|
Dorsal Raphe Nucleus
The dorsal raphe nucleus is one of the raphe nuclei. It is situated in the brainstem at the midline. It has rostral and caudal subdivisions: * The rostral aspect of the ''dorsal'' raphe is further divided into interfascicular, ventral, ventrolateral and dorsal subnuclei. * The projections of the ''dorsal'' raphe have been found to vary topographically, and thus the subnuclei differ in their projections. Anatomy Efferents The DRN issues serotonergic efferents to the hippocampal formation, limbic lobe, and amygdala (these efferents are involved in regulation of memory processing). Neurophysiology Serotonergic neurotransmission The dorsal raphe is the largest serotonergic nucleus and provides a substantial proportion of the serotonin innervation to the forebrain. Serotonergic neurons are found throughout the dorsal raphe nucleus and tend to be larger than other cells. A substantial population of cells synthesizing substance P are found in the rostral aspects, many of these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus
The medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) is a prominent bundle of nerve fibres which pass within the ventral/anterior portion of periaqueductal gray of the mesencephalon (midbrain). It contains the interstitial nucleus of Cajal, responsible for oculomotor control, head posture, and vertical eye movement. The MLF interconnects interneurons of each abducens nucleus with motor neurons of the contralateral oculomotor nucleus; thus, the MLF mediates coordination of horizontal (side to side) eye movements, ensuring the two eyes move in unison (thus also enabling saccadic eye movements). The MLF also contains fibers projecting from the vestibular nuclei to the oculomotor and trochlear nuclei as well as the interstitial nucleus of Cajal; these connections ensure that eye movements are coordinated with head movements (as sensed by the vestibular system). The medial longitudinal fasciculus is the main central connection for the oculomotor nerve, trochlear nerve, and abduce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus (: hypothalami; ) is a small part of the vertebrate brain that contains a number of nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus and is part of the limbic system. It forms the Basal (anatomy), basal part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is about the size of an Almond#Nut, almond. The hypothalamus has the function of regulating certain metabolic biological process, processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It biosynthesis, synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of hormones from the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus controls thermoregulation, body temperature, hunger (physiology), hunger, important aspects o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroscience Information Framework
The Neuroscience Information Framework is a repository of global neuroscience web resources, including experimental, clinical, and translational neuroscience databases, knowledge bases, atlases, and genetic/ genomic resources and provides many authoritative links throughout the neuroscience portal of Wikipedia. Description The Neuroscience Information Framework (NIF) is an initiative of the NIH Blueprint for Neuroscience Research, which was established in 2004 by the National Institutes of Health. Development of the NIF started in 2008, when the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine obtained an NIH contract to create and maintain "a dynamic inventory of web-based neurosciences data, resources, and tools that scientists and students can access via any computer connected to the Internet". The project is headed by Maryann Martone, co-director of the National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR), part of the multi-disciplinary Center for Research in Bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
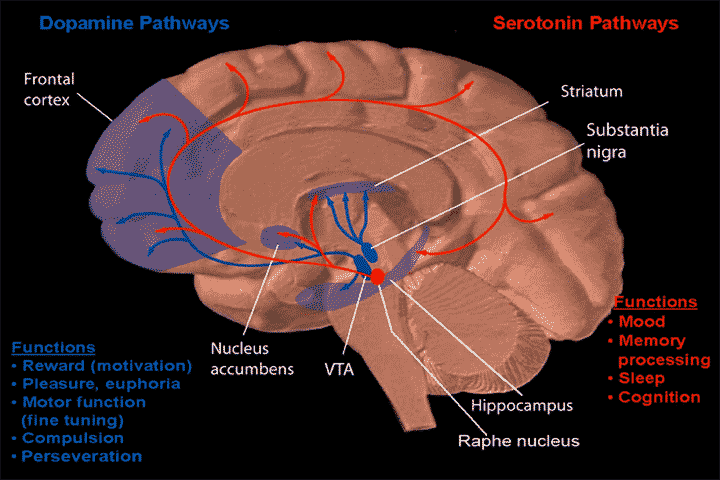
Raphe Nuclei
The raphe nuclei (, "seam") are a moderate-size cluster of nuclei found in the brain stem. They have 5-HT1 receptors which are coupled with Gi/Go-protein-inhibiting adenyl cyclase. They function as autoreceptors in the brain and decrease the release of serotonin. The anxiolytic drug Buspirone acts as partial agonist against these receptors. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressants are believed to act in these nuclei, as well as at their targets. Anatomy The raphe nuclei are traditionally considered to be the medial portion of the reticular formation, and appear as a ridge of cells in the center and most medial portion of the brain stem. In order from caudal to rostral, the raphe nuclei are known as the '' nucleus raphe obscurus'', the '' nucleus raphe pallidus'', the '' nucleus raphe magnus'', the '' nucleus raphe pontis'', the '' median raphe nucleus'', ''dorsal raphe nucleus'', ''caudal linear nucleus''. In the first systematic examination of the raph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amygdala
The amygdala (; : amygdalae or amygdalas; also '; Latin from Greek language, Greek, , ', 'almond', 'tonsil') is a paired nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclear complex present in the Cerebral hemisphere, cerebral hemispheres of vertebrates. It is considered part of the limbic system. In Primate, primates, it is located lateral and medial, medially within the temporal lobes. It consists of many nuclei, each made up of further subnuclei. The subdivision most commonly made is into the Basolateral amygdala, basolateral, Central nucleus of the amygdala, central, cortical, and medial nuclei together with the intercalated cells of the amygdala, intercalated cell clusters. The amygdala has a primary role in the processing of memory, decision making, decision-making, and emotions, emotional responses (including fear, anxiety, and aggression). The amygdala was first identified and named by Karl Friedrich Burdach in 1822. Structure Thirteen Nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei have been identif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Median Raphe Nucleus
The median raphe nucleus (MRN), also known as the superior central nucleus, is a nucleus in the brainstem composed of polygonal, fusiform, and piriform neurons, which exists rostral to the pontine raphe nucleus. The median raphe nucleus is one of several raphe nuclei that lies on the brainstem midline. It is one of two nuclei that are situated more superior to the others. The second of these nuclei is the dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN). The MRN extends from the lower part of the dorsal raphe nucleus to an approximate position at the decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncle . The MRN projects extensively to the hippocampus, which is known to be essential for the formation of long-term memory. One study found that this raphe–hippocampus pathway plays a critical role in regulating hippocampal activity and likely associated memory consolidation processes. It has also been found to play a role in anxiety and depression, as one of the few parts of the brain that creates tryptopha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbachol
Carbachol, also known as carbamylcholine and sold under the brand name Miostat among others, is a cholinomimetic drug that binds and activates acetylcholine receptors. Thus it is classified as a cholinergic agonist. It is primarily used for various ophthalmic purposes, such as for treating glaucoma, or for use during ophthalmic surgery. It is generally administered as an ophthalmic solution (i.e., eye drops). Carbachol produces effects comparable to those of sarin if a massive overdose is administered (as may occur following industrial and shipping accidents) and therefore it is classified as an extremely hazardous substance in the United States as defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act (42 U.S.C. 11002), and is subject to strict reporting requirements by facilities which produce, store, or use it in significant quantities. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Chemistry and pharmacology Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mephenesin
Mephenesin (INN), also called myanesin, is a centrally acting muscle relaxant. It can be used as an antidote for strychnine poisoning. Mephenesin however presents with the major drawbacks of having a short duration of action and a much greater effect on the spinal cord than the brain, resulting in pronounced respiratory depression at clinical doses and therefore a very low therapeutic index. It is especially dangerous and potentially fatal in combination with alcohol and other depressants. Mephenesin was the inspiration for the synthesis of a derivative of 1,3-propanediol, meprobamate, by Bernard Ludwig and Frank Berger, the first tranquilizer to see widespread clinical use. Mephenesin is no longer available in North America but is used in Italy and a few other countries. Its use has largely been replaced by the related drug methocarbamol, which is better absorbed. Mephenesin may be an NMDA receptor antagonist. Mephenesin was previously used in France as an OTC muscle relaxan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atonia
This glossary of medical terms is a list of definitions about medicine, its sub-disciplines, and related fields. A * Aarskog–Scott syndrome – (AAS) A rare, inherited (X-linked) disease characterized by short stature, facial abnormalities, skeletal and genital anomalies. *Abdomen – The part of the body between the chest and pelvis, which contains most of the tubelike organs of the digestive tract, as well as several solid organs. *Abdominal external oblique muscle – The largest, and outermost, of the three flat muscles of the lateral anterior abdominal wall. *Abdominal internal oblique muscle – A muscle of the abdominal wall, which lies below the external oblique and just above the transverse abdominal muscles. *Abductor pollicis brevis muscle – A muscle in the hand that abducts (straightens) the thumb. *Abductor pollicis longus muscle – One of the extrinsic muscles of the hand. Its major function is to abduct the thumb at the wrist. *Abscess – A collection of pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pons
The pons (from Latin , "bridge") is part of the brainstem that in humans and other mammals, lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum. The pons is also called the pons Varolii ("bridge of Varolius"), after the Italian anatomist and surgeon Costanzo Varolio (1543–75). This region of the brainstem includes neural pathways and tracts that conduct signals from the brain down to the cerebellum and medulla, and tracts that carry the sensory signals up into the thalamus. Structure The pons in humans measures about in length. It is the part of the brainstem situated between the midbrain and the medulla oblongata. The horizontal ''medullopontine sulcus'' demarcates the boundary between the pons and medulla oblongata on the ventral aspect of the brainstem, and the roots of cranial nerves VI/VII/VIII emerge from the brainstem along this groove. The junction of pons, medulla oblongata, and cerebellum forms the cerebellopontine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogenous compound involved in local immune responses communication, as well as regulating physiological functions in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter for the brain, spinal cord, and uterus. Discovered in 1910, histamine has been considered a local hormone ( autocoid) because it is produced without involvement of the classic endocrine glands; however, in recent years, histamine has been recognized as a central neurotransmitter. Histamine is involved in the inflammatory response and has a central role as a mediator of itching. As part of an immune response to foreign pathogens, histamine is produced by basophils and by mast cells found in nearby connective tissues. Histamine increases the permeability of the capillaries to white blood cells and some proteins, to allow them to engage pathogens in the infected tissues. It consists of an imidazole ring attached to an ethylamine chain; under physiological conditions, the amino grou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic compound, organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and human body, body as a hormone, neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. The name "noradrenaline" (from Latin '':wikt:ad-, ad'', "near", and '':wikt:ren, ren'', "kidney") is more commonly used in the United Kingdom and the rest of the world, whereas "norepinephrine" (from Ancient Greek :wikt:ἐπί, ἐπῐ́ (''epí''), "upon", and :wikt:νεφρός, νεφρός (''nephrós''), "kidney") is usually preferred in the United States. "Norepinephrine" is also the international nonproprietary name given to norepinephrine (drug), the drug. Regardless of which name is used for the substance itself, parts of the body that produce or are affected by it are referred to as noradrenergic. The general function of norepinephrine is to mobilize the brain and body for action. Norepinephrine release is lowest during sleep, rise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |