|
Dreams In Analytical Psychology
Dream psychology is a scientific research field in psychology. In analytical psychology, as in psychoanalysis generally, dreams are "the royal road" to understanding Unconscious mind, unconscious content.Entry "Rêve (interprétation du -)" by Roger Perron, p. 1472, Vol. II. However, for Swiss psychiatrist Carl Jung, its interpretation and function in the Psychology, psyche differ from the Sigmund Freud, Freudian perspective. Jung explains that "the general function of dreams is to try to re-establish our psychological equilibrium by means of dream material which, in a subtle way, reconstitutes the total equilibrium of our entire psyche. This is what [he] calls the complementary (or compensatory) function of dreams in our psychic constitution".''L'Homme et ses symboles'', Robert Laffont, 1964, p 49. In this sense, dreams play a part in the development of the personality, at the same time as linking the subject to the vast imaginary reservoir that is the collective unconscious. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Lukas Leopold Willmann 001
Michael may refer to: People * Michael (given name), a given name * Michael (surname), including a list of people with the surname Michael Given name * Michael (bishop elect), English 13th-century Bishop of Hereford elect * Michael (Khoroshy) (1885–1977), cleric of the Ukrainian Orthodox Church of Canada * Michael Donnellan (fashion designer), Michael Donnellan (1915–1985), Irish-born London fashion designer, often referred to simply as "Michael" * Michael (footballer, born 1982), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1983), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1993), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born February 1996), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born March 1996), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1999), Brazilian footballer Rulers Byzantine emperors *Michael I Rangabe (d. 844), married the daughter of Emperor Nikephoros I *Michael II (770–829), called "the Stammerer" and "the Amorian" *Michael III ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shamanism
Shamanism is a spiritual practice that involves a practitioner (shaman) interacting with the spirit world through altered states of consciousness, such as trance. The goal of this is usually to direct spirits or spiritual energies into the physical world for the purpose of healing, divination, or to aid human beings in some other way. Beliefs and practices categorized as shamanic have attracted the interest of scholars from a variety of disciplines, including anthropologists, archeologists, historians, religious studies scholars, philosophers, and psychologists. Hundreds of books and academic papers on the subject have been produced, with a peer-reviewed academic journal being devoted to the study of shamanism. Terminology Etymology The Modern English word ''shamanism'' derives from the Russian word , , which itself comes from the word from a Tungusic language – possibly from the southwestern dialect of the Evenki spoken by the Sym Evenki peoples, or from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Content (Freudian Dream Analysis)
Content in Freudian dream analysis refers to two closely connected aspects of the dream: the ''manifest'' content (the dream itself as it is remembered), and the ''latent'' content (the hidden meaning of the dream). Impulses and drives residing in the unconscious press toward consciousness during sleep, but are only able to evade the censorship mechanism of repression by associating themselves with words, ideas and images that are acceptable to consciousness. Thus the dream as consciously remembered upon waking (the manifest content) is interpreted in psychoanalysis as a disguised or distorted representation of repressed desires (the latent content). Definitions Manifest content The manifest content is the dream that the conscious individual remembers experiencing. It consists of all the elements—images, thoughts, emotions, and other content—of which the individual is cognitively aware upon awakening. Illustrated through the iceberg analogy, the manifest content would be identi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptomnesia
Cryptomnesia occurs when a forgotten memory returns without it being recognized as such by the subject, who believes it is something new and original. It is a memory bias whereby a person may falsely recall generating a thought, an idea, a tune, a name, or a joke; they are not deliberately engaging in plagiarism, but are experiencing a memory as if it were a new inspiration. Early use Cryptomnesia was first documented in 1874, involving the medium Stainton Moses, who during a séance believed himself to be in spiritual contact with two brothers from India who had recently been killed. Despite the apparent communication, he was unable to ascertain any details which had not already been given in newspaper coverage of the story the week before. Researchers concluded that Moses had read the story but forgotten that he had read it, instead mistaking the partial memory for a message from the spirit world. The word was first used by the psychiatrist Théodore Flournoy, in referenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synchronicity
Synchronicity () is a concept introduced by Carl Jung, founder of analytical psychology, to describe events that coincide in time and appear meaningfully related, yet lack a discoverable causal connection. Jung held that this was a healthy function of the mind, although it can become harmful within psychosis. Jung developed the theory as a hypothetical noncausal principle serving as the intersubjective or philosophically objective connection between these seemingly meaningful coincidences. After coining the term in the late 1920s Jung developed the concept with physicist Wolfgang Pauli through correspondence and in their 1952 work ''The Interpretation of Nature and the Psyche''. This culminated in the Pauli–Jung conjecture.Jung, Carl G. 9512005.Synchronicity. Pp. 91–98 in ''Jung on Synchronicity and the Paranormal'', edited by R. Main. London: Taylor & Francis. Jung and Pauli's view was that, just as causal connections can provide a meaningful understanding of the psyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Individuation
The principle of individuation, or ', describes the manner in which a thing is identified as distinct from other things. The concept appears in numerous fields and is encountered in works of Leibniz, Carl Jung, Gunther Anders, Gilbert Simondon, Bernard Stiegler, Friedrich Nietzsche, Arthur Schopenhauer, David Bohm, Henri Bergson, Gilles Deleuze, and Manuel DeLanda. Usage The word ''individuation'' occurs with different meanings and connotations in different fields. In philosophy Philosophically, "individuation" expresses the general idea of how a thing is identified as an individual thing that "is not something else". This includes how an individual person is held to be different from other elements in the world and how a person is distinct from other persons. By the seventeenth century, philosophers began to associate the question of individuation or what brings about individuality at any one time with the question of identity or what constitutes sameness at different p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telepathy
Telepathy () is the purported vicarious transmission of information from one person's mind to another's without using any known human sensory channels or physical interaction. The term was first coined in 1882 by the classical scholar Frederic W. H. Myers, a founder of the Society for Psychical Research (SPR), and has remained more popular than the earlier expression ''thought-transference''.Glossary of Parapsychological terms – Telepathy – Parapsychological Association. Retrieved December 19, 2006. Telepathy experiments have historically been criticized for a lack of proper controls and repeatability. There is no good evidence that telepathy exists, and the topic is gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
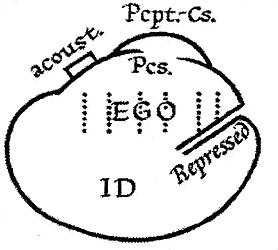
Ego (Freudian)
In psychoanalytic theory, the id, ego, and superego are three distinct, interacting agents in the psychic apparatus, outlined in Sigmund Freud's structural model of the psyche. The three agents are theoretical constructs that Freud employed to describe the basic structure of mental life as it was encountered in psychoanalytic practice. Freud himself used the German terms ''das Es'', ''Ich'', and ''Über-Ich'', which literally translate as "the it", "I", and "over-I". The Latin terms id, ego and superego were chosen by his original translators and have remained in use. The structural model was introduced in Freud's essay '' Beyond the Pleasure Principle'' (1920) and further refined and formalised in later essays such as '' The Ego and the Id'' (1923). Freud developed the model in response to the perceived ambiguity of the terms "conscious" and "unconscious" in his earlier ''topographical'' model. Broadly speaking, the id is the organism's unconscious array of uncoordinated i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personal Unconscious
In analytical psychology, the personal unconscious is a Jungian term referring to the part of the unconscious that can be brought to the conscious mind. It is Carl Jung's equivalent to the Freudian unconscious, in contrast to the Jungian concept of the collective unconscious. Often referred by him as "No man's land," the personal unconscious is located at the fringe of consciousness, between two worlds: "the exterior or spatial world and the interior or psychic objective world" (Ellenberger, 707). As Charles Baudouin states, "That the unconscious extends so far beyond consciousness is simply the counterpart of the fact that the exterior world extends so far beyond our visual field" (Ellenberger, 707). The personal unconscious is made up of both memories that are easily brought to mind and those that have been forgotten or repressed. Jung's theory of a personal unconscious is quite similar to Freud's creation of a region containing a person's repressed, forgotten or ignored experie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Adler
Alfred Adler ( ; ; 7 February 1870 – 28 May 1937) was an Austrian medical doctor, psychotherapist, and founder of the school of individual psychology. His emphasis on the importance of feelings of belonging, relationships within the family, and birth order set him apart from Freud and others in their common circle. He proposed that contributing to others (social interest or ) was how the individual feels a sense of worth and belonging in the family and society. His earlier work focused on inferiority, coining the term inferiority complex, an isolating element which he argued plays a key role in personality development. Alfred Adler considered a human being as an individual whole, and therefore he called his school of psychology "individual psychology". Adler was the first to emphasize the importance of the social element in the re-adjustment process of the individual and to carry psychiatry into the community. A ''Review of General Psychology'' survey, published in 2002, rank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |