was intended to provide a short-cut between the River Thames and the River Lee Navigation. It allowed traffic on the Lea heading for the Thames to bypass the tidal, tortuous and often silted Bow Back Rivers of the Lea via a short stretch of the Regent's Canal, and provided a short-cut from the Lea to places west along the Regent's Canal. The canal was promoted by Sir George Duckett who succeeded in obtaining an Act of Parliament that gained its Royal Assent on 17 May 1824, entitled ''An Act for making and maintaining a navigable Canal from the River Lee Naviga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Giles
Francis Giles (1787–1847) was a canal engineer and surveyor who worked under John Rennie and later became a railway engineer. Works and appointments * Kent & Sussex Junction Canal 1811 – with Netlam Giles surveyed the route as part of John Rennie's check of Alexander Sutherland's work. * Stort - Cam Canal 1811 – re-surveyed the route with Netlam Giles under the direction of John Rennie. * Wey and Arun Junction Canal 1815 – with Netlam Giles surveyed a route from the Croydon Canal to Newbridge in the Arun valley * Portsmouth & Arundel Canal 1815 – with Netlam Giles surveyed a route for the canal on behalf of John Rennie. * Western Union Canal project 1819 – plan of the canal for the Kennet & Avon Canal committee. * River Ivel – 1821 – costed river navigation from Biggleswade to Langford Bridge and to Hitchin and Baldock. * River Ivel 1822 – costed river navigation to Shefford. * Aire & Calder Navigation – Wakefield Section 1822 - worked on alternative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grove Road
The A1205 is a road in east London which runs north to south parallel to the Regent's Canal and connects South Hackney and Victoria Park with the A13 at Limehouse. It is approximately 2 miles (3 km) in length, and runs in a roughly SSW direction. Route Lauriston Road The road starts at a roundabout junction with Victoria Park Road in South Hackney in the London Borough of Hackney, and for the short distance it is in that borough it is called ''Lauriston Road''. Grove Road The road then enters the London Borough of Tower Hamlets and forms a divide between the two halves of Victoria Park, until a roundabout junction with Old Ford Road (the B118). By the roundabout is the Lakeview Estate, designed by Berthold Lubetkin. From there until it crosses Mile End Road, the A1205 is called Grove Road and for much of the distance after crossing Roman Road it forms the eastern boundary of Mile End Park. Where the road passes under the Great Eastern Main Line, there is a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
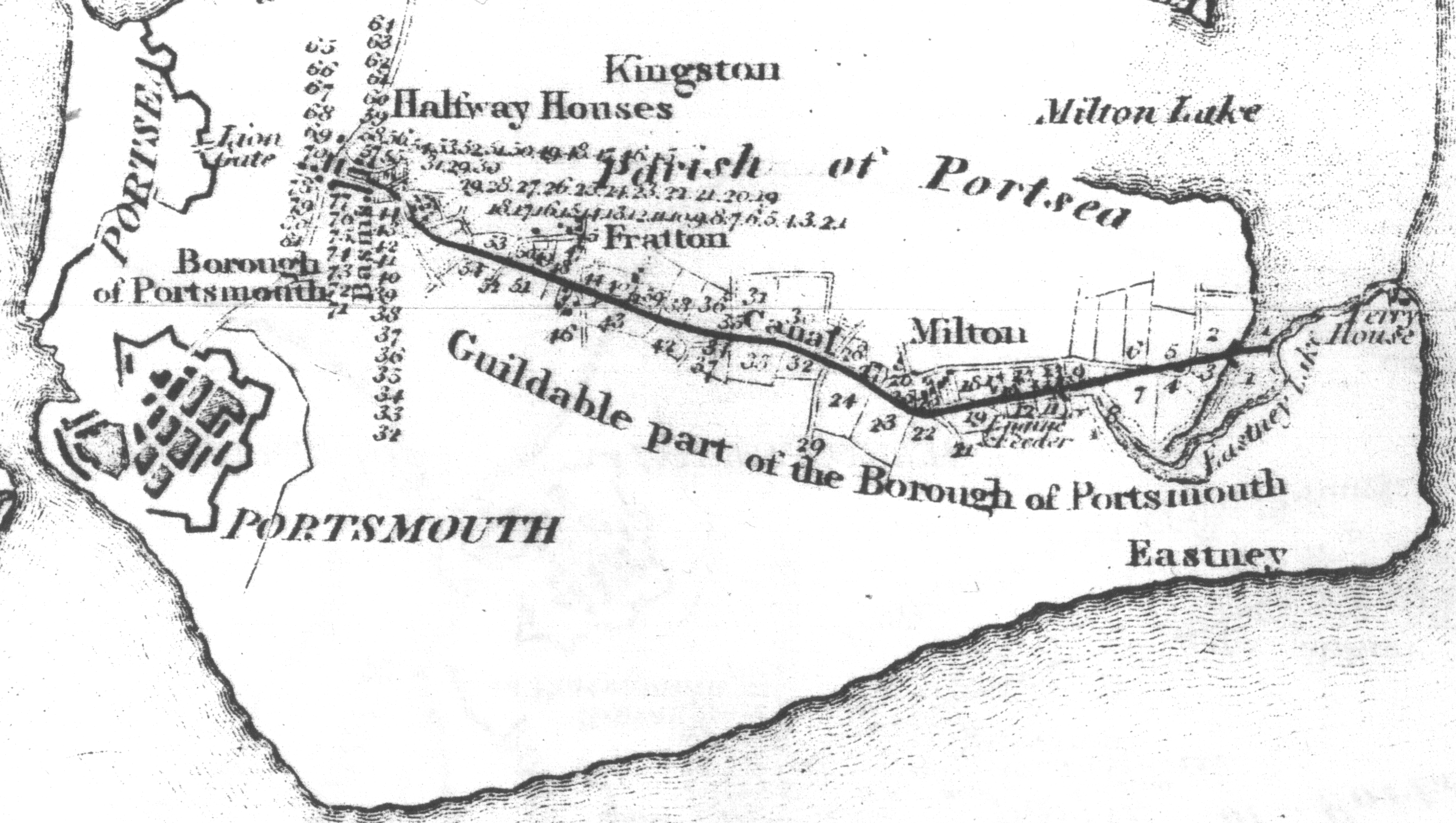
Hackney Wick
Hackney Wick is a neighbourhood in east London, England. The area forms the south-eastern part of the district of Hackney, and also of the wider London Borough of Hackney. Adjacent areas of the London Borough of Tower Hamlets are sometimes also described as being part of Hackney Wick. The area lies 4.2 miles (6.8 km) northeast of Charing Cross. Geography Hackney Wick is the south-eastern part of the historic district of Hackney, and also of the wider modern London Borough of Hackney. Adjacent parts of Old Ford (including Fish Island) in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets are also sometimes described as Hackney Wick, due to similar post-industrial land uses and their proximity to Hackney Wick railway station. The boundary runs along Wallis Road and the railway. The core area lies west of the Lee Navigation, here called Hackney Cut, however the parts of the Queen Elizabeth Olympic Park within Hackney have often also been described as Hackney Wick, and the ''Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Müller
Franz Müller (31 October 184014 November 1864), was a German tailor who was hanged for the murder of Thomas Briggs, the first killing on a British train by a German national. The case caught the imagination of the public due to increasing safety fears about rail travel at the time and the pursuit of Müller across the Atlantic Ocean to New York City by Scotland Yard. Crime On 9 July 1864, Thomas Briggs, a 69-year-old City of London banker, was beaten and robbed while he travelled on the 9:50 pm North London Railway train from Fenchurch Street to Chalk Farm. The assailant took his gold watch and chain, but left £5 in Briggs' pockets and threw him from the compartment. Just after 10:00 pm, the driver of a train travelling in the opposite direction spotted Briggs lying on the embankment next to the tracks between the old Bow and Victoria Park stations, described as "his foot towards London and his head towards Hackney, at a spot about two-thirds of the distance 1 mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public House
A pub (short for public house) is a kind of drinking establishment which is licensed to serve alcoholic drinks for consumption on the premises. The term ''public house'' first appeared in the United Kingdom in late 17th century, and was used to differentiate private houses from those which were, quite literally, open to the public as "alehouses", " taverns" and " inns". By Georgian times, the term had become common parlance, although taverns, as a distinct establishment, had largely ceased to exist by the beginning of the 19th century. Today, there is no strict definition, but CAMRA states a pub has four characteristics:GLA Economics, Closing time: London's public houses, 2017 # is open to the public without membership or residency # serves draught beer or cider without requiring food be consumed # has at least one indoor area not laid out for meals # allows drinks to be bought at a bar (i.e., not only table service) The history of pubs can be traced to Roman taverns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Listed Building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Ireland Environment Agency in Northern Ireland. The term has also been used in the Republic of Ireland, where buildings are protected under the Planning and Development Act 2000. The statutory term in Ireland is "protected structure". A listed building may not be demolished, extended, or altered without special permission from the local planning authority, which typically consults the relevant central government agency, particularly for significant alterations to the more notable listed buildings. In England and Wales, a national amenity society must be notified of any work to a listed building which involves any element of demolition. Exemption from secular listed building control is provided for some buildings in current use for worsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Waterways
British Waterways, often shortened to BW, was a statutory corporation wholly owned by the government of the United Kingdom. It served as the navigation authority for the majority of canals and a number of rivers and docks in England, Scotland and Wales. On 2 July 2012, all of British Waterways' assets and responsibilities in England and Wales were transferred to the newly founded charity the Canal & River Trust. In Scotland, British Waterways continues to operate as a standalone public corporation under the trading name Scottish Canals. The British Waterways Board was initially established as a result of the Transport Act 1962 and took control of the inland waterways assets of the British Transport Commission in 1963. By the final years of its existence, British Waterways was sponsored by the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (DEFRA) in England and Wales, and by the Scottish Government in Scotland. British Waterways managed and maintained of canals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Ford
Old Ford is an area in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets that is named after the natural ford which provided a crossing of the River Lea. History Administration and boundaries Historically, Old Ford was a cluster of houses and a mill, around the ford. It formed a part of the Ancient Parish of Stepney. Together with the rest of Bow, it separated from Stepney to become a (late formed) Ancient Parish of Bow in 1719. Ancient Parishes were, until the 19th century responsible for both civil and ecclesiastical local administration, after that there were divergent civil and ecclesiastical parish areas. It expanded rapidly in the Victorian era and was designated an independent Anglican parish in the mid-Victorian period, although civil administration has always been associated with Bow. Location of the ford Victorian OS maps show an illustrative location of the, by then, former ford, which was just to the south of the Northern Outfall Sewer and immediately south of the confluence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
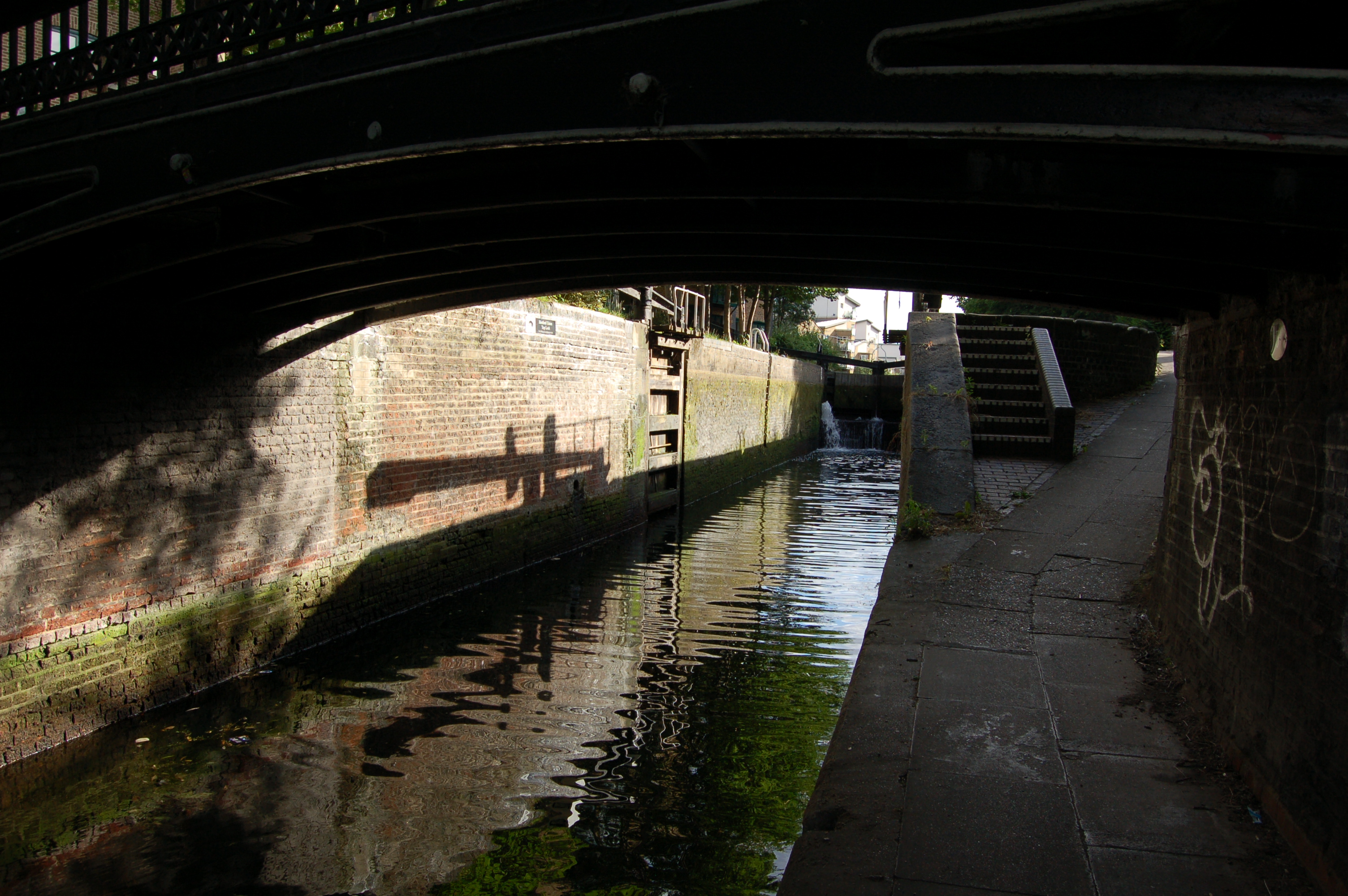
Lock (water Transport)
A lock is a device used for raising and lowering boats, ships and other watercraft between stretches of water of different levels on river and canal waterways. The distinguishing feature of a lock is a fixed chamber in which the water level can be varied; whereas in a caisson lock, a boat lift, or on a canal inclined plane, it is the chamber itself (usually then called a caisson) that rises and falls. Locks are used to make a river more easily navigable, or to allow a canal to cross land that is not level. Later canals used more and larger locks to allow a more direct route to be taken. Pound lock A ''pound lock'' is most commonly used on canals and rivers today. A pound lock has a chamber with gates at both ends that control the level of water in the pound. In contrast, an earlier design with a single gate was known as a flash lock. Pound locks were first used in China during the Song Dynasty (960–1279 AD), having been pioneered by the Song politician and n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Ford Lower Lock
The Hertford Union Canal or Duckett's Cut, just over long, connects the Regent's Canal to the Lee Navigation in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets in East London. It was opened in 1830 but quickly proved to be a commercial failure. It was acquired by the Regents Canal Company in 1857, and became part of the Grand Union Canal in 1927. History Like its 1766 predecessor, the Limehouse Cut, the Hertford Union Canal was intended to provide a short-cut between the River Thames and the River Lee Navigation. It allowed traffic on the Lea heading for the Thames to bypass the tidal, tortuous and often silted Bow Back Rivers of the Lea via a short stretch of the Regent's Canal, and provided a short-cut from the Lea to places west along the Regent's Canal. The canal was promoted by Sir George Duckett who succeeded in obtaining an Act of Parliament that gained its Royal Assent on 17 May 1824, entitled ''An Act for making and maintaining a navigable Canal from the River Lee Naviga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |