|
Donnell Óg O'Donnell
Donnell Óg O'Donnell (Irish language, Irish: ''Domhnall Óg Ó Domhnaill''; – 1281), was a medieval Irish king of Tyrconnell and member of the O'Donnell dynasty. He was a leading figure in the resistance to Anglo-Norman rule in the north west and closely related to many of the movement's most prominent figures, such as Hugh McFelim O'Connor, who is often credited as being the first to import Scottish gallowglass warriors. He should not be confused with a Donal Oge O'Donnell, descendant of the same name who was a nephew of Rory O'Donnell, 1st Earl of Tyrconnell, and was the ultimate beneficiary-in-remainder to the Lordship of Tyrconnell. Background and early career Domhnall Óg was the posthumous son of Domhnall Mór Ó Domhnaill, King of Tír Chonaill and his wife, Lasairfhíona, daughter of Cathal Crobhdhearg Ó Conchobhair, King of Connacht. Lasairfhíona's aunt, Beanmhidhe, daughter of Tairrdelbach Ua Conchobair, Toirdhealbhach Ó Conchobhair, was wife to the Scottish l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domhnall Óg Ó Domhnaill (Oxford Bodleian Library Rawlinson B 489, Folio 68r)
Donald is a Scottish masculine given name. It is derived from the Goidelic languages, Gaelic name ''Dòmhnall''.. This comes from the Proto-Celtic language, Proto-Celtic *''Dumno-ualos'' ("world-ruler" or "world-wielder"). The final -''d'' in ''Donald'' is partly derived from a misinterpretation of the Gaelic pronunciation by English speakers. A short form of Donald is Don (given name), Don, and pet forms of Donald include Donnie and Donny. The feminine given name Donella (other) , Donella is derived from Donald. ''Donald'' has cognates in other Celtic languages: Irish language, Modern Irish ''Dónal'' (anglicised as ''Donal'' and ''Donall'');. Scottish Gaelic ''Dòmhnall'', ''Domhnull'' and ''Dòmhnull''; Welsh language, Welsh ''Dyfnwal (other), Dyfnwal'' and Cumbric ''Dumnagual''. Although the feminine given name ''Donna (given name), Donna'' is sometimes used as a feminine form of ''Donald'', the names are not etymologically related. Variations King ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gofraidh Ó Domhnaill
Gofraid O'Donnell ( Irish: ''Gofraidh Ó Domhnaill'') was a king of Tyrconnell and the first chieftain of mark in the O'Donnell dynasty. Biography O'Donnell was a son of Donal Mor O'Donnell (died 1241). O'Donnell rapidly came to power, initially with the support of the FitzGerald dynasty. In 1248, he was inaugurated as "The O'Donnell", meaning chief of the clan. He made a successful inroad into Tyrone against Brian O'Neill in 1252. In 1257, he drove the Normans out of northern Connacht after the battle of Creadran-Cille killing Maurice FitzGerald, 2nd Lord of Offaly, in personal combat, but suffering severe injuries. O'Donnell, while still incapacitated by his wound, was summoned by O'Neill to give hostages in token of submission. Carried on a litter at the head of his clan, he gave battle to Brian, whom he defeated with severe loss in prisoners and cattle. O'Donnell died of his wound immediately afterwards outside of where the town of Letterkenny Letterkenny ( , meani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aedh Mac Felim Ó Conchobair
Aodh ( , , ; ) is a masculine Irish and Scottish Gaelic given name, which was traditionally anglicized as Hugh. The name means "fire" and was the name of a god in Irish mythology.The modern word meaning 'inflammation' or as a phrase with the Irish word for 'itch' (), giving , 'burning itch' or 'urtication' - (Foclóir Gaeilg-Béarla, eds Tomás de Bhaldraithe, Niall Ó Dónaill, Dublin 1977), is clearly cognate with the original meaning. The name features in the Irish surnames (lit. "son of Aodh"; anglicized as McGee/ McHugh/ McKee) and (lit. "descendant of Aodh"; anglicized as Hayes/ Hughes/O'Hea), and the Scottish surname (lit. "son of Aodh"; anglicized McKay). The name has a number of derived forms, including: * The feminine forms and . * (), anglicized as Aidan, formed by the addition of the diminutive suffix . * (traditionally ), a double diminutive. This form features in the surname (lit. "son of Aodhagán"; anglicized as Egan and Keegan). * (), angli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clanricarde
Clanricarde ( ), also known as Mac William Uachtar (Upper Mac William) or the Galway Burkes, were a fully Gaelicised branch of the Hiberno-Norman House of Burgh who were important landowners in Ireland from the 13th to the 20th centuries. Territory The territory, in what is now County Galway, Ireland, stretched from the barony of Clare in the north-west along the borders of County Mayo, to the River Shannon in the east. Territories Clannricarde claimed dominion over included Uí Maine, Kinela, de Bermingham's Country, Síol Anmchadha and southern Sil Muirdeagh were at times at war. Those clans accepted the family’s claims on varying occasions as well, and many family members were ceremonially brought into the Irish heritage. Title The Clanricarde, was a Gaelic title meaning ''"Richard's family"'', or ''"(head of) Richard's family"''. The Richard in question was Richard Mór de Burgh, 1st Lord of Connacht (died 1243), son of William de Burgh, whose great-great-grandson becam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Longford
County Longford () is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster. It is named after the town of Longford. Longford County Council is the Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local authority for the county. The population of the county was 46,634 at the 2022 census. The county is based on the historic Gaelic Ireland, Gaelic territory of Annaly (''Anghaile''), formerly known as Tethbae, Teffia (''Teathbha''). Geography Most of Longford lies in the basin of the River Shannon with Lough Ree forming much of the county's western boundary. The north-eastern part of the county, however, drains towards the River Erne and Lough Gowna. Lakeland, bogland, pasture-land and wetland typify Longford's generally low-lying landscapes: the highest point of the county is in the north-west – Carn Clonhugh (also known as Cairn Hill or Corn Hill) between Drumlish and Ballinalee in the parish of Killoe, at . Cairn H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermanagh
Historically, Fermanagh (), as opposed to the modern County Fermanagh, was a kingdom of Gaelic Ireland, associated geographically with present-day County Fermanagh. ''Fir Manach'' originally referred to a distinct kin group of alleged Laigin origins. The kingdom of Fermanagh was formed in the 10th century, out of the larger kingdom of Uí Chremthainn, which was part of the overkingdom of Airgíalla.MacCotter, Paul. ''Medieval Ireland: territorial, political and economic divisions''. Four Courts Press, 2008, p.243 By the late 11th century it had grown to cover all of what is now County Fermanagh. The kingdom came to be ruled by the Mag Uidhir (Maguire) clan from the late 13th century onward. They were based at Lisnaskea, and their royal inauguration site was nearby Sgiath Gabhra (Skeagoura), now called Cornashee. Under Hugh Maguire, Fermanagh was involved in the Nine Years' War against English rule. His successor, Cú Chonnacht Óg Mag Uidhir, was one of the Gaelic Irish lead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airgíalla
Airgíalla (; Modern Irish: Oirialla, English: Oriel, Latin: ''Ergallia'') was a medieval Irish over-kingdom and the collective name for the confederation of tribes that formed it. The confederation consisted of nine minor kingdoms, all independent of each other but paying nominal suzerainty to an overking, usually from the most powerful dynasty. Airgíalla at its peak roughly matched the modern dioceses of Armagh and Clogher, spanning parts of counties Armagh, Monaghan, Louth, Fermanagh, Tyrone and Londonderry. Its main towns were Armagh and Clogher. The name's usage survives as a cultural area of folk tradition in South East Ulster and adjoining areas of County Louth. According to legend, Airgíalla was founded by the Three Collas, who are said to have conquered what is now central Ulster from the Ulaid. The decisive victory was the battle of Achadh Leithdheirg, said to have been fought around the year 331. However, this tale is thought to be mostly fiction, and the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tír Eoghain
Tír Eoghain (), also known as Tyrone, was a kingdom and later earldom of Gaelic Ireland, comprising parts of present-day County Tyrone, County Armagh, County Londonderry and County Donegal (Raphoe). The kingdom represented the core homeland of the Cenél nEógain people of the Northern Uí Néill and although they ruled, there were smaller groups of other Gaels in the area. One part of the realm to the north-east broke away and expanded, becoming Clandeboye, ruled by a scion branch of the O'Neill dynasty. In one form or another, Tyrone existed for over a millennium. Its main capital was Dungannon, though kings were inaugurated at Tullyhogue Fort. Upon its foundation in the 5th century, Tyrone was a sub-kingdom of the larger Aileach, which represented the powerbase of the Uí Néill (descendants of Niall of the Nine Hostages) in the north of Ireland. The territory of Eoghan mac Néill was initially based in Inishowen and expanded out from there under his descendants. Periodicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
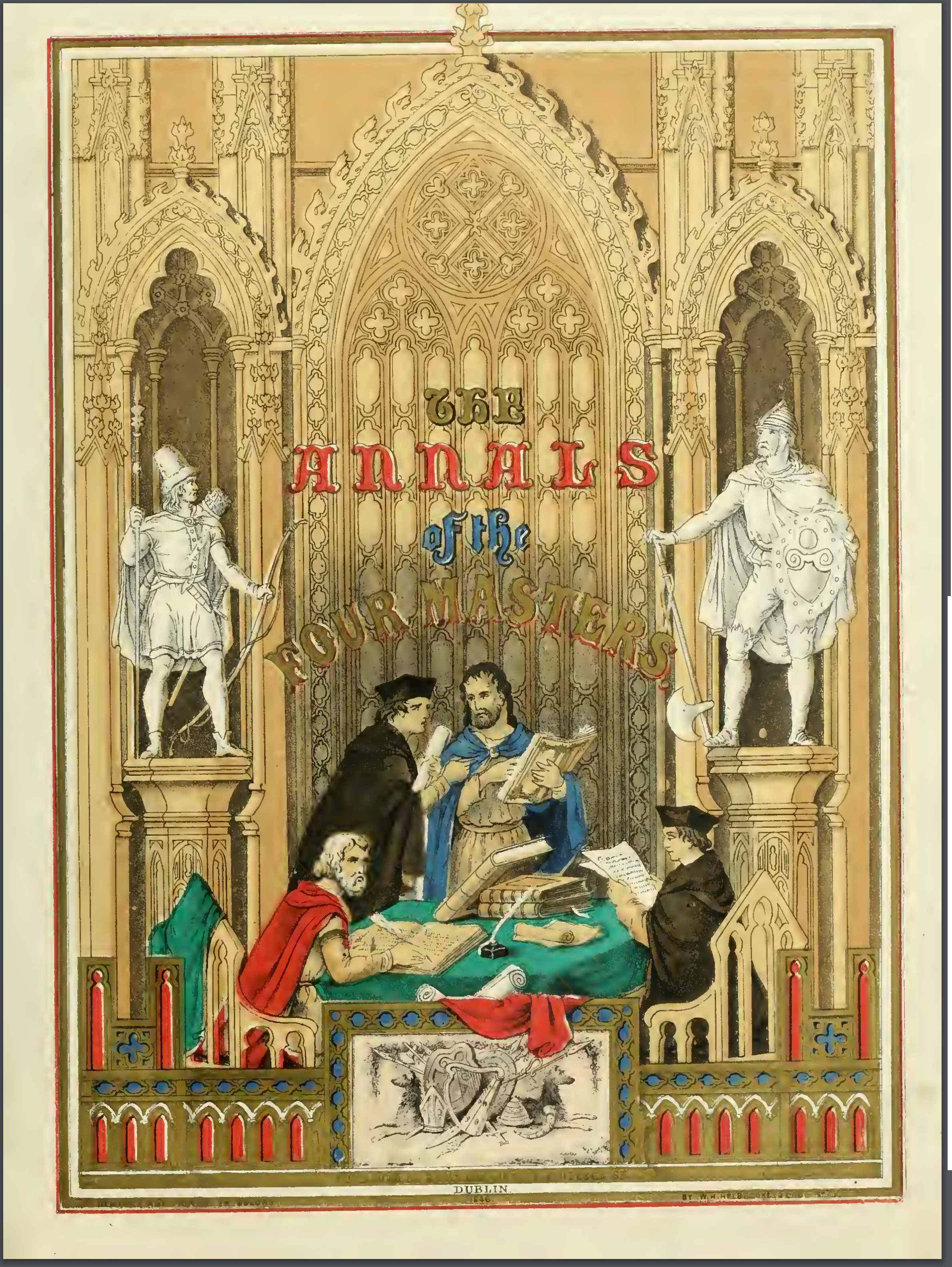
Annals Of The Four Masters
The ''Annals of the Kingdom of Ireland'' () or the ''Annals of the Four Masters'' () are chronicles of Middle Ages, medieval Irish history. The entries span from the Genesis flood narrative, Deluge, dated as 2,242 Anno Mundi, years after creation to AD 1616. Publication delay Due to the criticisms by 17th-century Irish historian Tuileagna Ó Maol Chonaire, the text was not published in the lifetimes of any of the participants. Text The annals are mainly a compilation of earlier annals, although there is some original work. They were compiled between 1632 and 1636, allegedly in a cottage beside the ruins of Donegal Abbey, just outside Donegal (town), Donegal Town. At this time, however, the Franciscans had a house of refuge by the River Drowes in County Leitrim, just outside Ballyshannon, and it was here, according to others, that the ''Annals'' were compiled. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connacht
Connacht or Connaught ( ; or ), is the smallest of the four provinces of Ireland, situated in the west of Ireland. Until the ninth century it consisted of several independent major Gaelic kingdoms (Uí Fiachrach, Uí Briúin, Uí Maine, Conmhaícne, and Delbhna). Between the reigns of Conchobar mac Taidg Mór (died 882) and his descendant, Aedh mac Ruaidri Ó Conchobair (reigned 1228–33), it became a kingdom under the rule of the Uí Briúin Aí dynasty, whose ruling sept adopted the surname Ua Conchobair. At its greatest extent, it incorporated the often independent Kingdom of Breifne, as well as vassalage from the lordships of western Mide and west Leinster. Two of its greatest kings, Tairrdelbach Ua Conchobair (1088–1156) and his son Ruaidri Ua Conchobair (c. 1115–1198) greatly expanded the kingdom's dominance, so much so that both became High King of Ireland. The Kingdom of Connacht collapsed in the 1230s because of civil war within the royal dynasty, which enab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clann Suibhne
Clan Sweeney is an Irish clan of Scotland, Scottish origin. The Mac Suibhne family did not permanently settle in Ireland before the beginning of the 14th century, when they became Gallowglass soldiers for the O'Donnell dynasty, Ua Domnaill dynasty of Tyrconnell, Tír Chonaill. The clan also claims an Irish descent from a prince of the O'Neill dynasty, Uí Néill dynasty, Ánrothán Ua Néill, son of Áed, son of Flaithbertach Ua Néill, King of Ailech and Cenél nEógain, died 1036. Through this descent the clan can claim a descent from Niall Noigíallach (''Niall of the Nine Hostages''). Origins ''Leabhar Clainne Suibhne'' states that after Áed's death, although his older brother Domnall was the rightful heir, Ánrothán was chosen instead to be king. Ánrothán then gave up the kingship to his brother and made for Argyll, Scotland where he married a daughter of the King of Scotland. Ánrothán's great-grandson was Suibhne mac Duinnshléibhe, Suibhne, from whom the clan deriv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Branches Of The Cenél NEógain
A branch, also called a ramus in botany, is a stem that grows off from another stem, or when structures like veins in leaves are divided into smaller veins. History and etymology In Old English, there are numerous words for branch, including , , , and . There are also numerous descriptive words, such as (that is, something that has bled, or 'bloomed', out), (literally 'little bough'), (literally 'on growth'), and (literally 'offspringing'). Numerous other words for twigs and boughs abound, including , which still survives as the ''-toe'' in ''mistletoe''. Latin words for branch are or . The latter term is an affix found in other modern words such as '' cladodont'' (prehistoric sharks with branched teeth), '' cladode'' (flattened leaf-like branches), or ''cladogram'' (a branched diagram showing relations among organisms). Woody branches Large branches are known as boughs and small branches are known as twigs. The term '' twig'' usually refers to a terminus, while ''b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |