|
Dopaminergic Cell Groups
Dopaminergic cell groups, DA cell groups, or dopaminergic nuclei are collections of neurons in the central nervous system that synthesize the neurotransmitter dopamine. In the 1960s, dopaminergic neurons or ''dopamine neurons'' were first identified and named by Annica Dahlström and Kjell Fuxe, who used histochemical fluorescence. The subsequent discovery of genes encoding enzymes that synthesize dopamine, and transporters that incorporate dopamine into synaptic vesicles or reclaim it after synaptic release, enabled scientists to identify dopaminergic neurons by labeling gene or protein expression that is specific to these neurons. In the mammalian brain, dopaminergic neurons form a semi-continuous population extending from the midbrain through the forebrain, with eleven named collections or clusters among them. Cell group A8 Group A8 is a small group of dopaminergic cells in rodents and primates. It is located in the midbrain reticular formation dorsolateral to the sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural network in the nervous system. They are located in the nervous system and help to receive and conduct impulses. Neurons communicate with other cells via synapses, which are specialized connections that commonly use minute amounts of chemical neurotransmitters to pass the electric signal from the presynaptic neuron to the target cell through the synaptic gap. Neurons are the main components of nervous tissue in all Animalia, animals except sponges and placozoans. Plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. Molecular evidence suggests that the ability to generate electric signals first appeared in evolution some 700 to 800 million years ago, during the Tonian period. Predecessors of neurons were the peptidergic secretory cells. They eventually ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tegmentum
The tegmentum (from Latin for "covering") is a general area within the brainstem. The tegmentum is the ventral part of the midbrain and the tectum is the dorsal part of the midbrain. It is located between the ventricular system and distinctive basal or ventral structures at each level. It forms the floor of the midbrain (mesencephalon) whereas the tectum forms the ceiling. It is a multisynaptic network of neurons that is involved in many subconscious homeostatic and reflexive pathways. It is a motor center that relays inhibitory signals to the thalamus and basal nuclei preventing unwanted body movement. The tegmentum area includes various different structures, such as the rostral end of the reticular formation, several nuclei controlling eye movements, the periaqueductal gray matter, the red nucleus, the substantia nigra, and the ventral tegmental area. The tegmentum is the location of several cranial nerve nuclei. The nuclei of CN III and IV are located in the tegmentum port ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrosine Hydroxylase
Tyrosine hydroxylase or tyrosine 3-monooxygenase is the enzyme responsible for catalyzing the conversion of the amino acid L-tyrosine to L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA). It does so using molecular oxygen (O2), as well as iron (Fe2+) and tetrahydrobiopterin as cofactors. L-DOPA is a precursor for dopamine, which, in turn, is a precursor for the important neurotransmitters norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and epinephrine (adrenaline). Tyrosine hydroxylase catalyzes the rate limiting step in this synthesis of catecholamines. In humans, tyrosine hydroxylase is encoded by the ''TH'' gene, and the enzyme is present in the central nervous system (CNS), peripheral sympathetic neurons and the adrenal medulla. Tyrosine hydroxylase, phenylalanine hydroxylase and tryptophan hydroxylase together make up the family of aromatic amino acid hydroxylases (AAAHs). Reaction Tyrosine hydroxylase catalyzes the reaction in which L-tyrosine is hydroxylated in the meta position to obt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunoreactivity
An immunoassay (IA) is a biochemical test that measures the presence or concentration of a macromolecule or a small molecule in a solution through the use of an antibody (usually) or an antigen (sometimes). The molecule detected by the immunoassay is often referred to as an "analyte" and is in many cases a protein, although it may be other kinds of molecules, of different sizes and types, as long as the proper antibodies that have the required properties for the assay are developed. Analytes in biological liquids such as serum or urine are frequently measured using immunoassays for medical and research purposes. Immunoassays come in many different formats and variations. Immunoassays may be run in multiple steps with reagents being added and washed away or separated at different points in the assay. Multi-step assays are often called separation immunoassays or heterogeneous immunoassays. Some immunoassays can be carried out simply by mixing the reagents and samples and making a ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preoptic Area
The preoptic area is a region of the hypothalamus. MeSH classifies it as part of the anterior hypothalamus. TA lists four nuclei in this region, (medial, median, lateral, and periventricular). Functions The preoptic area is responsible for thermoregulation and receives nervous stimulation from thermoreceptors in the skin, mucous membranes, and hypothalamus itself. Nuclei Median preoptic nucleus The median preoptic nucleus is located along the midline in a position significantly dorsal to the other three preoptic nuclei, at least in the crab-eating macaque brain. It wraps around the top (dorsal), front, and bottom (ventral) surfaces of the anterior commissure. The median preoptic nucleus generates thirst. Drinking decreases noradrenaline release in the median preoptic nucleus. Medial preoptic nucleus The medial preoptic nucleus is bounded laterally by the lateral preoptic nucleus, and medially by the preoptic periventricular nucleus. It releases gonadotropin-releasing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalamus
The thalamus (: thalami; from Greek language, Greek Wikt:θάλαμος, θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter on the lateral wall of the third ventricle forming the wikt:dorsal, dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of the forebrain). Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all directions, known as the thalamocortical radiations, allowing hub (network science), hub-like exchanges of information. It has several functions, such as the relaying of sensory neuron, sensory and motor neuron, motor signals to the cerebral cortex and the regulation of consciousness, sleep, and alertness. Anatomically, the thalami are paramedian symmetrical structures (left and right), within the vertebrate brain, situated between the cerebral cortex and the midbrain. It forms during embryonic development as the main product of the diencephalon, as first recognized by the Swiss embryologist and anatomist Wilhelm His Sr. in 1893. Anatomy The thalami ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammillothalamic Tract
The mammillothalamic tract (MMT) (also mammillary fasciculus, mammillothalamic fasciculus, thalamomammillary fasciculus, bundle of Vicq d'Azyr) is an efferent pathway of the mammillary bodies which project to the anterior nuclei of the thalamus. The mammillothalamic tract is part of the Papez circuit (involved in spatial memory), starting and finishing in the hippocampus.Shah, A., Jhawar, S. S., & Goel, A. (2012). Analysis of the anatomy of the Papez circuit and adjoining limbic system by fiber dissection techniques. rticle Journal of Clinical Neuroscience, 19(2), 289-298. . The fibers of the MMT are heavily myelinated. It arises from the medial and lateral nuclei of the mammillary bodies, and from fibers that are directly continued from the fornix of the hippocampus. It connects the mammillary bodies to the dorsal tegmental nuclei, the ventral tegmental nuclei, and the anterior thalamic nuclei. Structure Axons divide within the gray matter; the thicker fibres form the MT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraventricular Nucleus Of Hypothalamus
The paraventricular nucleus (PVN) is a nucleus in the hypothalamus, located next to the third ventricle. Many of its neurons project to the posterior pituitary where they secrete oxytocin, and a smaller amount of vasopressin. Other secretions are corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) and thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH). CRH and TRH are secreted into the hypophyseal portal system, and target different neurons in the anterior pituitary. Dysfunctions of the PVN can cause hypersomnia in mice. In humans, the dysfunction of the PVN and the other nuclei around it can lead to drowsiness for up to 20 hours per day. The PVN is thought to mediate many diverse functions through different hormones, including osmoregulation, appetite, wakefulness, and the response of the body to stress. Location The paraventricular nucleus lies adjacent to the third ventricle. It lies within the periventricular zone and is not to be confused with the periventricular nucleus, which occupies a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcuate Nucleus
The arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus (ARH), or ARC, is also known as the infundibular nucleus to distinguish it from the arcuate nucleus of the medulla oblongata in the brainstem. The arcuate nucleus is an aggregation of neurons in the mediobasal hypothalamus, adjacent to the third ventricle and the median eminence. The arcuate nucleus includes several important and diverse populations of neurons that help mediate different neuroendocrine and physiological functions, including neuroendocrine neurons, centrally projecting neurons, and astrocytes. The populations of neurons found in the arcuate nucleus are based on the hormones they secrete or interact with and are responsible for hypothalamic function, such as regulating hormones released from the pituitary gland or secreting their own hormones. Neurons in this region are also responsible for integrating information and providing inputs to other nuclei in the hypothalamus or inputs to areas outside this region of the brain. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
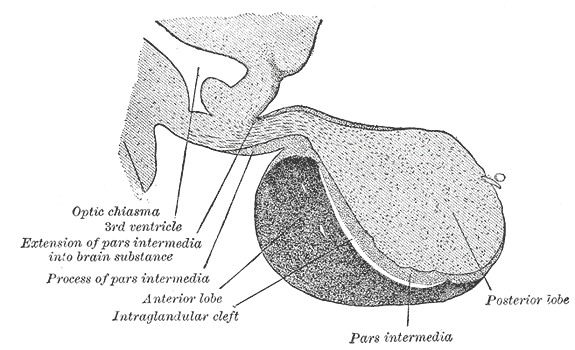
Mammillary Body
The mammillary bodies also mamillary bodies, are a pair of small round brainstem nuclei. They are located on the undersurface of the brain that, as part of the diencephalon, form part of the limbic system. They are located at the ends of the anterior arches of the fornix. They consist of two groups of nuclei, the medial mammillary nuclei and the lateral mammillary nuclei. Neuroanatomists have often categorized the mammillary bodies as part of the posterior part of hypothalamus. Structure Connections They are connected to other parts of the brain (as shown in the schematic, below left), and act as a relay for impulses coming from the amygdalae and hippocampi, via the mamillothalamic tract to the thalamus. The lateral mammillary nucleus has bidirectional connections with the dorsal tegmental nucleus. The medial mammillary nucleus connects with the ventral tegmental nucleus. Function File:Slide5dd.JPG, Mammillary body Mammillary bodies, and their projections to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus (: hypothalami; ) is a small part of the vertebrate brain that contains a number of nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus and is part of the limbic system. It forms the Basal (anatomy), basal part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is about the size of an Almond#Nut, almond. The hypothalamus has the function of regulating certain metabolic biological process, processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It biosynthesis, synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of hormones from the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus controls thermoregulation, body temperature, hunger (physiology), hunger, important aspects o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periventricular Nucleus
The periventricular nucleus is a thin sheet of small neurons located in the wall of the third ventricle, a composite structure of the hypothalamus. It functions in analgesia. It is located in the rostral, intermediate, and caudal regions of the hypothalamus. The rostral region aids in the production of both somatostatin and thyroid releasing hormone. The intermediate portion aids in production of thyroid releasing hormone, somatostatin, leptin, gastrin, and neuropeptide Y. In humans and primates it also produces GnRH. Lastly the caudal region aids in sympathetic nervous system regulation, and is regarded as the rage center. The periventricular nucleus does not have an effective blood–brain barrier. 11β-HSD2 expression turns cortisol into cortisone. Role in LH and GnRH release This nucleus has been shown to affect the release of GnRH (gonadotropin-releasing hormone) in several ways. One way is its expression of neuropeptide Y, which has an impact on the hypothalami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |