|
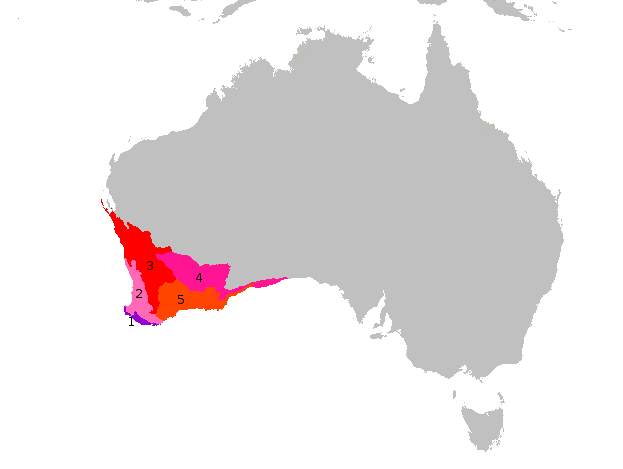
Dryandra Ser. Folliculosae
''Banksia'' ser. ''Dryandra'' is a series of 94 species of shrub to small tree in the plant genus ''Banksia''. It was considered a separate genus named ''Dryandra'' until early 2007, when it was merged into ''Banksia'' on the basis of extensive molecular and morphological evidence that ''Banksia'' was paraphyletic with respect to ''Dryandra''. Taxonomy The dryandras were named in honour of Swedish botanist Jonas C. Dryander. The first specimens of a ''Dryandra'' were collected by Archibald Menzies, surgeon and naturalist to the Vancouver Expedition. At the request of Joseph Banks, Menzies collected natural history specimens wherever possible during the voyage. During September and October 1791, while the expedition were anchored at King George Sound, he collected numerous plant specimens, including the first specimens of '' B. sessilis'' (Parrotbush) and '' B. pellaeifolia''. Upon Menzies' return to England, he turned his specimens over to Banks; as with most other s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banksia Sessilis
''Banksia sessilis'', commonly known as parrot bush, is a species of shrub or tree in the plant genus ''Banksia'' of the family Proteaceae. It had been known as ''Dryandra sessilis'' until 2007, when the genus ''Dryandra'' was sunk into ''Banksia''. The Noongar peoples know the plant as budjan or butyak. Widespread throughout southwest Australia, southwest Western Australia, it is found on sandy soils over laterite or limestone, often as an understory, understorey plant in open forest, woodland or shrubland. Encountered as a shrub or small tree up to in height, it has prickly dark green leaves and dome-shaped cream-yellow Head (botany), flowerheads. Flowering from winter through to late spring, it provides a key source of food—both the nectar and the insects it attracts—for honeyeaters in the cooler months, and Biodiversity, species diversity is reduced in areas where there is little or no parrot bush occurring. Several species of honeyeater, some species of native bee, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margaret Pieroni
Margaret Pieroni (born 1936) is a Western Australian botanical artist, photographer and botanist Botany, also called plant science, is the branch of natural science and biology studying plants, especially Plant anatomy, their anatomy, Plant taxonomy, taxonomy, and Plant ecology, ecology. A botanist or plant scientist is a scientist who s ... who has authored, co-authored or illustrated many books on Australian botany. Her works include ''Brush with Gondwana: Botanical Artists Group of Western Australia'' (2008), ''The Dryandras'' (2006), ''Verticordia: the turner of hearts'' (2002), ''Discovering the wildflowers of Western Australia '' (1993), ''Exploring granite outcrops'' (1990) and ''Leaf and branch: trees and tall shrubs of Perth'' (1990). Pieroni is also recognised for a significant contribution to specimen collection, photography and horticultural research into dryandras, series ''Banksia'' ser. ''Dryandra'', formerly regarded as genus ''Dryandra''. She was award ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Series
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria to produce sugars from carbon dioxide and water, using the green pigment chlorophyll. Exceptions are parasitic plants that have lost the genes for chlorophyll and photosynthesis, and obtain their energy from other plants or fungi. Most plants are multicellular, except for some green algae. Historically, as in Aristotle's biology, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi. Definitions have narrowed since then; current definitions exclude fungi and some of the algae. By the definition used in this article, plants form the clade Viridiplantae (green plants), which consists of the green algae and the embryophytes or land plants ( hornworts, liverworts, mosses, lycophytes, ferns, conifers and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South West Botanic Province
Southwest Australia is a biogeographic region in Western Australia. It includes the Mediterranean-climate area of southwestern Australia, which is home to a diverse and distinctive flora and fauna. The region is also known as the Southwest Australia Global Diversity Hotspot. Geography The region includes the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub ecoregions of Western Australia. The region covers 356,717 km2, consisting of a broad coastal plain 20–120 kilometres wide, transitioning to gently undulating uplands made up of weathered granite, gneiss and laterite. Bluff Knoll in the Stirling Range is the highest peak in the region, at 1,099 metres (3,606 ft) elevation. Desert and xeric shrublands lie to the north and east across the centre of Australia, separating Southwest Australia from the other Mediterranean and humid-climate regions of the continent. Climate The region has a wet-winter, dry-summer Mediterranean climate, one of five such regions in the world ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Australia
Western Australia (WA) is the westernmost state of Australia. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east, and South Australia to the south-east. Western Australia is Australia's largest state, with a land area of , and is also the List of country subdivisions by area, second-largest subdivision of any country on Earth. Western Australia has a diverse range of climates, including tropical conditions in the Kimberley (Western Australia), Kimberley, deserts in the interior (including the Great Sandy Desert, Little Sandy Desert, Gibson Desert, and Great Victoria Desert) and a Mediterranean climate on the south-west and southern coastal areas. the state has 2.965 million inhabitants—10.9 percent of the national total. Over 90 percent of the state's population live in the South-West Land Division, south-west corner and around 80 percent live in the state capital Perth, leaving the remainder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banksia Ser
''Banksia'' is a genus of around 170 species of flowering plants in the family Proteaceae. These Australian wildflowers and popular garden plants are easily recognised by their characteristic flower spikes, and woody fruiting "cones" and heads. ''Banksias'' range in size from prostrate woody shrubs to trees up to 30 metres (100 ft) tall. They are found in a wide variety of landscapes: sclerophyll forest, (occasionally) rainforest, shrubland, and some more arid landscapes, though not in Australia's deserts. Heavy producers of nectar, banksias are a vital part of the food chain in the Australian bush. They are an important food source for nectarivorous animals, including birds, bats, rats, possums, stingless bees and a host of invertebrates. Further, they are of economic importance to Australia's nursery and cut flower industries. However, these plants are threatened by a number of processes including land clearing, frequent burning and disease, and a number of spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dryandra Moth
The dryandra moth (''Carthaea saturnioides'') is a species of moth that is considered to be the sole member of the family Carthaeidae. Its closest relatives are the Saturniidae and it bears a resemblance to many species of that family, bearing prominent eyespots on all wings. The common name is derived from the '' Dryandra'' shrubs of the genus ''Banksia'', on which the larva of this species feed, and is hence restricted to the south-west of Western Australia where these shrubs grow. Other '' Grevillea'' shrubs may also be used as host plants. Description The larva (caterpillar) of this species is grey on the dorsal side, and yellow on the ventral side. Along the prolegs there is a line of clear markings, as well as markings in the form of an eye, following the line of spiracles. In the adult, each wing presents a large eyespot. The eyespots on the hindwings are distinct, whereas the eyespots on the forewings are smaller and often duller. These eyespots are visible on both sid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lepidoptera
Lepidoptera ( ) or lepidopterans is an order (biology), order of winged insects which includes butterflies and moths. About 180,000 species of the Lepidoptera have been described, representing 10% of the total described species of living organisms, making it the second largest insect order (behind Coleoptera) with 126 family (biology), families and 46 Taxonomic rank, superfamilies, and one of the most widespread and widely recognizable insect orders in the world. Lepidopteran species are characterized by more than three derived features. The most apparent is the presence of scale (anatomy), scales that cover the torso, bodies, large triangular Insect wing, wings, and a proboscis for siphoning nectars. The scales are modified, flattened "hairs", and give butterflies and moths their wide variety of colors and patterns. Almost all species have some form of membranous wings, except for a few that have reduced wings or are wingless. Mating and the laying of eggs is normally performe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larva
A larva (; : larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into their next life stage. Animals with indirect development such as insects, some arachnids, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle. A larva's appearance is generally very different from the adult form (''e.g.'' caterpillars and butterflies) including different unique structures and organs that do not occur in the adult form. Their diet may also be considerably different. In the case of smaller primitive arachnids, the larval stage differs by having three instead of four pairs of legs. Larvae are frequently adapted to different environments than adults. For example, some larvae such as tadpoles live almost exclusively in aquatic environments but can live outside water as adult frogs. By living in a distinct environment, larvae may be given shelter from predators and reduce competition for resources with the adult population. Animals in the lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banksia Nivea
''Banksia nivea'', commonly known as honeypot dryandra, is a species of rounded shrub that is endemic to Western Australia. The Noongar peoples know the plant as bulgalla. It has linear, pinnatipartite leaves with triangular lobes, heads of cream-coloured and orange or red flowers and glabrous, egg-shaped follicles. Description ''Banksia nivea'' is a rounded, much-branched shrub that typically grows to high and wide but does not form a lignotuber. It has linear, pinnatipartite leaves that are long and wide on a petiole long. There are between 45 and 85 triangular lobes on each side of the leaves. Between seventy and ninety cream-coloured and orange or red flowers are borne in head on the ends of branches with oblong to egg-shaped involucral bracts long at the base of the head. The perianth is long and the pistil long. Flowering occurs in April or from July to November and the follicles are egg-shaped, long and almost glabrous. Taxonomy and naming ''Banksia nivea' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esperance Bay
Esperance Bay is a bay on the south coast of Western Australia. Nominally located at , it is the site of the town of Esperance. The bay was discovered on 9 December 1792 by a French expedition under Bruni d'Entrecasteaux, which sailed in search of the lost expedition of Jean-François de Galaup, comte de Lapérouse. Stormy weather had blown the ships into hazardous waters surrounded by islands, but acting ensign Jacques-Bertrand Le Grand sighted a navigable passage and a somewhat sheltered anchorage, providing what d'Entrecasteaux regarded as a "miraculous" escape from being wrecked. Ship botanist Jacques Labillardière Jacques-Julien Houtou de Labillardière (28 October 1755 – 8 January 1834) was a French biologist noted for his descriptions of the flora of Australia. Labillardière was a member of a voyage in search of the Jean-François de Galaup, comte ... was in favour of naming the bay after Le Grand, and indeed he refers to the bay on his specimen slips as "Baie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |