|
Drinking
Drinking is the act of ingesting water or other liquids into the body through the mouth, proboscis, or elsewhere. Humans drink by swallowing, completed by peristalsis in the esophagus. The physiological processes of drinking vary widely among other animals. Most animals drink water to maintain bodily hydration, although many can survive on the water gained from their food. Water is required for many physiological processes. Both inadequate and (less commonly) excessive water intake are associated with health problems. Methods of drinking In humans When a liquid enters a human mouth, the swallowing process is completed by peristalsis which delivers the liquid through the esophagus to the stomach; much of the activity is assisted by gravity. The liquid may be poured from the hands or drinkware may be used as vessels. Drinking can also be by sipping or sucking, typically when imbibing hot liquids or drinking from a spoon. Infants employ a method of suction wherein the lip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drinking Water
Drinking water or potable water is water that is safe for ingestion, either when drunk directly in liquid form or consumed indirectly through food preparation. It is often (but not always) supplied through taps, in which case it is also called tap water. The amount of drinking water required to maintain good health varies, and depends on physical activity level, age, health-related issues, and environmental conditions. This 2004 article focuses on the USA context and uses data collected from the US military. For those who work in a hot climate, up to a day may be required. About 1 to 2 billion people lack safe drinking water. Water can carry vectors of disease and is a major cause of death and illness worldwide. Developing countries are most affected by unsafe drinking water. Sources Potable water is available in almost all populated areas of the world, although it may be expensive, and the supply may not always be sustainable. Sources where drinking water is commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a solvent). It is vital for all known forms of life, despite not providing food energy or organic micronutrients. Its chemical formula, , indicates that each of its molecules contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms, connected by covalent bonds. The hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom at an angle of 104.45°. In liquid form, is also called "water" at standard temperature and pressure. Because Earth's environment is relatively close to water's triple point, water exists on Earth as a solid, a liquid, and a gas. It forms precipitation in the form of rain and aerosols in the form of fog. Clouds consist of suspended droplets of water and ice, its solid state. When finely divided, crystalline ice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
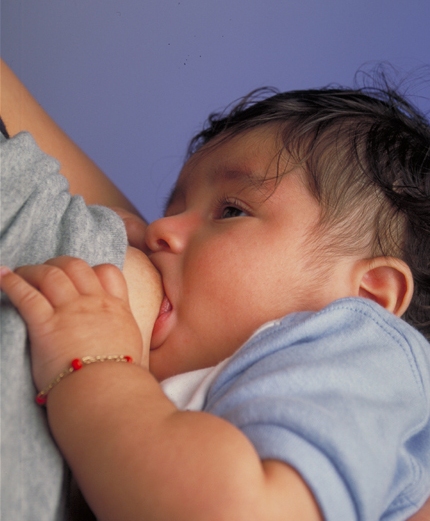
Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding, also known as nursing, is the process where breast milk is fed to a child. Infants may suck the milk directly from the breast, or milk may be extracted with a Breast pump, pump and then fed to the infant. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommend that breastfeeding begin within the first hour of a baby's birth and continue as the baby wants. Health organizations, including the WHO, recommend breastfeeding exclusively for six months. This means that no other foods or drinks, other than vitamin D, are typically given. The WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months of life, followed by continued breastfeeding with appropriate complementary foods for up to 2 years and beyond. Of the 135 million babies born every year, only 42% are breastfed within the first hour of life, only 38% of mothers practice exclusive breastfeeding during the first six months, and 58% of mothers continue breastfeeding up to the age of two years and beyond. Breastfee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drinkware
upTypical drinkware. This list of glassware includes drinking vessels (drinkware), tableware used to set a table for eating a meal and generally glass items such as vases, and glasses used in the catering industry. It does not include laboratory glassware. Drinkware Drinkware, beverageware (in other words, cups, jugs and ewers) is a general term for a vessel intended to contain beverages or liquid foods for drinking or consumption. * Beaker * Beer glassware * Bottle * Coffee cup * Cup * Dwarf ale glass * Heavy baluster glass * Jar * Mazagran * Mug * Pythagorean cup * Quaich * Sake cup (''ochoko'') * Stemware * Tazza * Teacup * Tiki mug * Trembleuse * Tumblers * Vitrolero The word ''cup'' comes from Middle English ', from Old English, from Late Latin ', drinking vessel, perhaps variant of Latin ', tub, cask. The first known use of the word cup is before the 12th century. Tumblers Tumblers are flat-bottomed drinking glasses. * Collins glass, for a tall mixed drink ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ingestion
Ingestion is the consumption of a substance by an organism. In animals, it normally is accomplished by taking in a substance through the mouth into the gastrointestinal tract, such as through eating or drinking. In single-celled organisms, ingestion takes place by absorbing a substance through the cell membrane. Besides nutritional items, substances that may be ingested include medication (where ingestion is termed oral administration), recreational drugs, and substances considered inedible, such as foreign bodies or excrement. Ingestion is a common route taken by pathogenic organisms and poisons entering the body. Ingestion can also refer to a mechanism picking up something and making it enter an internal hollow of that mechanism, e.g. "''a grille was fitted to prevent the pump from ingesting driftwood''". Pathogens Some pathogens are transmitted via ingestion, including viruses, bacteria, and parasites. Most commonly, this takes place via the faecal-oral route. An interm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giraffes
The giraffe is a large African hoofed mammal belonging to the genus ''Giraffa.'' It is the tallest living terrestrial animal and the largest ruminant on Earth. It is classified under the family Giraffidae, along with its closest extant relative, the okapi. Traditionally, giraffes have been thought of as one species, '' Giraffa camelopardalis'', with nine subspecies. Most recently, researchers proposed dividing them into four extant species which can be distinguished by their fur coat patterns. Six valid extinct species of ''Giraffa'' are known from the fossil record. The giraffe's distinguishing characteristics are its extremely long neck and legs, horn-like ossicones, and spotted coat patterns. Its scattered range extends from Chad in the north to South Africa in the south and from Niger in the west to Somalia in the east. Giraffes usually inhabit savannahs and woodlands. Their food source is leaves, fruits, and flowers of woody plants, primarily acacia species, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cats
The cat (''Felis catus''), also referred to as the domestic cat or house cat, is a small domesticated carnivorous mammal. It is the only domesticated species of the family Felidae. Advances in archaeology and genetics have shown that the domestication of the cat occurred in the Near East around 7500 BC. It is commonly kept as a pet and working cat, but also ranges freely as a feral cat avoiding human contact. It is valued by humans for companionship and its ability to kill vermin. Its retractable claws are adapted to killing small prey species such as mice and rats. It has a strong, flexible body, quick reflexes, and sharp teeth, and its night vision and sense of smell are well developed. It is a social species, but a solitary hunter and a crepuscular predator. Cat intelligence is evident in their ability to adapt, learn through observation, and solve problems. Research has shown they possess strong memories, exhibit neuroplasticity, and display cognitive skill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cat Lapping Water Off Ground In Slow Motion
The cat (''Felis catus''), also referred to as the domestic cat or house cat, is a small Domestication, domesticated carnivorous mammal. It is the only domesticated species of the family Felidae. Advances in archaeology and genetics have shown that the domestication of the cat occurred in the Near East around 7500 BC. It is commonly kept as a pet and working cat, but also ranges freely as a feral cat avoiding human contact. It is valued by humans for companionship and its ability to kill vermin. Its retractable claws are adapted to killing small prey species such as mice and rats. It has a strong, flexible body, quick reflexes, and sharp teeth, and its night vision and sense of smell are well developed. It is a social species, but a solitary hunter and a crepuscular predator. Cat intelligence is evident in their ability to adapt, learn through observation, and solve problems. Research has shown they possess strong memories, exhibit neuroplasticity, and display cognitive skil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elephants
Elephants are the Largest and heaviest animals, largest living land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant (''Loxodonta africana''), the African forest elephant (''L. cyclotis''), and the Asian elephant (''Elephas maximus''). They are the only surviving members of the Family (biology), family Elephantidae and the Order (biology), order Proboscidea; extinct relatives include mammoths and mastodons. Distinctive features of elephants include a long proboscis called a trunk, tusks, large ear flaps, pillar-like legs, and tough but sensitive grey skin. The trunk is Prehensility, prehensile, bringing food and water to the mouth and grasping objects. Tusks, which are derived from the incisor teeth, serve both as weapons and as tools for moving objects and digging. The large ear flaps assist in maintaining a constant body temperature as well as in communication. African elephants have larger ears and concave backs, whereas Asian elephants hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swallowing
Swallowing, also called deglutition or inglutition in scientific and medical contexts, is a physical process of an animal's digestive tract (e.g. that of a human body) that allows for an ingested substance (typically food) to pass from the mouth to the pharynx and then into the esophagus. In colloquial English, the term "swallowing" is also used to describe the action of ''gulping'', i.e. taking in a large mouthful of food without any biting. Swallowing is performed by an initial push from back part of the tongue (with the tongue tip contacting the hard palate for mechanical anchorage) and subsequent coordinated muscle contraction, contractions of the pharyngeal muscles. The portion of food, drink and/or other material (e.g. mucus, secretions and medications) that moves into the gullet in one swallow is called a bolus, which is then propelled through to the stomach for further digestion by autonomic peristalsis of the esophagus. Swallowing is an important part of eating and dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
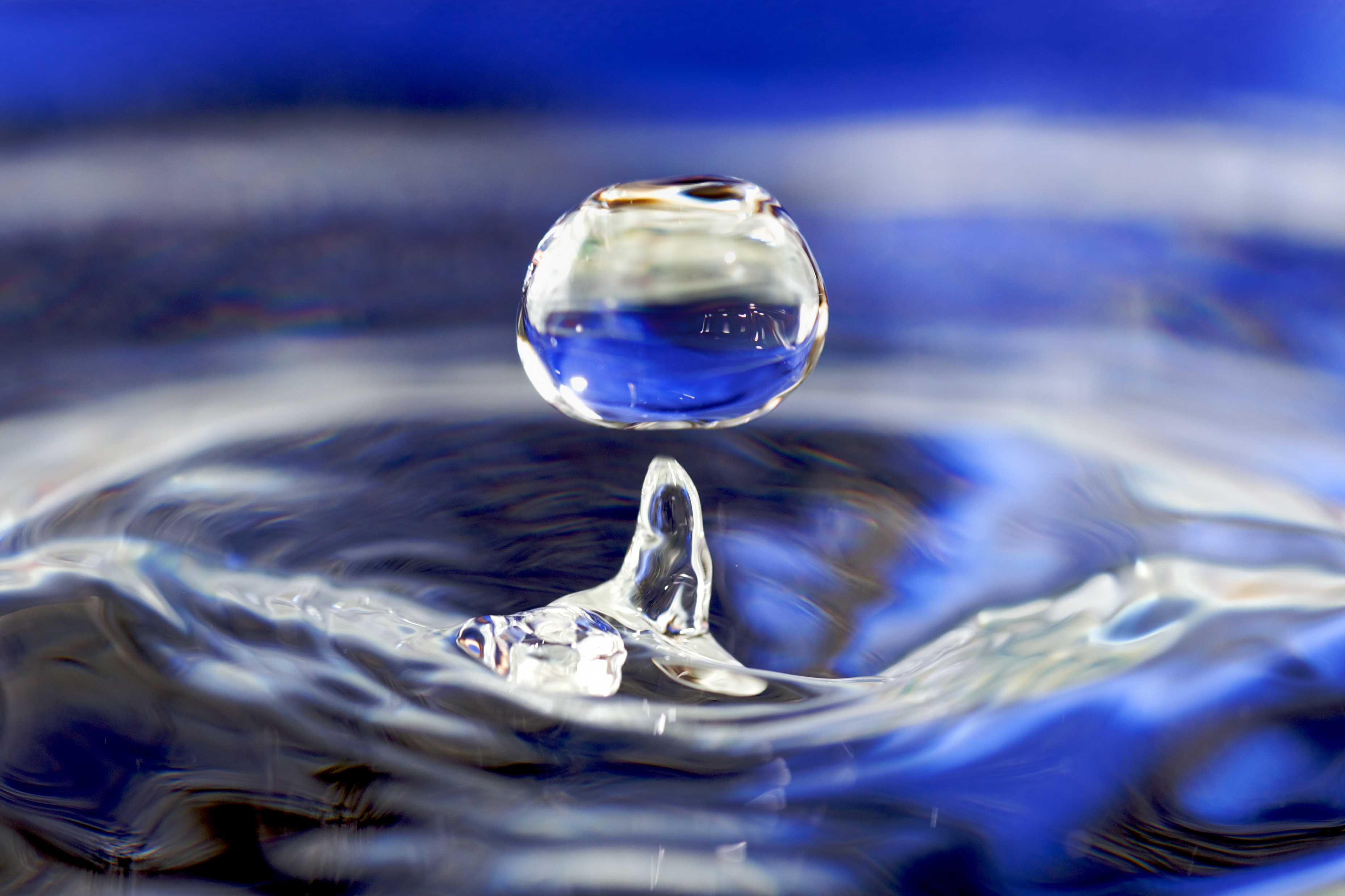
Liquid
Liquid is a state of matter with a definite volume but no fixed shape. Liquids adapt to the shape of their container and are nearly incompressible, maintaining their volume even under pressure. The density of a liquid is usually close to that of a solid, and much higher than that of a gas. Therefore, liquid and solid are classified as condensed matter. Meanwhile, since both liquids and gases can flow, they are categorized as fluids. A liquid is composed of atoms or molecules held together by intermolecular bonds of intermediate strength. These forces allow the particles to move around one another while remaining closely packed. In contrast, solids have particles that are tightly bound by strong intermolecular forces, limiting their movement to small vibrations in fixed positions. Gases, on the other hand, consist of widely spaced, freely moving particles with only weak intermolecular forces. As temperature increases, the molecules in a liquid vibrate more intensely, causi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proboscis
A proboscis () is an elongated appendage from the head of an animal, either a vertebrate or an invertebrate. In invertebrates, the term usually refers to tubular arthropod mouthparts, mouthparts used for feeding and sucking. In vertebrates, a proboscis is an elongated nose or snout. Etymology First attested in English in 1609 from Latin , the latinisation (literature), latinisation of the Ancient Greek (), which comes from () 'forth, forward, before' + (), 'to feed, to nourish'. The plural as derived from the Greek is , but in English the plural form ''proboscises'' occurs frequently. Invertebrates The most common usage is to refer to the tubular feeding and sucking organ of certain invertebrates such as insects (e.g., Insect mouthparts#Proboscis, moths, butterflies, and mosquitoes), worms (including Acanthocephala, Nemertea, proboscis worms) and gastropod molluscs. Acanthocephala The Acanthocephala, the thorny-headed worms or spiny-headed worms, are characterized by the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |