|
Doublecortin Positive Cells
Neuronal migration protein doublecortin, also known as doublin or lissencephalin-X is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DCX'' gene. Function Doublecortin (DCX) is a microtubule-associated protein expressed by neuronal precursor cells and immature neurons in embryonic and adult cortical structures. Neuronal precursor cells begin to express DCX while actively dividing, and their neuronal daughter cells continue to express DCX for 2–3 weeks as the cells mature into neurons. Downregulation of DCX begins after 2 weeks, and occurs at the same time that these cells begin to express NeuN, a neuronal marker. Due to the nearly exclusive expression of DCX in developing neurons, this protein has been used increasingly as a marker for neurogenesis. Indeed, levels of DCX expression increase in response to exercise, and that increase occurs in parallel with increased BrdU labeling, which is currently a "gold standard" in measuring neurogenesis. Doublecortin was found to bind to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippocampus Anatomy
Hippocampus anatomy describes the physical aspects and properties of the hippocampus, a neural structure in the medial temporal lobe of each cerebral hemisphere of the brain. It has a distinctive, curved shape that has been likened to the hippocampus (mythology), sea-horse creature of Greek mythology, and the Sheep, ram's horns of Amun#New Kingdom, Amun in Egyptian mythology. The general layout holds across the full range of mammals, although the details vary. For example, in the rat, the two hippocampi look similar to a pair of bananas, joined at the stems. In humans and other primates, the portion of the hippocampus near the base of the temporal lobe is much broader than the part at the top. Due to the three-dimensional curvature of the hippocampus, two-dimensional sections are commonly presented. Neuroimaging can show a number of different shapes, depending on the angle and location of the cut. Cerebral cortex, Cortical parts from the temporal lobe, parietal lobe, and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
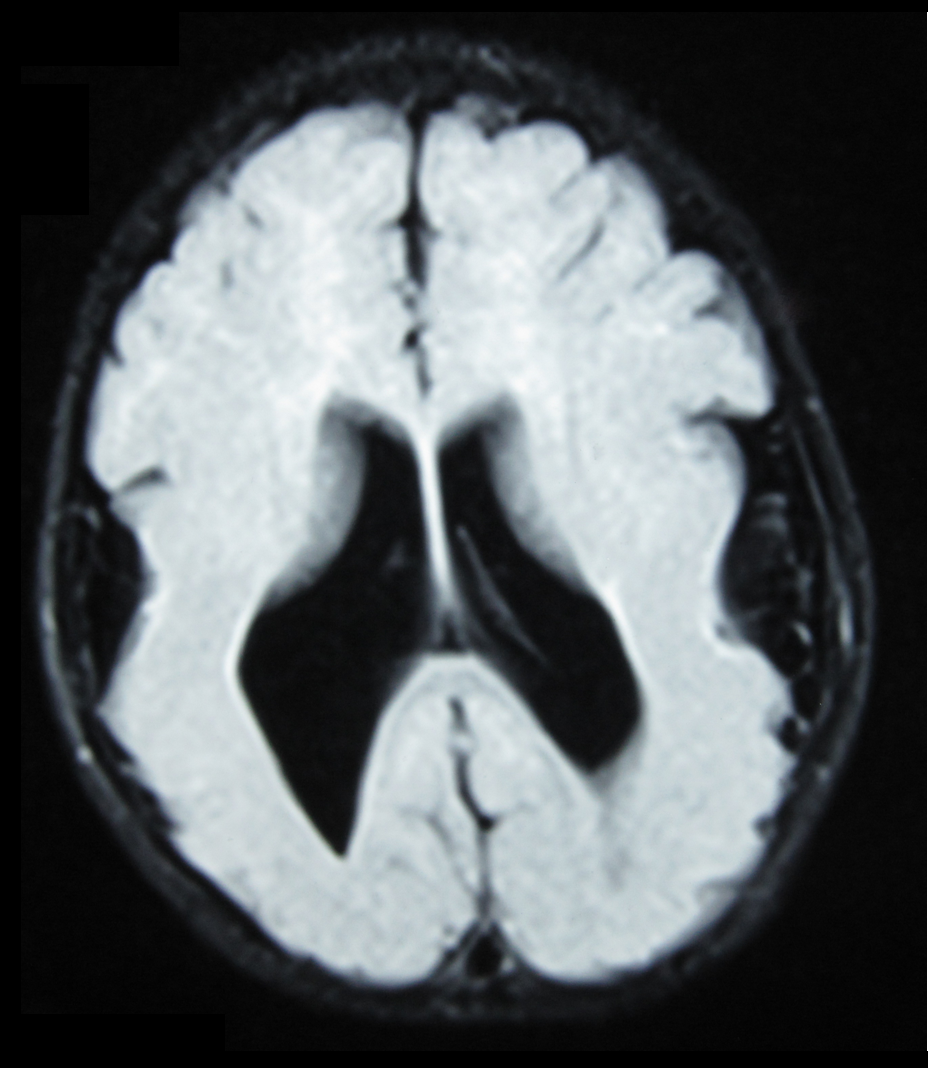
Lissencephaly
Lissencephaly (, meaning 'smooth brain') is a set of rare brain disorders whereby the whole or parts of the surface of the brain are smooth. It is caused by defective neuronal migration during the 12th to 24th weeks of gestation, resulting in a lack of development of brain folds (gyri) and grooves (sulci). It is a form of cephalic disorder. Terms such as ''agyria'' (no gyri) and '' pachygyria'' (broad gyri) are used to describe the appearance of the surface of the brain. Children with lissencephaly generally have significant developmental delays, but these vary greatly from child to child depending on the degree of brain malformation and seizure control. Life expectancy can be shortened, generally due to respiratory problems. Signs and symptoms Affected children display severe psychomotor impairment, failure to thrive, seizures, and muscle spasticity or hypotonia. Other symptoms of the disorder may include unusual facial appearance, difficulty swallowing, and anomalies of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christopher A
Christopher is the English version of a Europe-wide name derived from the Greek name Χριστόφορος (''Christophoros'' or '' Christoforos''). The constituent parts are Χριστός (''Christós''), "Christ" or " Anointed", and φέρειν (''phérein''), "to bear"; hence the "Christ-bearer". As a given name, 'Christopher' has been in use since the 10th century. In English, Christopher may be abbreviated as " Chris", "Topher", and sometimes " Kit". It was frequently the most popular male first name in the United Kingdom, having been in the top twenty in England and Wales from the 1940s until 1995, although it has since dropped out of the top 100. Within the United Kingdom, the name is most common in England and not so common in Wales, Scotland, or Northern Ireland. Cognates in other languages *Afrikaans: Christoffel, Christoforus * Albanian: Kristofer, Kristofor, Kristoforid, Kristo *Arabic: كريستوفر (''Krīstafor, Kristūfar, Krístufer''), اصطفر (''� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph G
Joseph is a common male name, derived from the Hebrew (). "Joseph" is used, along with " Josef", mostly in English, French and partially German languages. This spelling is also found as a variant in the languages of the modern-day Nordic countries. In Portuguese and Spanish, the name is "José". In Arabic, including in the Quran, the name is spelled , . In Kurdish (''Kurdî''), the name is , Persian, the name is , and in Turkish it is . In Pashto the name is spelled ''Esaf'' (ايسپ) and in Malayalam it is spelled ''Ousep'' (ഔസേപ്പ്). In Tamil, it is spelled as ''Yosepu'' (யோசேப்பு). The name has enjoyed significant popularity in its many forms in numerous countries, and ''Joseph'' was one of the two names, along with '' Robert'', to have remained in the top 10 boys' names list in the US from 1925 to 1972. It is especially common in contemporary Israel, as either "Yossi" or "Yossef", and in Italy, where the name "Giuseppe" was the most co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lissencephaly
Lissencephaly (, meaning 'smooth brain') is a set of rare brain disorders whereby the whole or parts of the surface of the brain are smooth. It is caused by defective neuronal migration during the 12th to 24th weeks of gestation, resulting in a lack of development of brain folds (gyri) and grooves (sulci). It is a form of cephalic disorder. Terms such as ''agyria'' (no gyri) and '' pachygyria'' (broad gyri) are used to describe the appearance of the surface of the brain. Children with lissencephaly generally have significant developmental delays, but these vary greatly from child to child depending on the degree of brain malformation and seizure control. Life expectancy can be shortened, generally due to respiratory problems. Signs and symptoms Affected children display severe psychomotor impairment, failure to thrive, seizures, and muscle spasticity or hypotonia. Other symptoms of the disorder may include unusual facial appearance, difficulty swallowing, and anomalies of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PAFAH1B1
Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase IB subunit alpha or Lisencephaly protein-1 (LIS-1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PAFAH1B1'' gene. The protein plays an important role in regulating the motor protein dynein. Function ''PAFAH1B1'' was identified as encoding a gene that when mutated or lost caused the lissencephaly associated with Miller–Dieker syndrome. ''PAFAH1B1'' encodes the non-catalytic alpha subunit of the intracellular Ib isoform of platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase, a heterotrimeric enzyme that specifically catalyzes the removal of the acetyl group at the stereospecific numbering, ''sn''-2 position of platelet-activating factor (identified as 1-''O''-alkyl-2-acetyl-''sn''-glyceryl-3-phosphorylcholine). Two other isoforms of intracellular platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase exist: one composed of multiple subunits, the other, a single subunit. In addition, a single-subunit isoform of this enzyme is found in serum. According to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubulin
Tubulin in molecular biology can refer either to the tubulin protein superfamily of globular proteins, or one of the member proteins of that superfamily. α- and β-tubulins polymerize into microtubules, a major component of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton. It was discovered and named by Hideo Mōri in 1968. Microtubules function in many essential cellular processes, including mitosis. Discovery and development of tubulin inhibitors, Tubulin-binding drugs kill cancerous cells by inhibiting microtubule dynamics, which are required for DNA segregation and therefore cell division. #Eukaryotic, In eukaryotes, there are six members of the tubulin superfamily, although not all are present in all species.Turk E, Wills AA, Kwon T, Sedzinski J, Wallingford JB, Stearns "Zeta-Tubulin Is a Member of a Conserved Tubulin Module and Is a Component of the Centriolar Basal Foot in Multiciliated Cells"Current Biology (2015) 25:2177-2183. Both α and β tubulins have a mass of around 50 kDa and are thus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 appear in the genetic code of life. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups ( alpha- , beta- , gamma- amino acids, etc.); other categories relate to polarity, ionization, and side-chain group type ( aliphatic, acyclic, aromatic, polar, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino-acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life on Earth and its emergence. Amino acids are formally named by the IUPAC- IUBMB Joint Commi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N Terminus
N, or n, is the fourteenth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages, and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''en'' (pronounced ), plural ''ens''. History One of the most common hieroglyphs, snake, was used in Egyptian writing to stand for a sound like the English , because the Egyptian word for "snake" was ''djet''. It is speculated by some, such as archeologist Douglas Petrovich, that Semitic speakers working in Egypt adapted hieroglyphs to create the first alphabet. Some hold that they used the same snake symbol to represent N, with a great proponent of this theory being Alan Gardiner, because their word for "snake" may have begun with n (an example of a possible word being ''nahash''). However, this theory has become disputed. The name for the letter in the Phoenician, Hebrew, Aramaic, and Arabic alphabets is '' nun'', which means " fish" in some of these languages. This possibly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Domain
In molecular biology, a protein domain is a region of a protein's Peptide, polypeptide chain that is self-stabilizing and that Protein folding, folds independently from the rest. Each domain forms a compact folded Protein tertiary structure, three-dimensional structure. Many proteins consist of several domains, and a domain may appear in a variety of different proteins. Molecular evolution uses domains as building blocks and these may be recombined in different arrangements to create proteins with different functions. In general, domains vary in length from between about 50 amino acids up to 250 amino acids in length. The shortest domains, such as zinc fingers, are stabilized by metal ions or Disulfide bond, disulfide bridges. Domains often form functional units, such as the calcium-binding EF-hand, EF hand domain of calmodulin. Because they are independently stable, domains can be "swapped" by genetic engineering between one protein and another to make chimera (protein), chimeric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |